平衡二叉树
前言
这道题中的平衡二叉树的定义是:二叉树的每个节点的左右子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 $1$,则二叉树是平衡二叉树。根据定义,一棵二叉树是平衡二叉树,当且仅当其所有子树也都是平衡二叉树,因此可以使用递归的方式判断二叉树是不是平衡二叉树,递归的顺序可以是自顶向下或者自底向上。
方法一:自顶向下的递归
定义函数 $\texttt{height}$,用于计算二叉树中的任意一个节点 $p$ 的高度:
$$
\texttt{height}(p) =
\begin{cases}
0 & p \text{ 是空节点}\
\max(\texttt{height}(p.\textit{left}), \texttt{height}(p.\textit{right}))+1 & p \text{ 是非空节点}
\end{cases}
$$
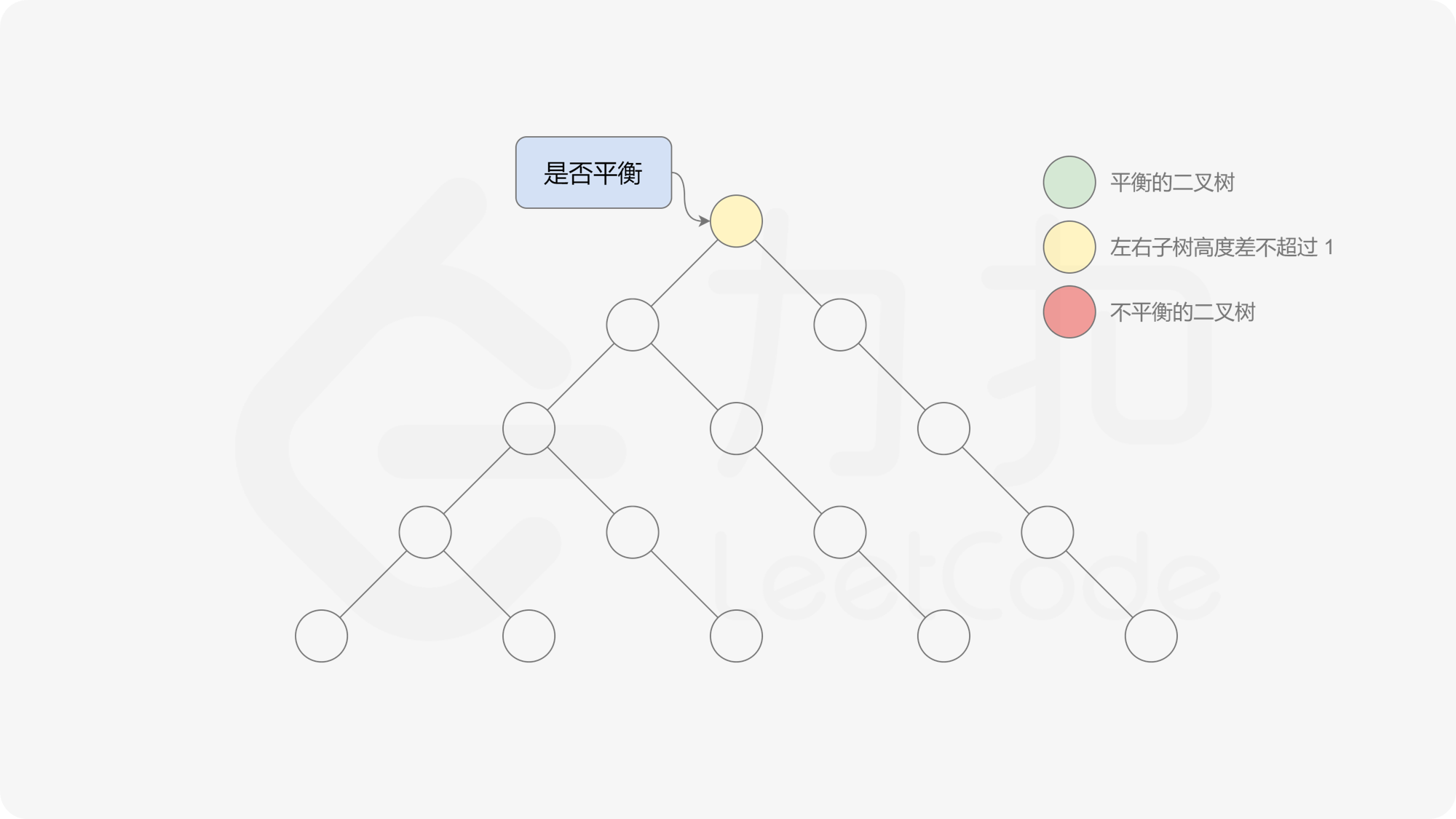
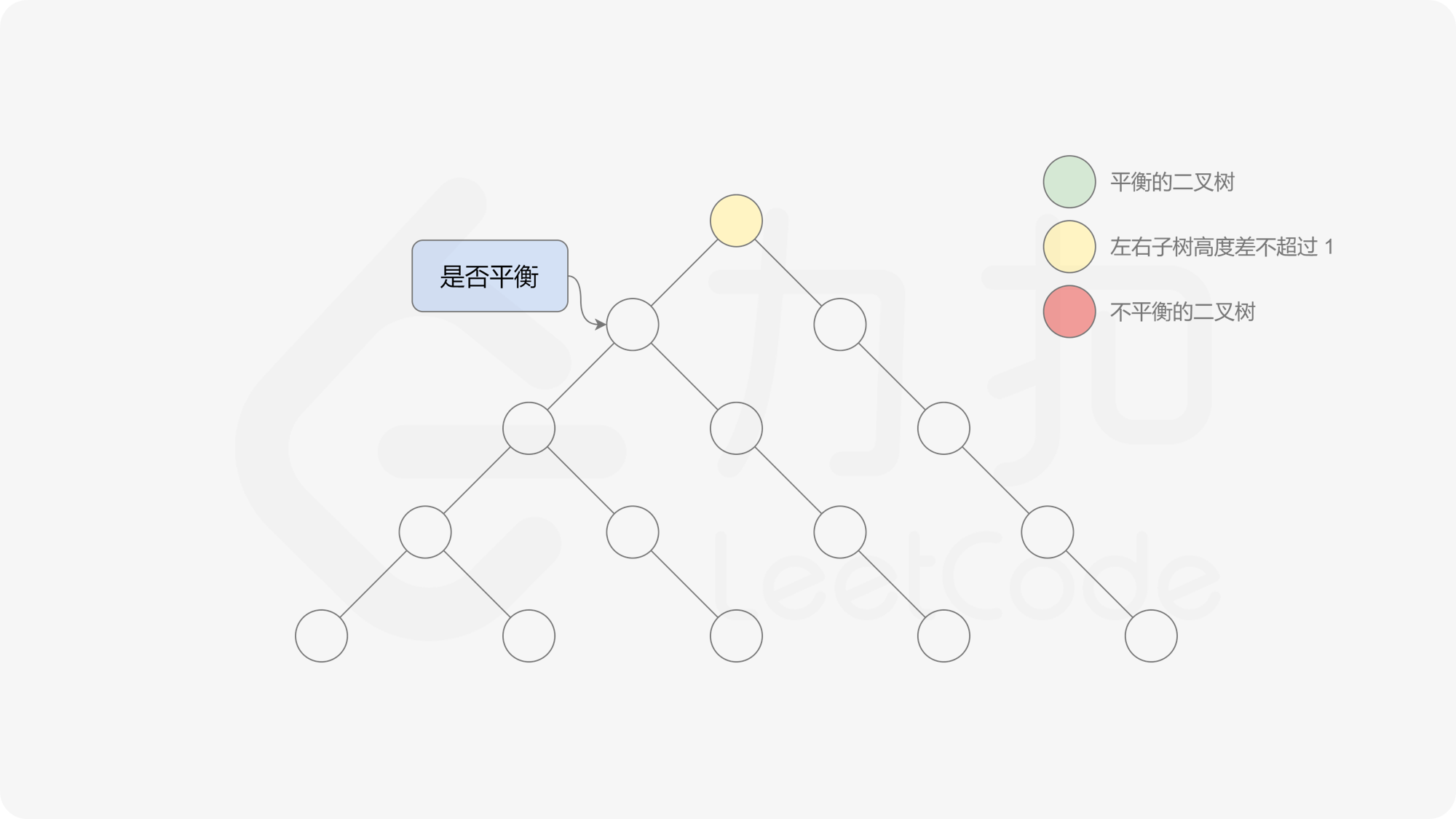
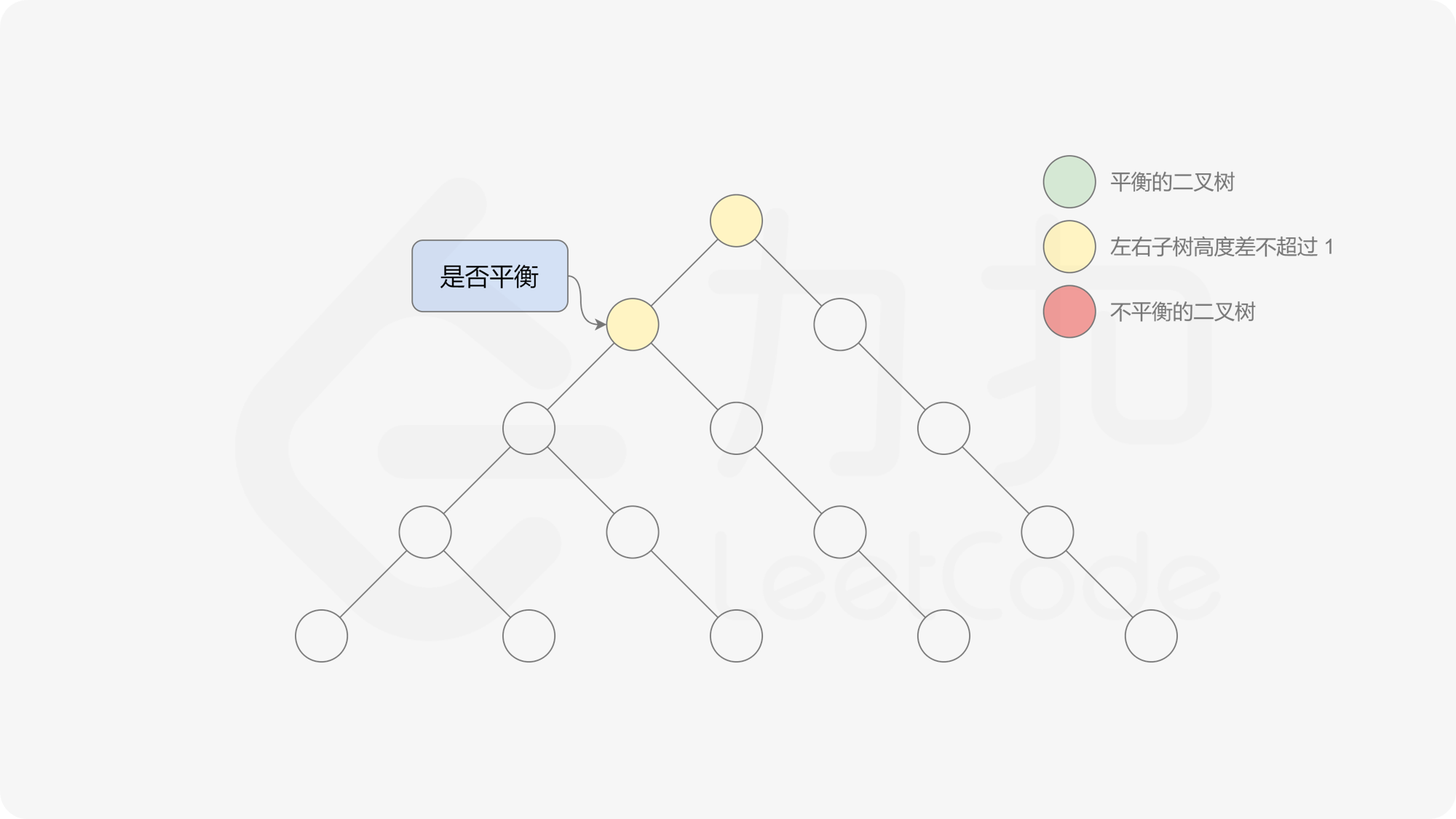
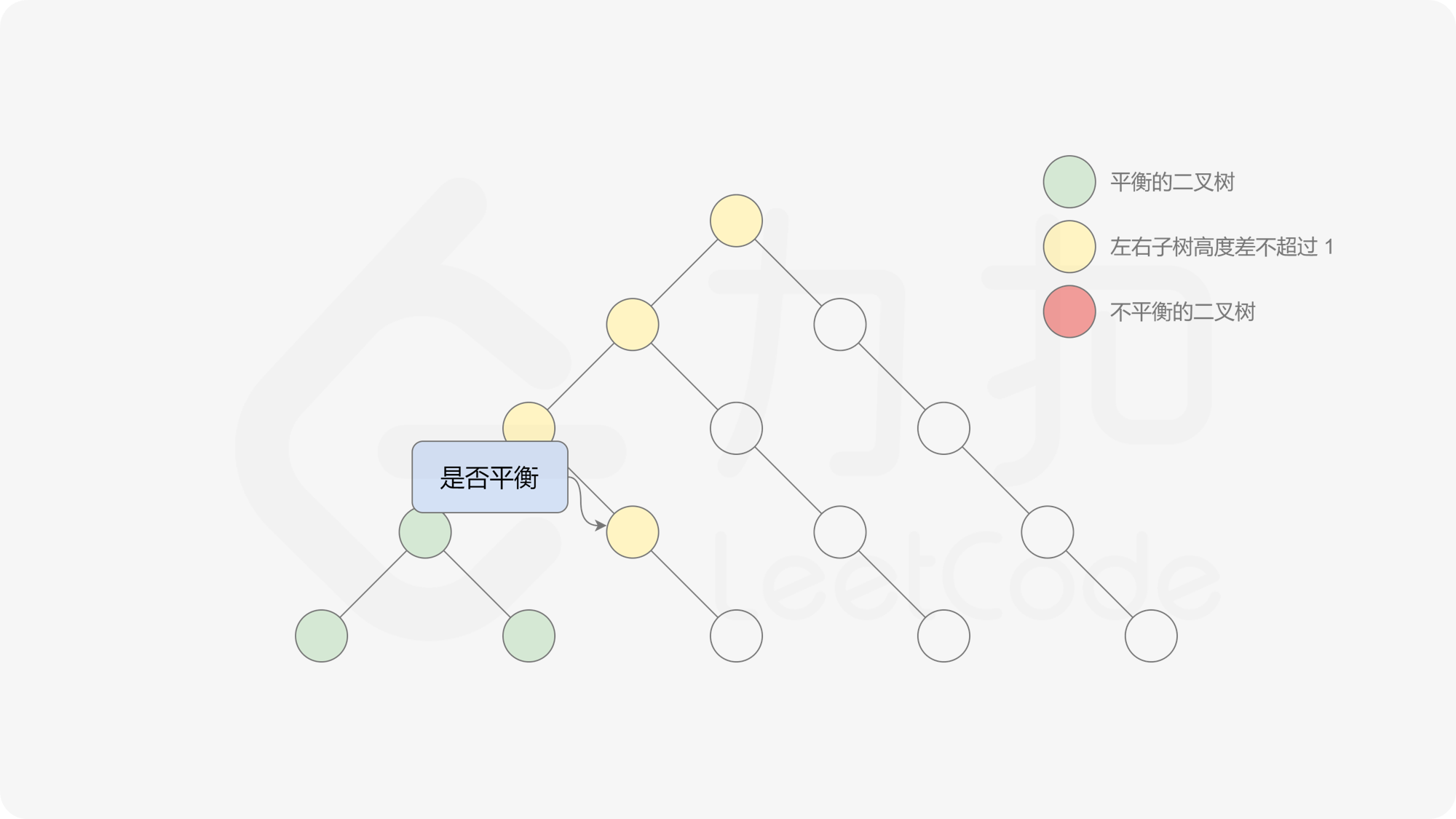
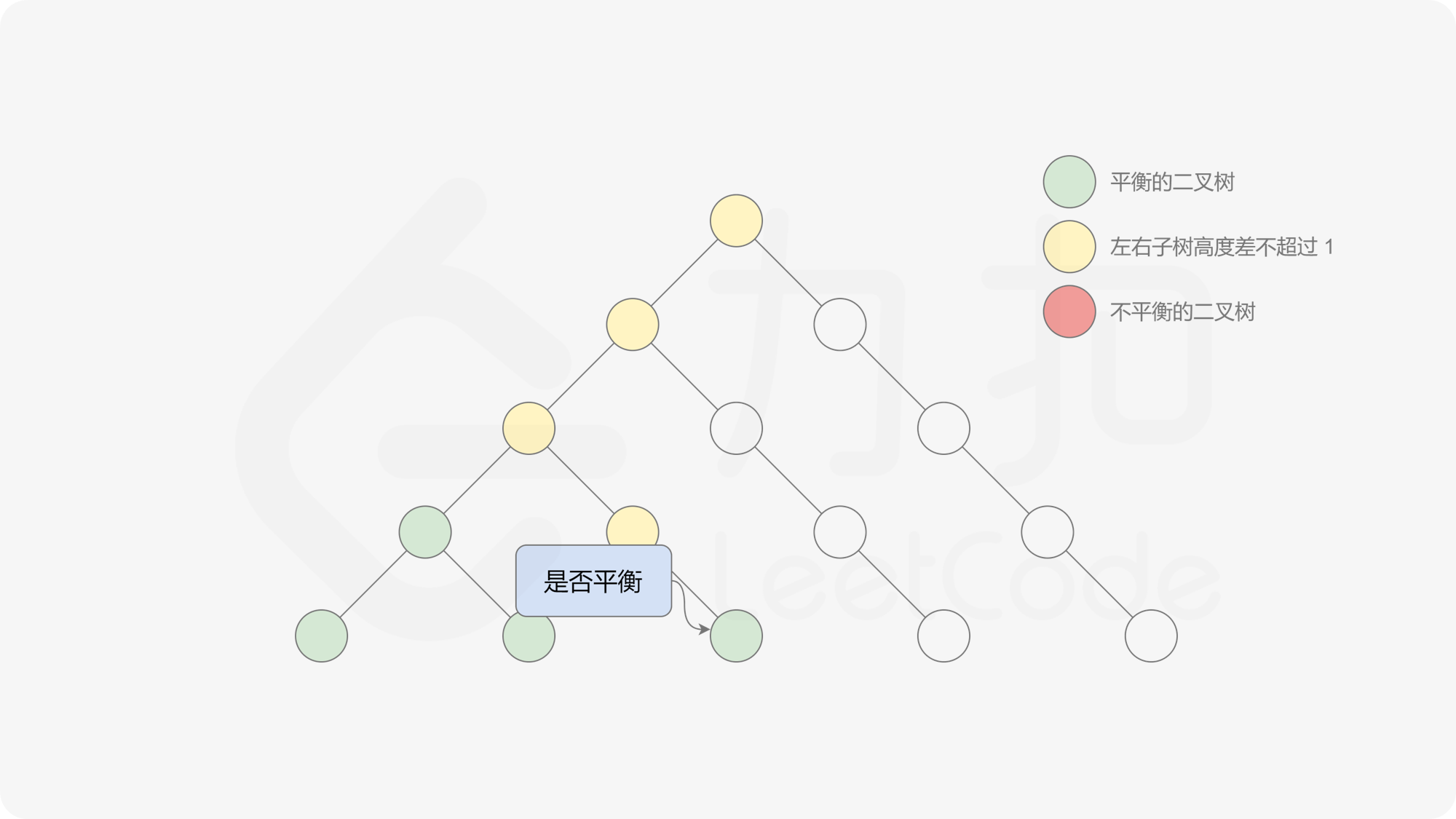
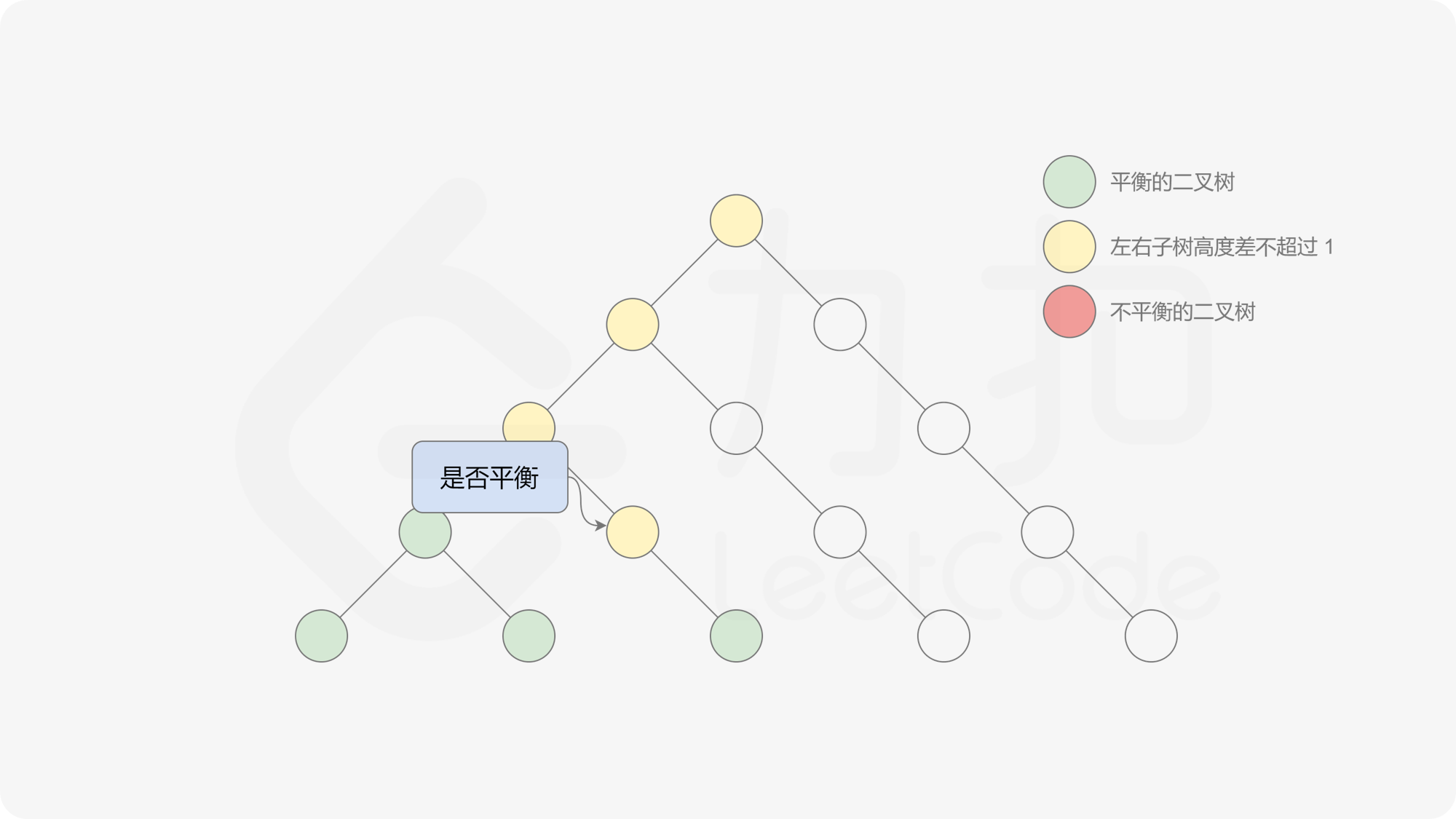
