How to Install Google Chrome Web Browser on Ubuntu 24.04
Google Chrome is a fast and secure web browser built for the modern web. It is available for all major operating systems and allows you to sync bookmarks, history, and passwords across devices.
This guide explains how to install Google Chrome on Ubuntu 24.04 using the official Google package and repository.
.deb package is available for 64-bit x86 (amd64) systems only. On ARM devices, use Chromium
or another ARM-compatible browser.Quick Reference
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Download package | wget https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb |
| Install package | sudo apt install ./google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb |
| Start Chrome | google-chrome |
| Set as default browser | xdg-settings set default-web-browser google-chrome.desktop |
| Update Chrome | sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade |
| Uninstall Chrome | sudo apt remove google-chrome-stable |
| Verify repo file | cat /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list |
Installing Google Chrome on Ubuntu
Chrome is not open source and is not included in the standard Ubuntu repositories. The official .deb package
adds the Google signing key and repository so Chrome stays updated automatically.
Download Google Chrome
Open a terminal and use wget to download the latest stable package:
wget https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.debInstall Google Chrome
Install the package with apt. Running this command requires sudo privileges
:
sudo apt install ./google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.debWhen prompted, enter your password to complete the installation.
Starting Google Chrome
Open the Activities overview by pressing the Super key, search for “Google Chrome”, and launch it:
You can also start Chrome from the terminal:
google-chromeWhen you start Chrome for the first time, you will be asked whether you want to set it as the default browser and enable crash reports:

Chrome then opens the welcome page:
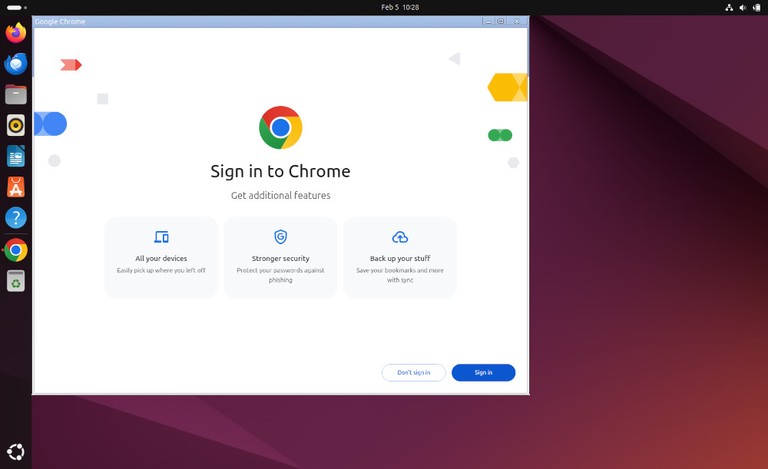
From here, you can sign in with your Google account and sync your settings.
Set Chrome as Default Browser
To set Chrome as the default browser from the command line, run:
xdg-settings set default-web-browser google-chrome.desktopTo verify the current default browser:
xdg-settings get default-web-browsergoogle-chrome.desktopUpdating Google Chrome
During installation, the official Google repository is added to your system. Verify the repository file with cat
:
cat /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.listExample output:
### THIS FILE IS AUTOMATICALLY CONFIGURED ###
# You may comment out this entry, but any other modifications may be lost.
deb [arch=amd64] https://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable mainChrome updates are delivered through the standard Ubuntu update process:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeUninstalling Google Chrome
To remove Google Chrome from your system, run:
sudo apt remove google-chrome-stableThen clean up unused dependencies:
sudo apt autoremoveTroubleshooting
The installation fails with dependency errors
Fix broken dependencies and re-run the install:
sudo apt --fix-broken install
sudo apt install ./google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.debChrome does not start after installation
Close any running Chrome processes and start it again:
pkill -f chrome
google-chromeRepository file is missing
Reinstall the package to recreate the repository file:
sudo apt install ./google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.debFAQ
What is the difference between Chrome and Chromium?
Chromium is the open-source project that Chrome is built on. Chrome adds proprietary features such as automatic updates, licensed media codecs (AAC, H.264), and tighter Google account integration.
How do I import bookmarks from another browser?
Open Chrome, go to Settings > Import bookmarks and settings, and select the browser you want to import from.
Can I install Chrome Beta or Dev channels?
Yes. Replace google-chrome-stable with google-chrome-beta or google-chrome-unstable in the download URL and install command.
Conclusion
Google Chrome installs on Ubuntu 24.04 using the official .deb package, which also configures the Google repository for automatic updates.
If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.