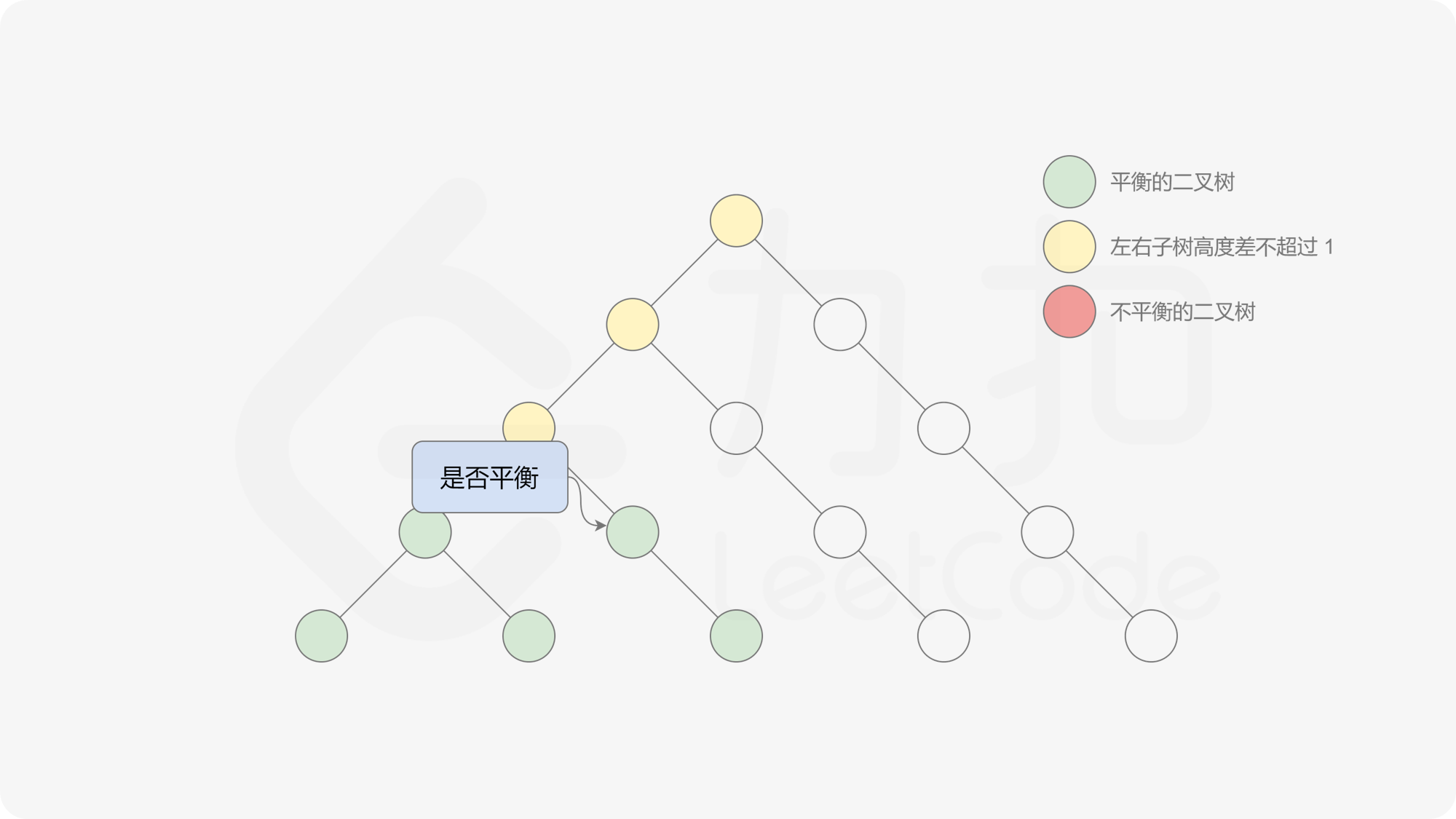
有了计算节点高度的函数,即可判断二叉树是否平衡。具体做法类似于二叉树的前序遍历,即对于当前遍历到的节点,首先计算左右子树的高度,如果左右子树的高度差是否不超过 $1$,再分别递归地遍历左右子节点,并判断左子树和右子树是否平衡。这是一个自顶向下的递归的过程。
<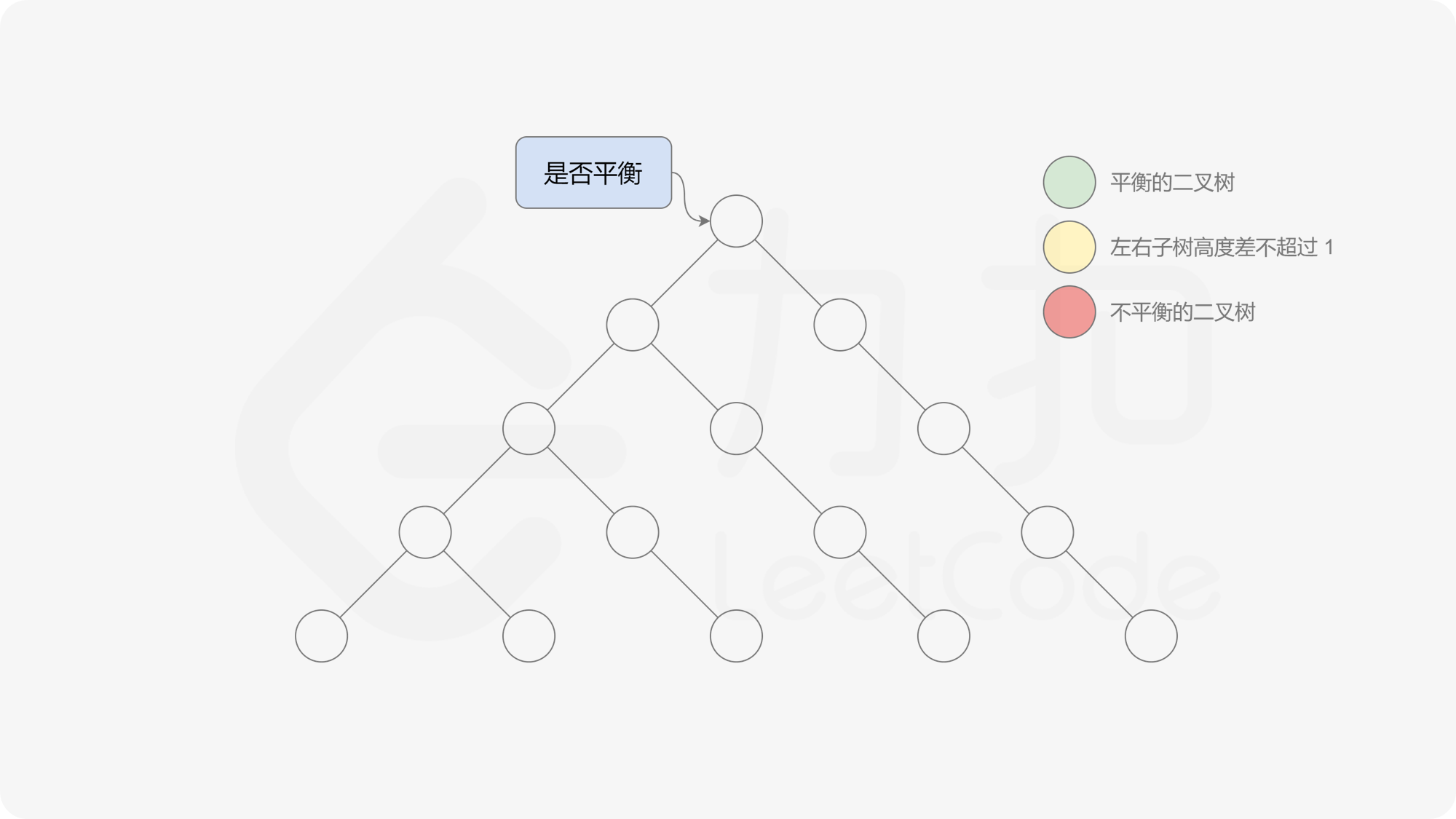 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
,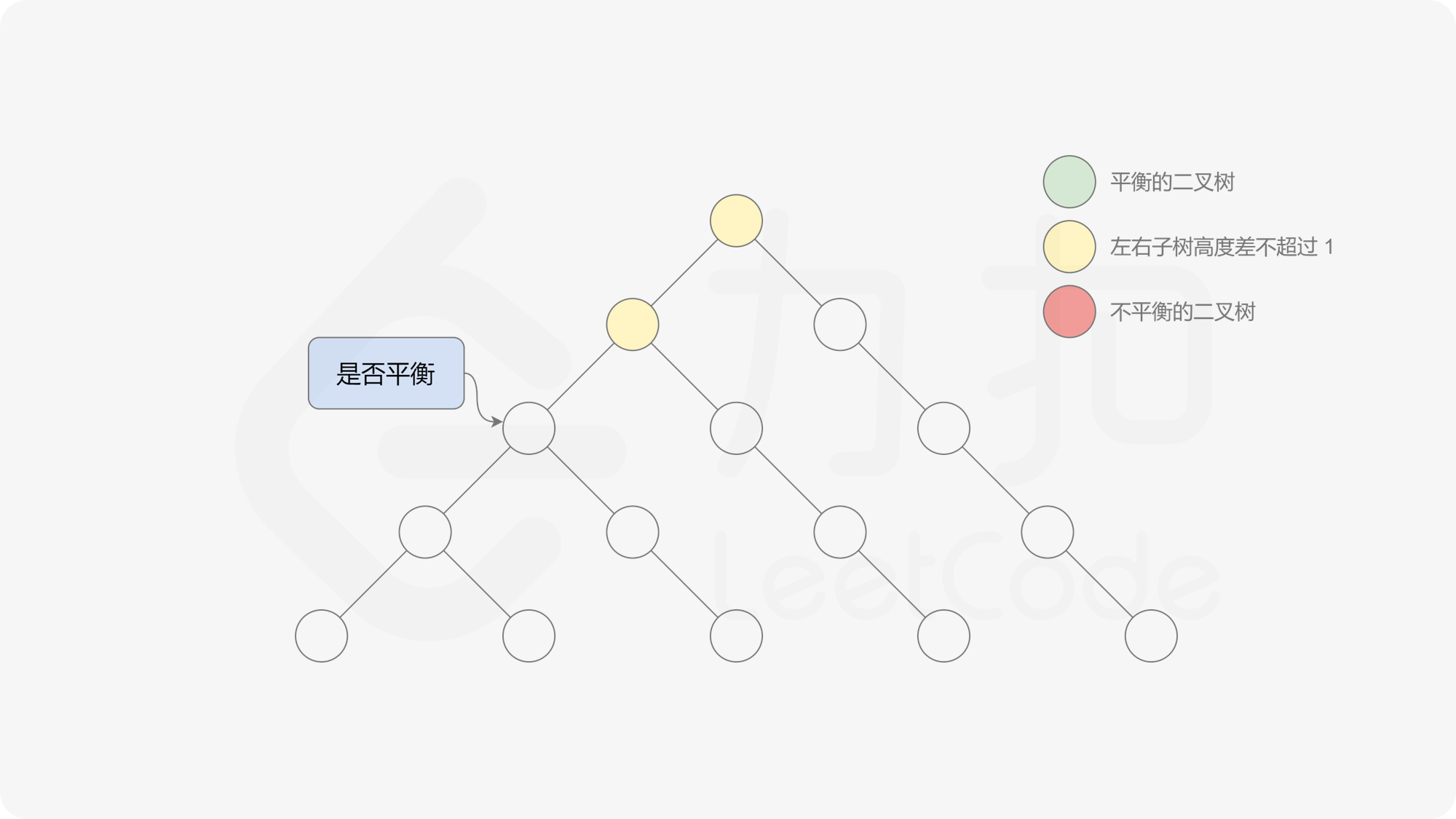 ,
,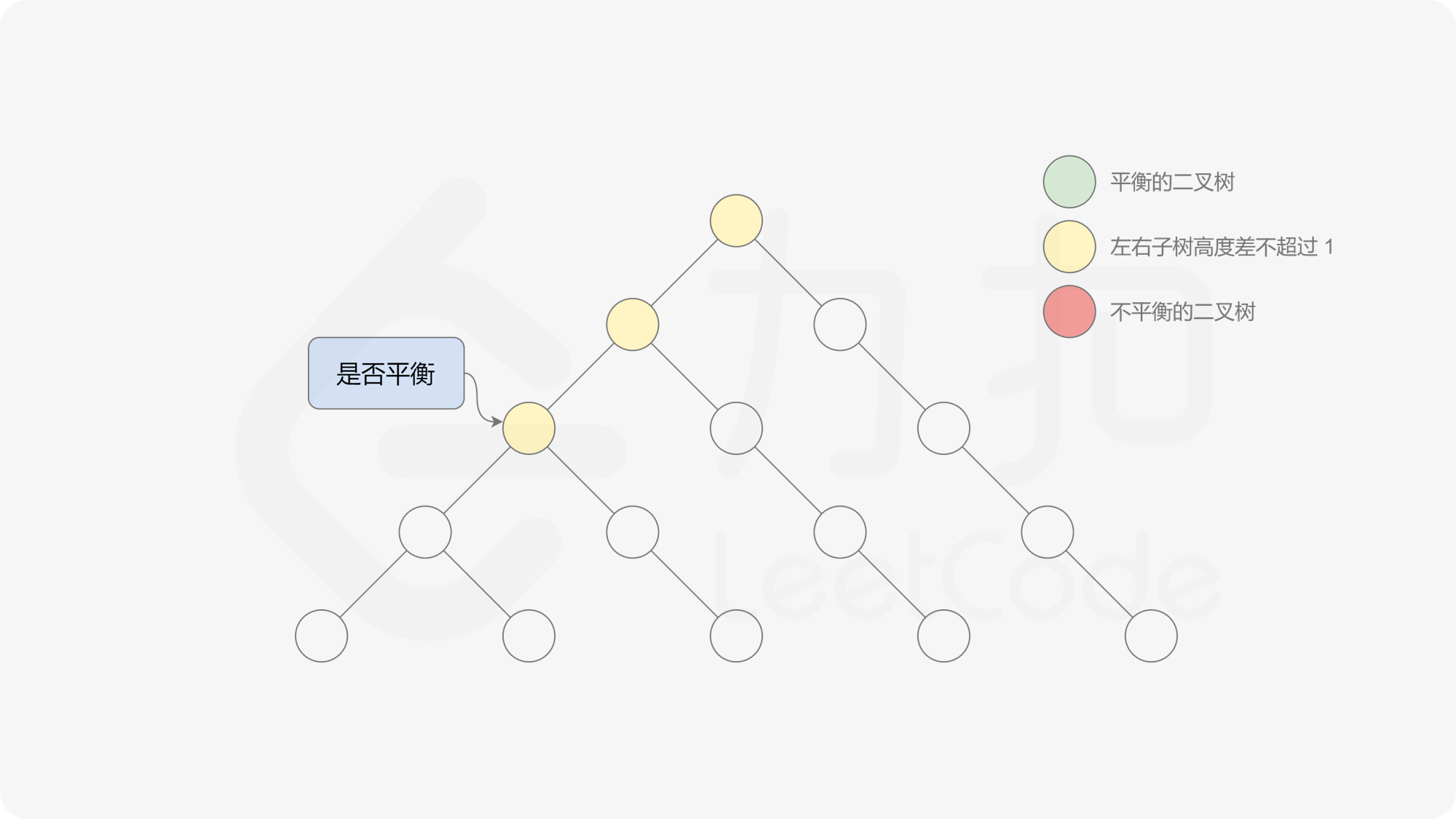 ,
,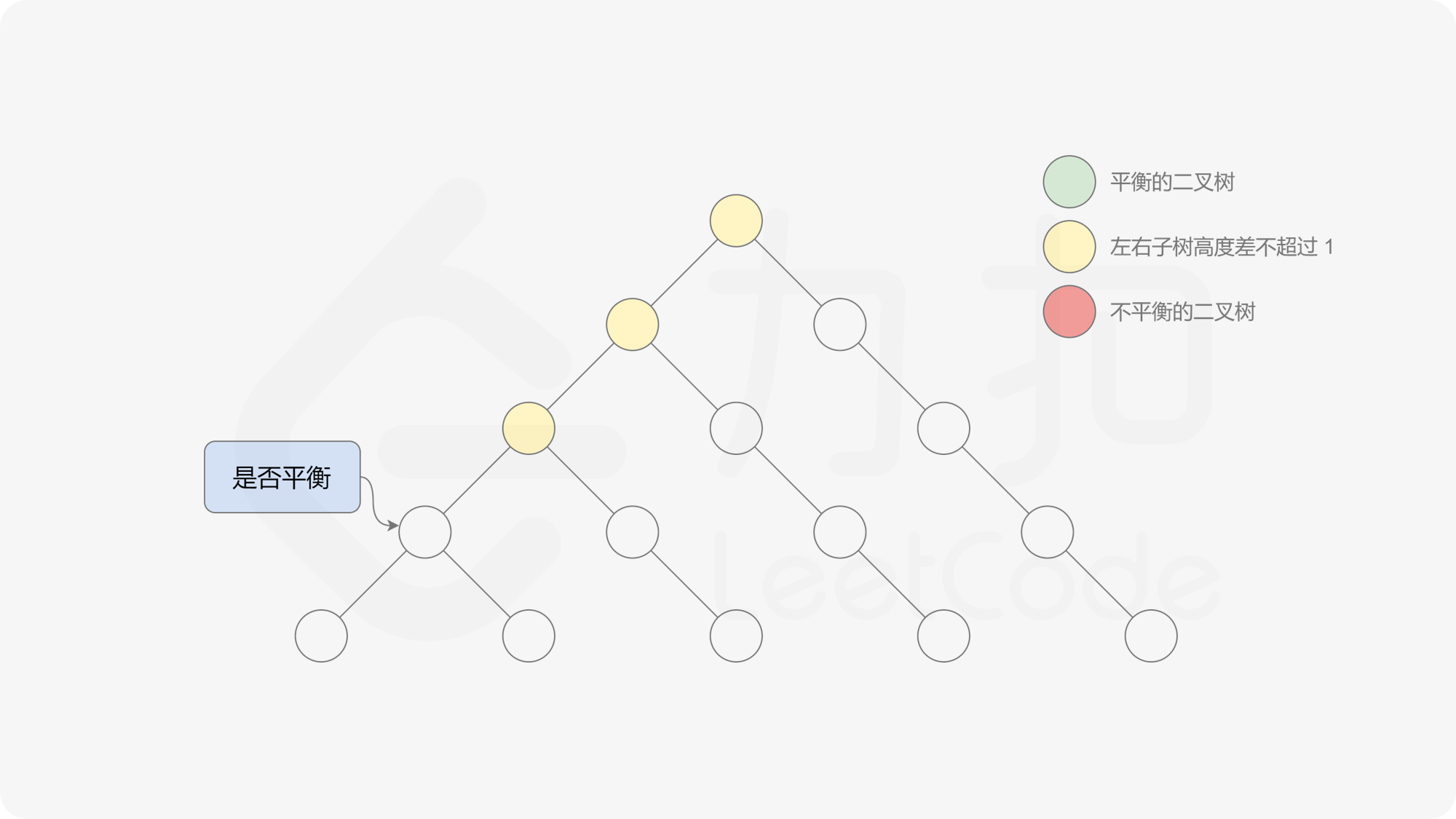 ,
,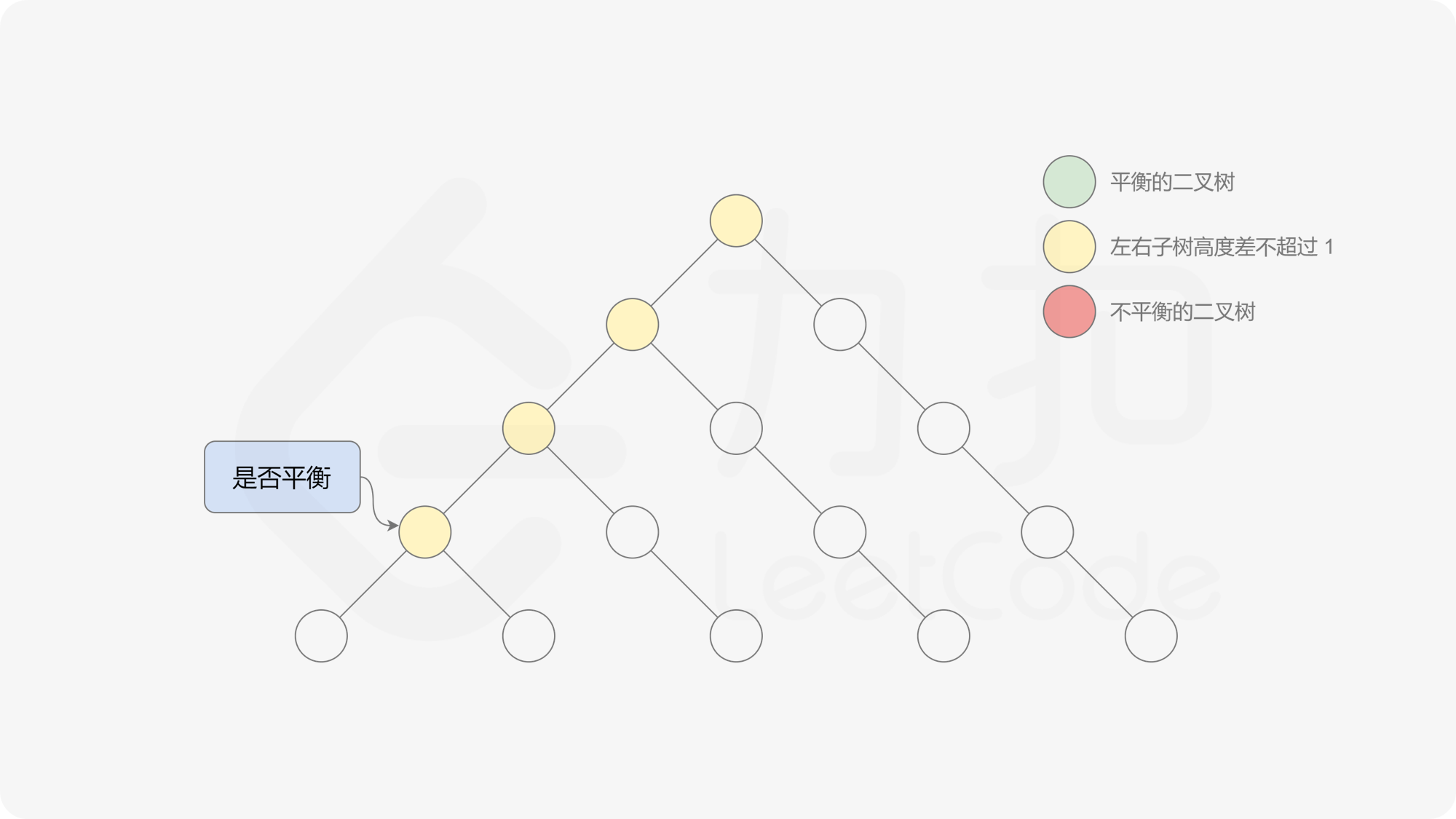 ,
,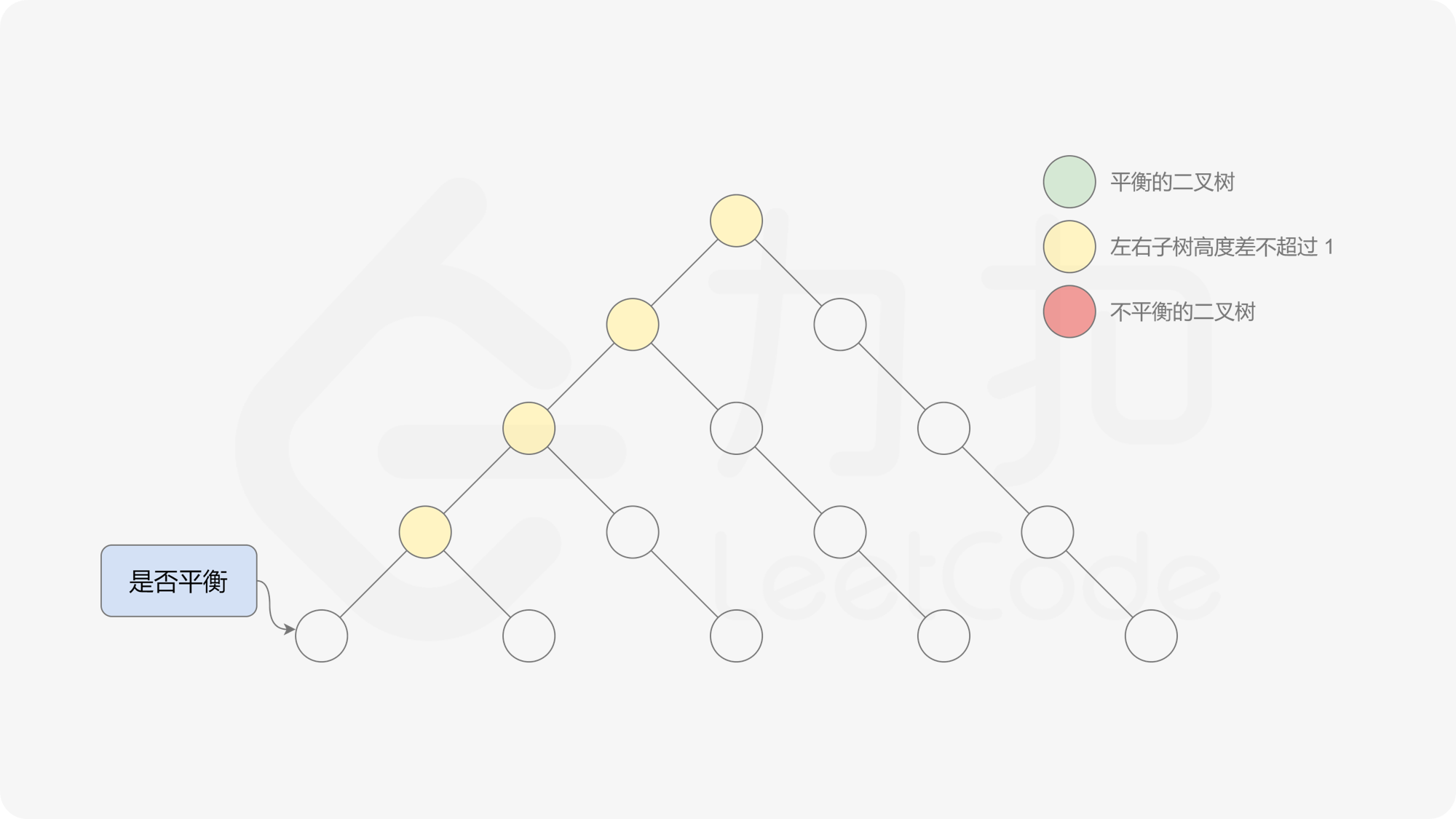 ,
,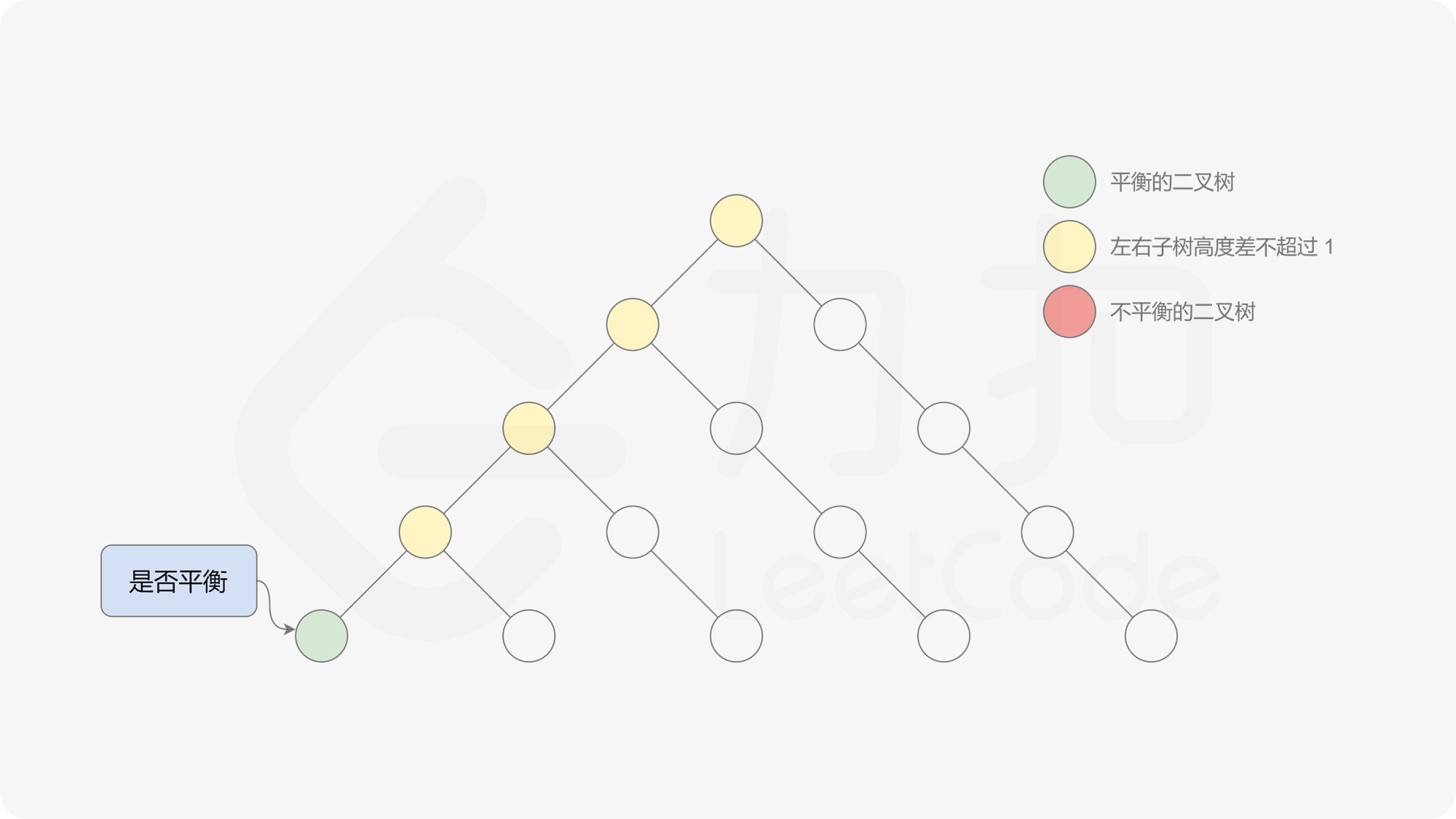 ,
,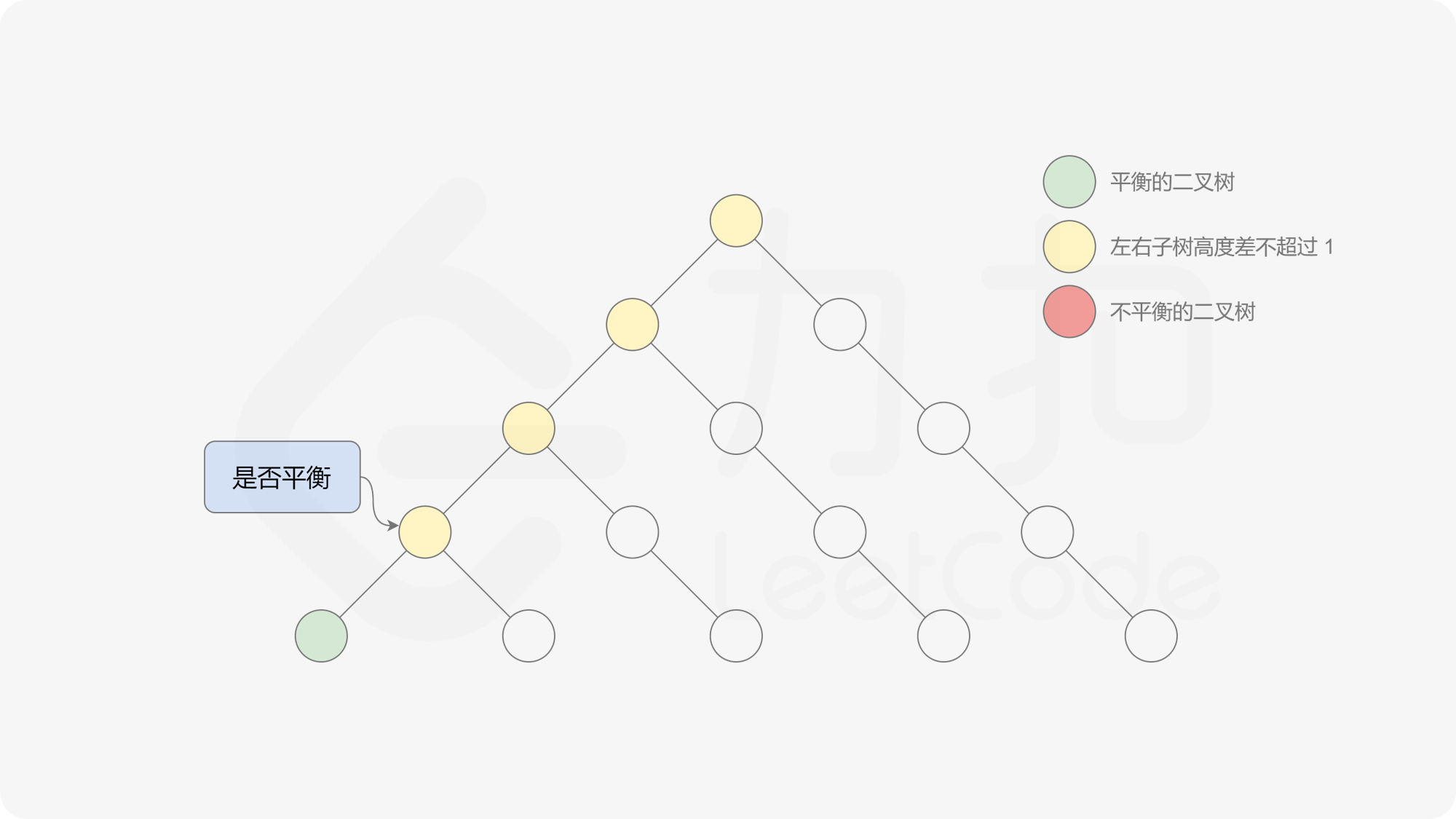 ,
, ,
,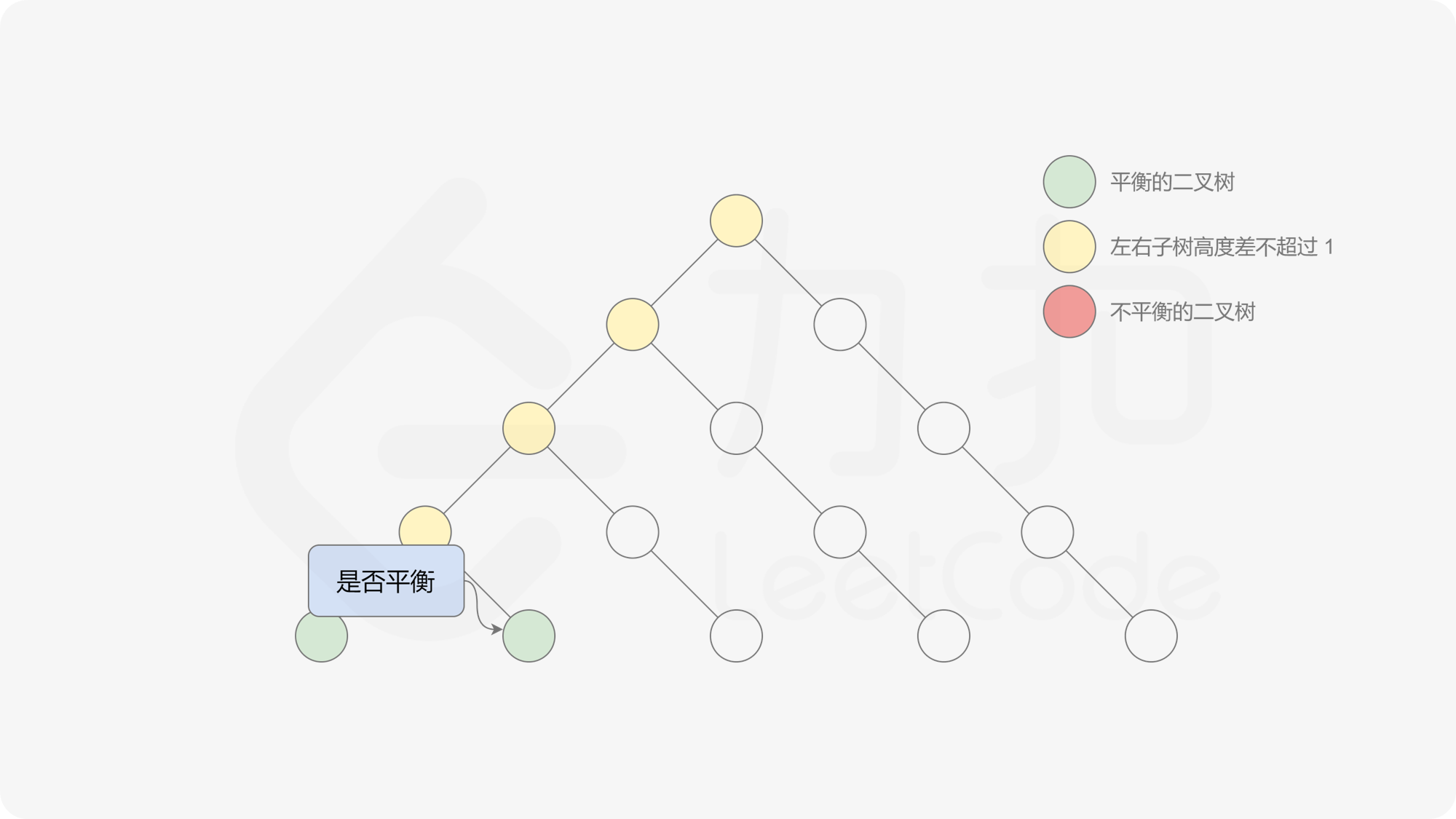 ,
,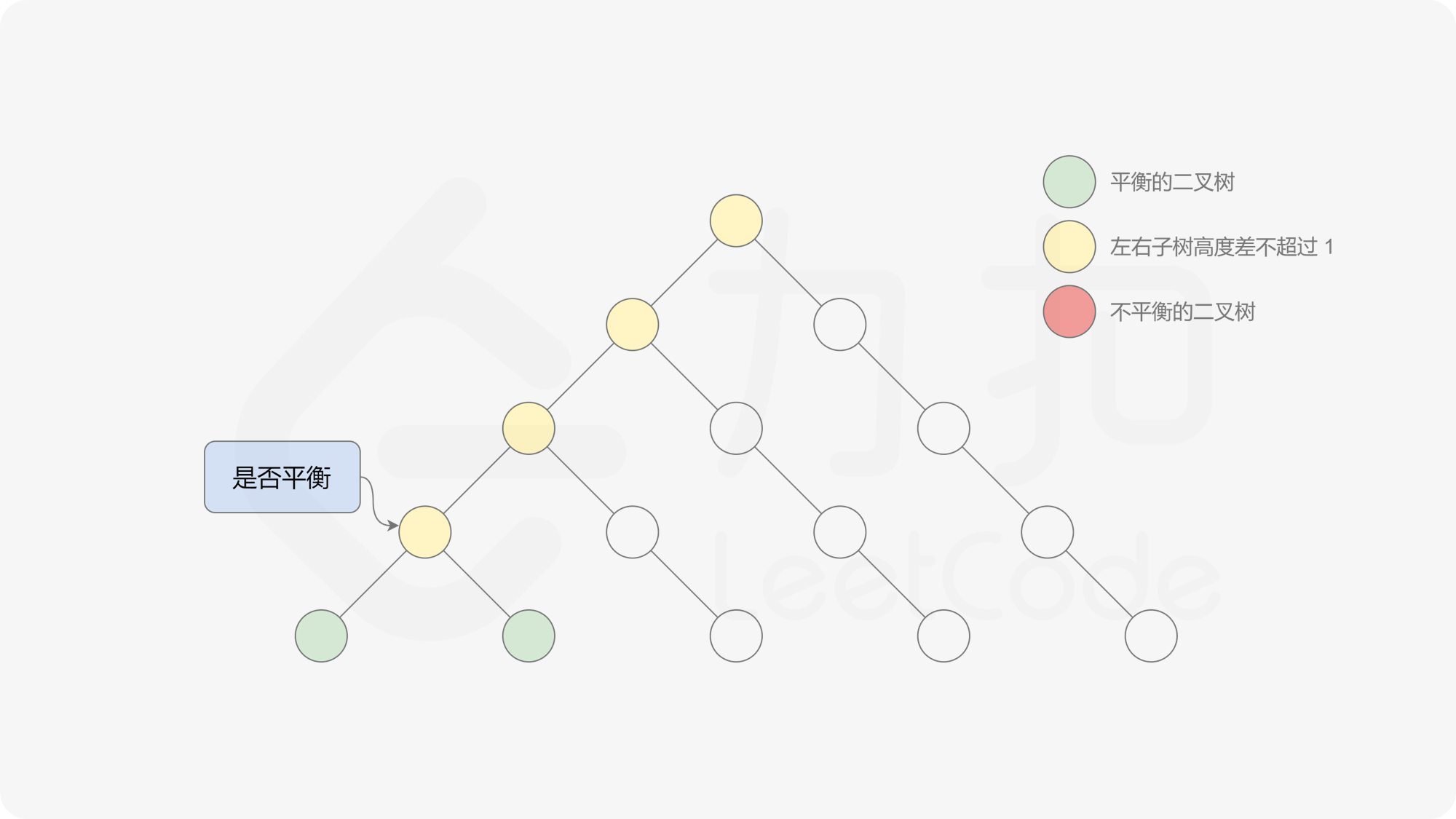 ,
,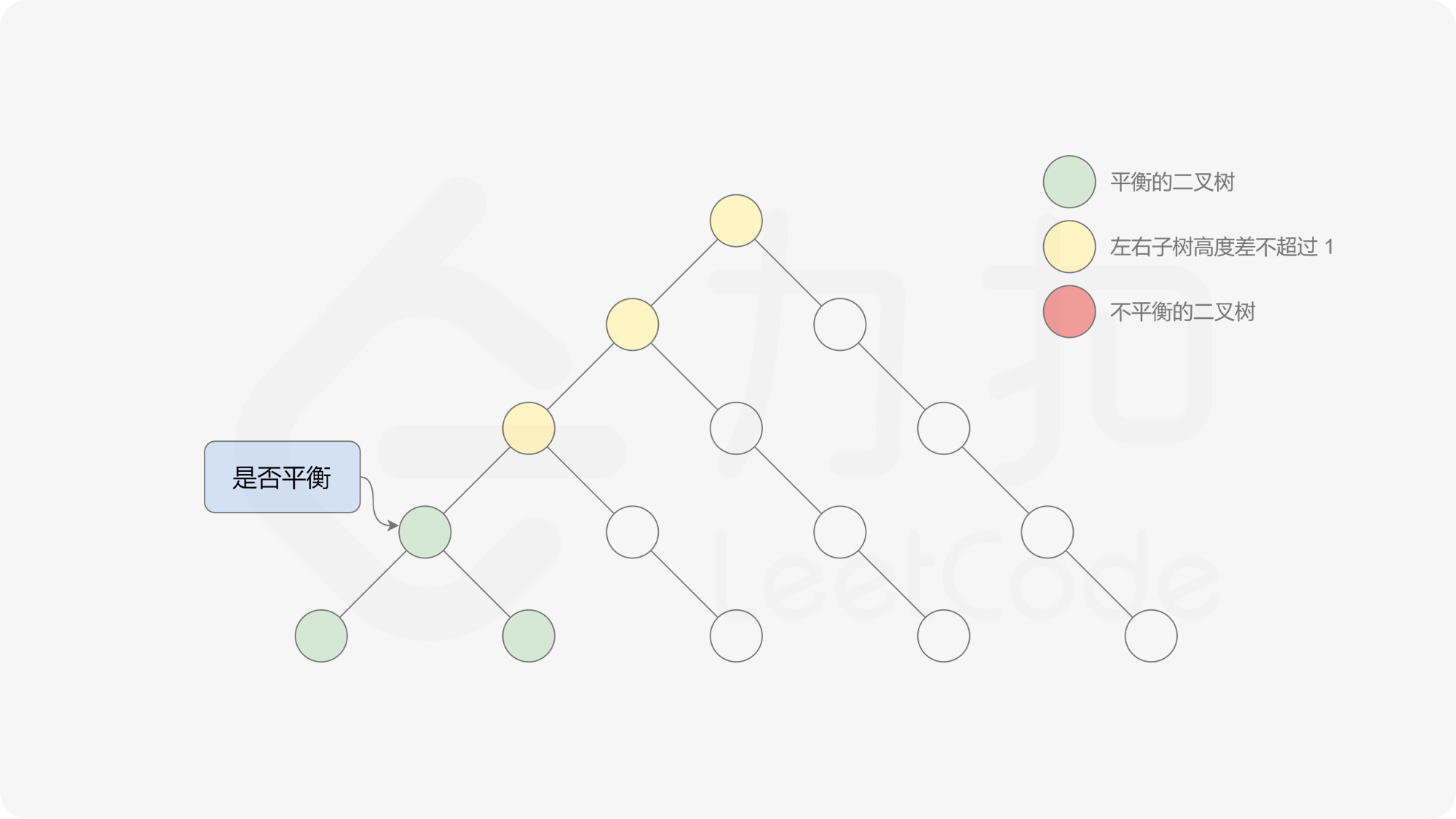 ,
,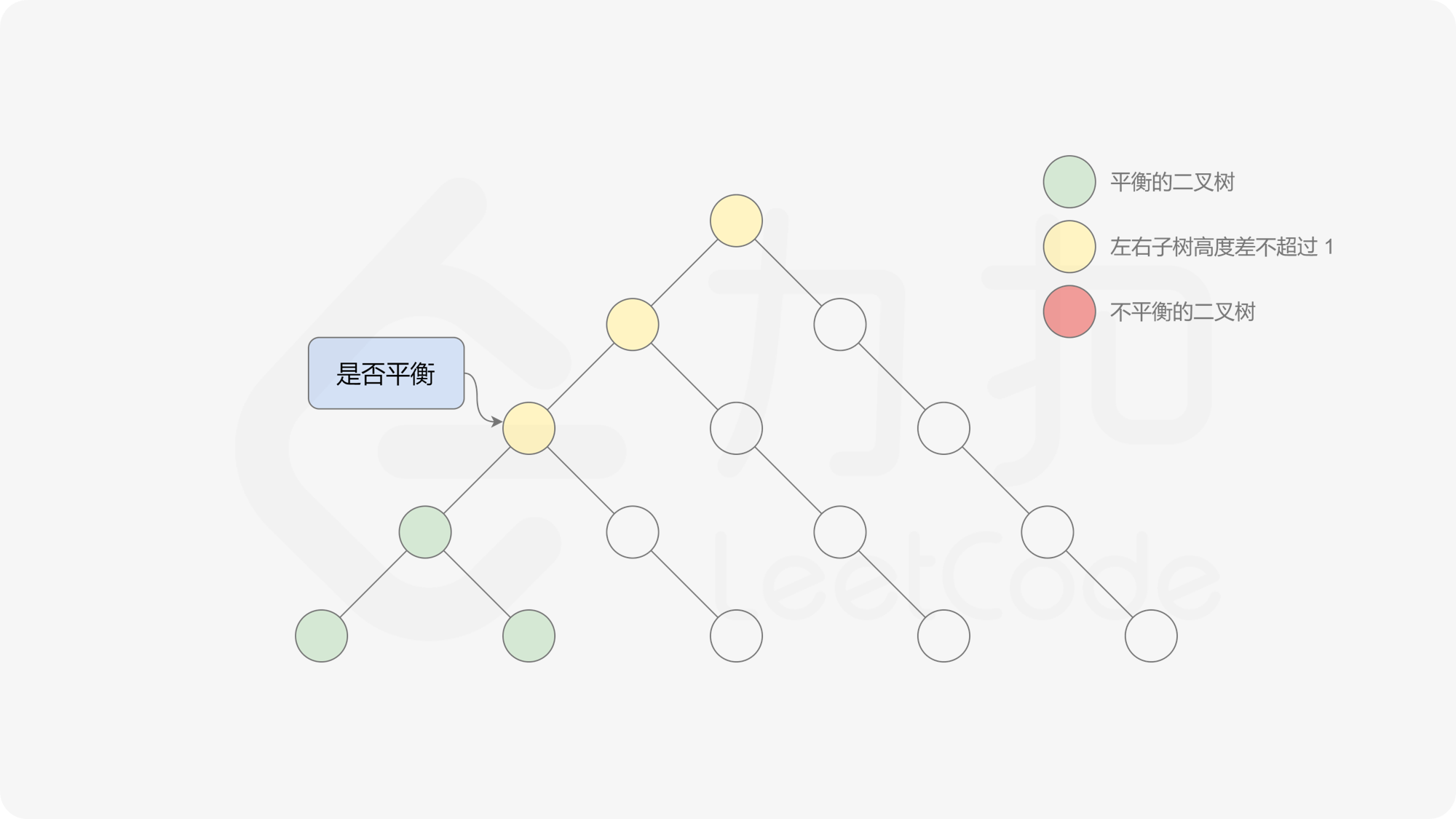 ,
,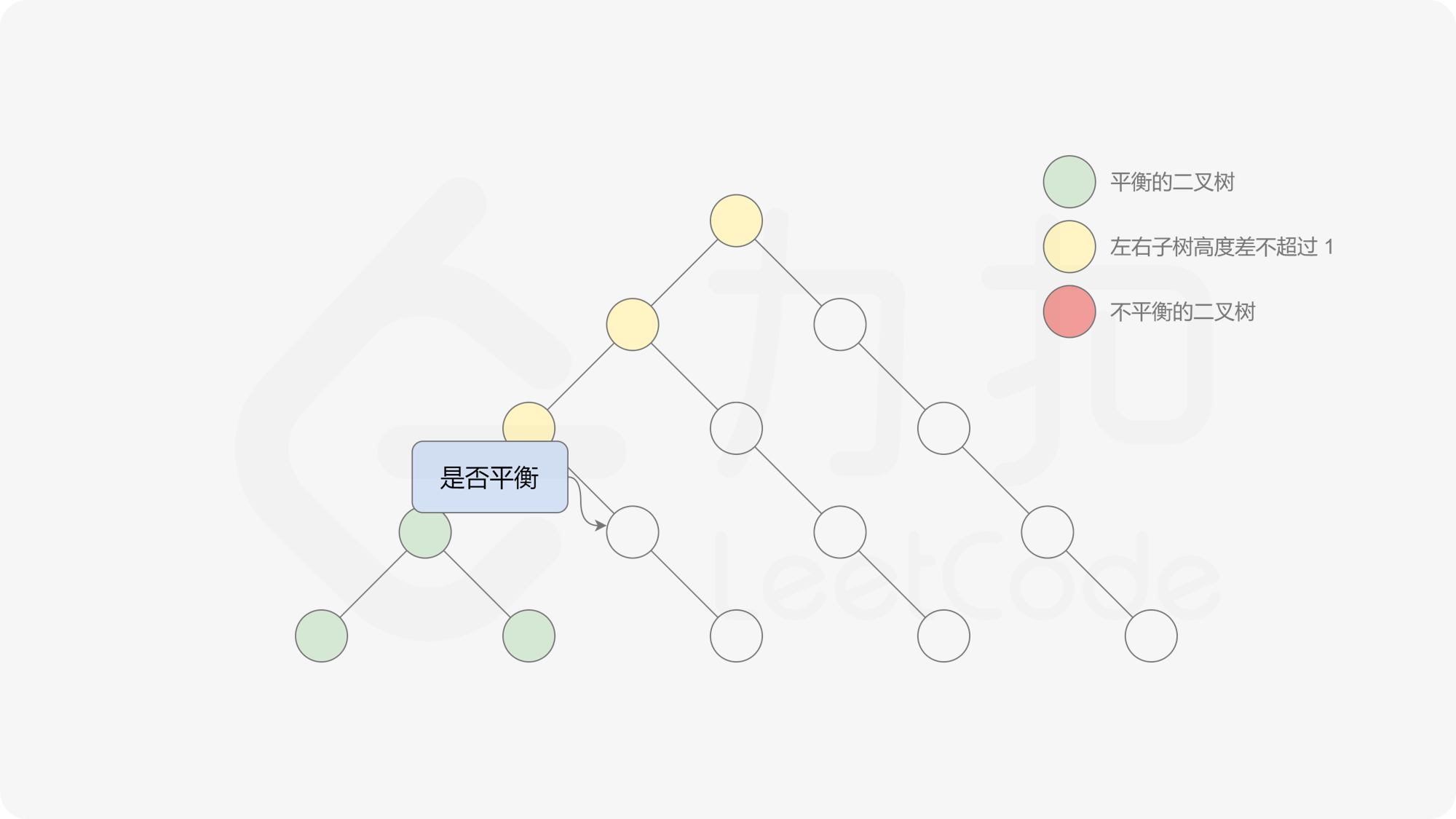 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
,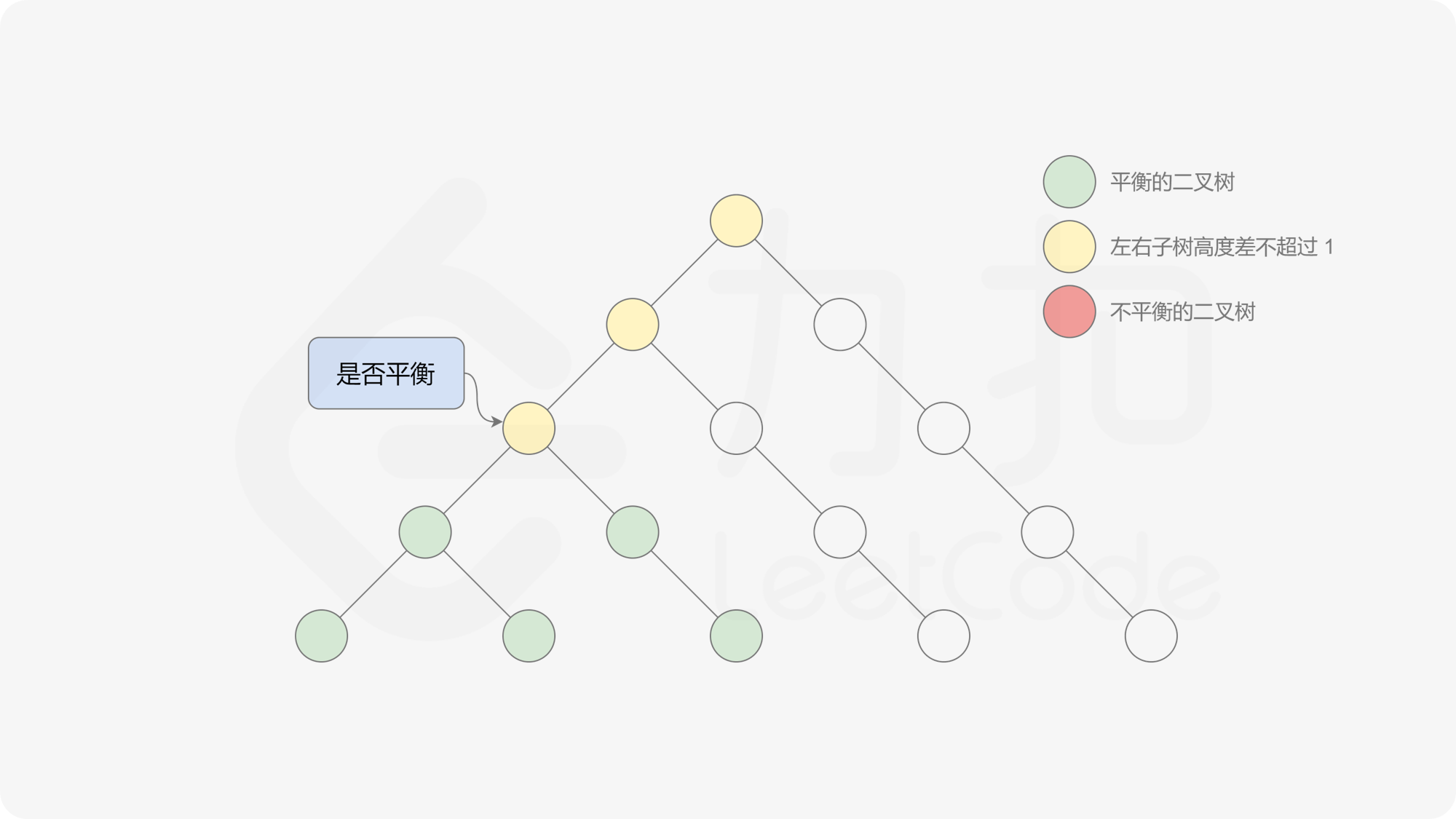 ,
,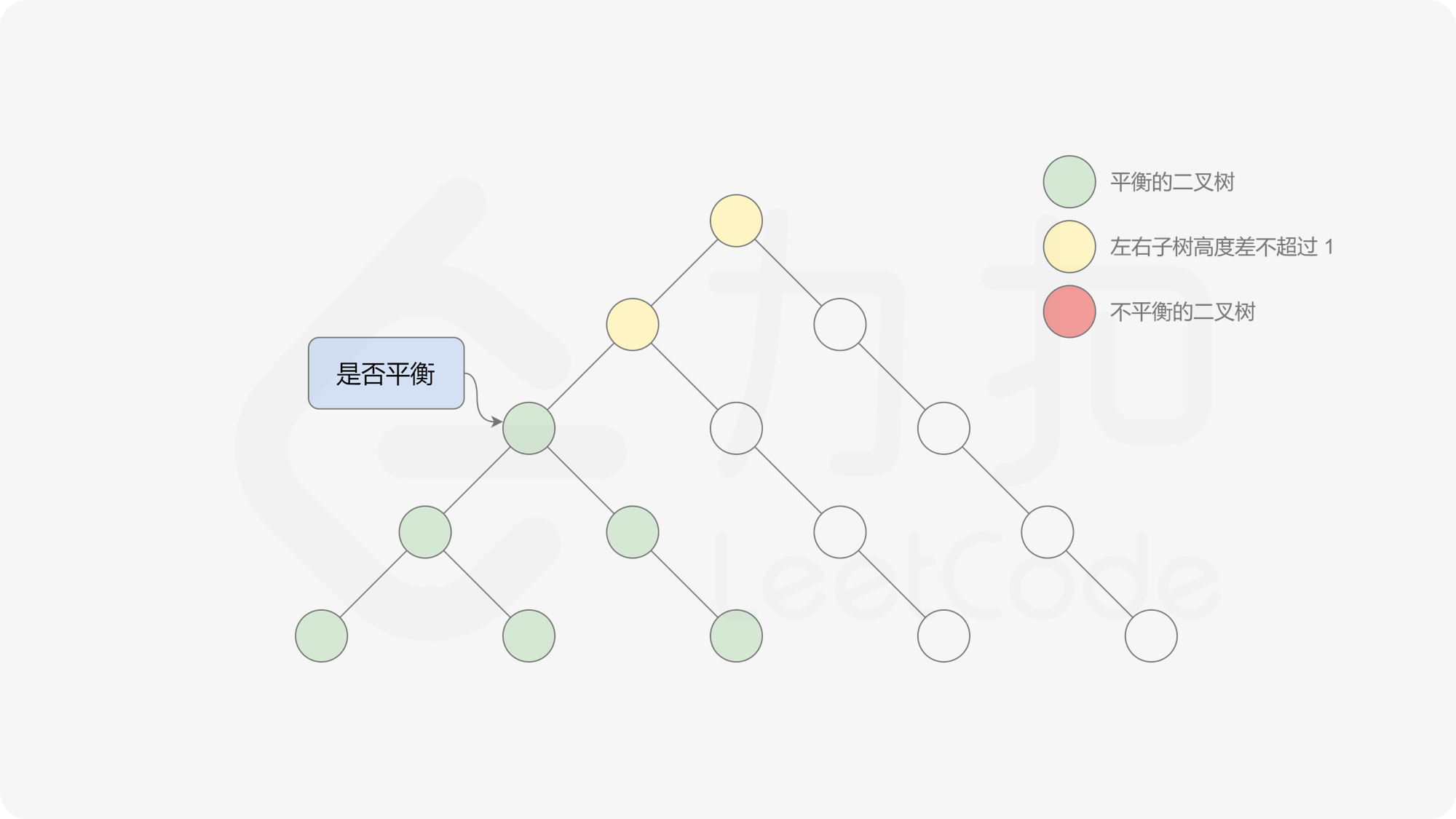 ,
,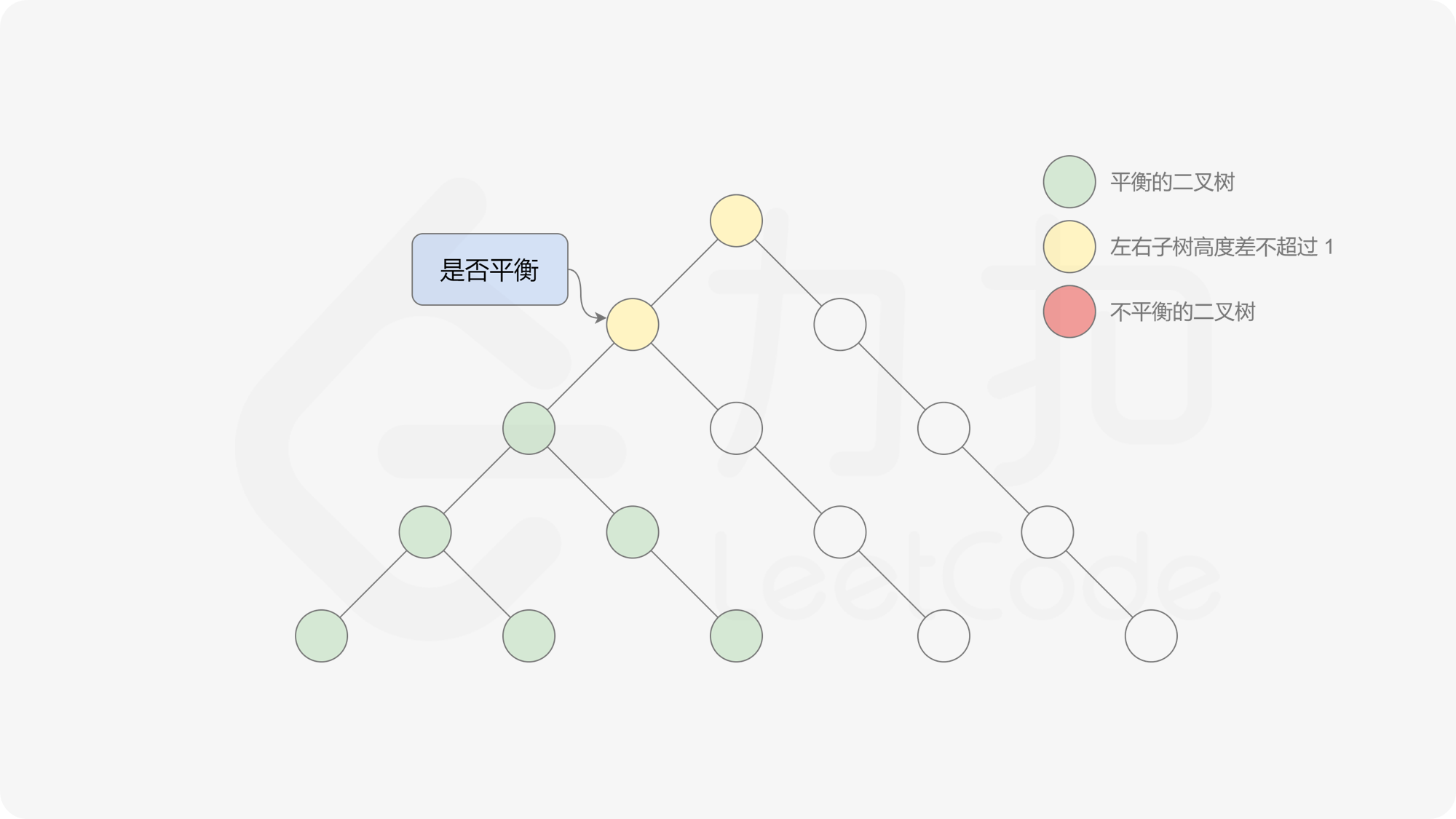 ,
,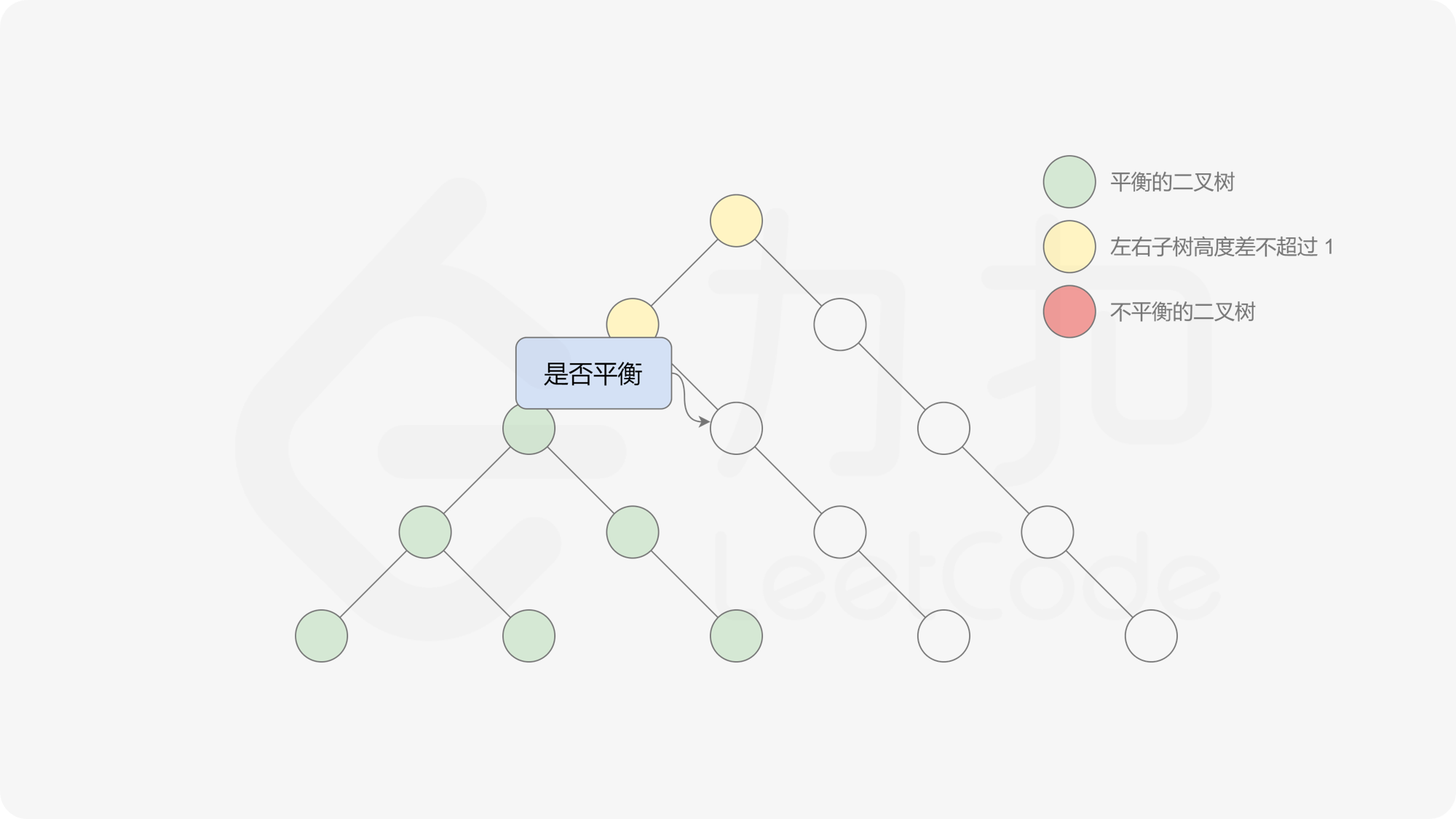 ,
,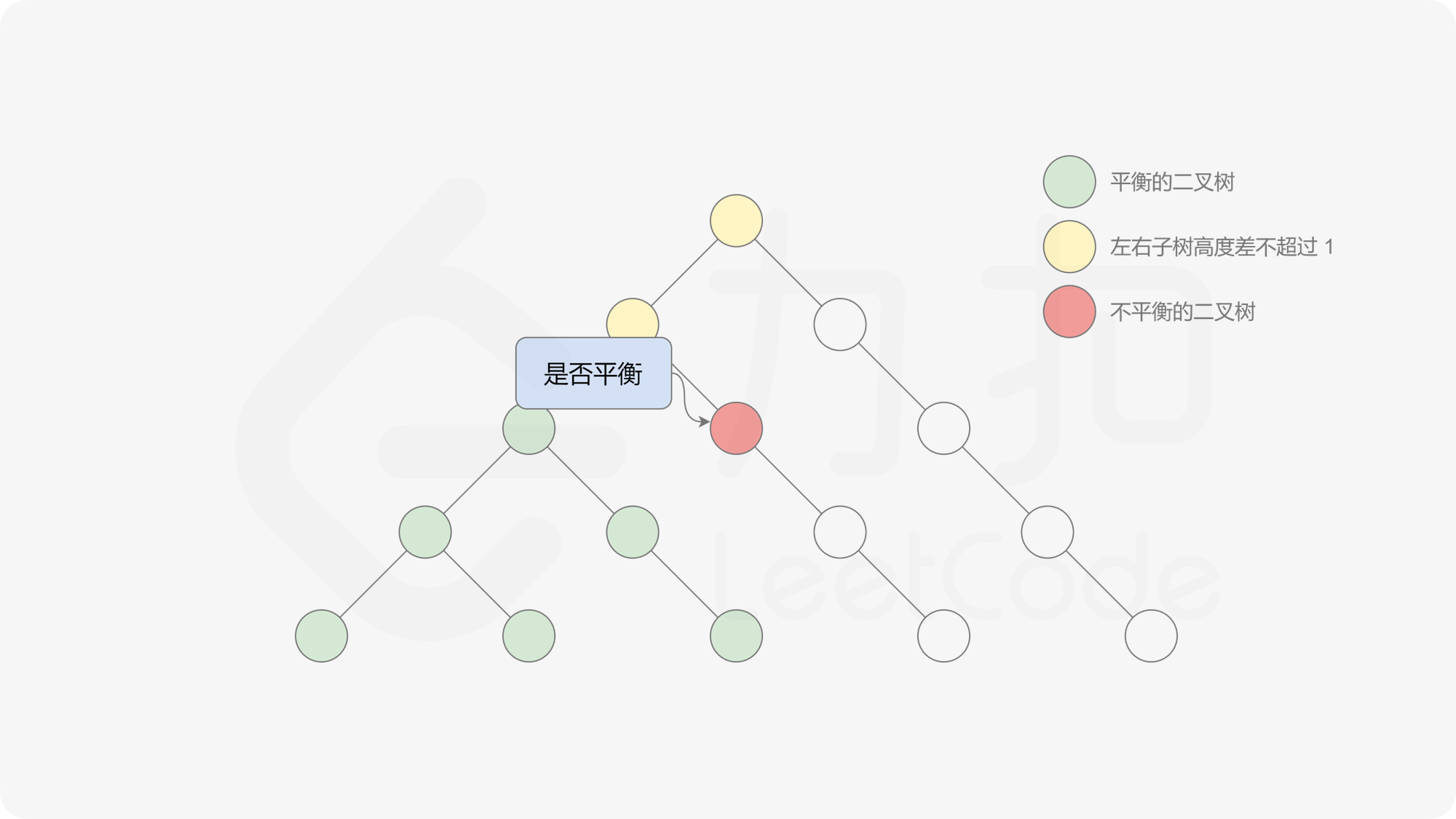 ,
,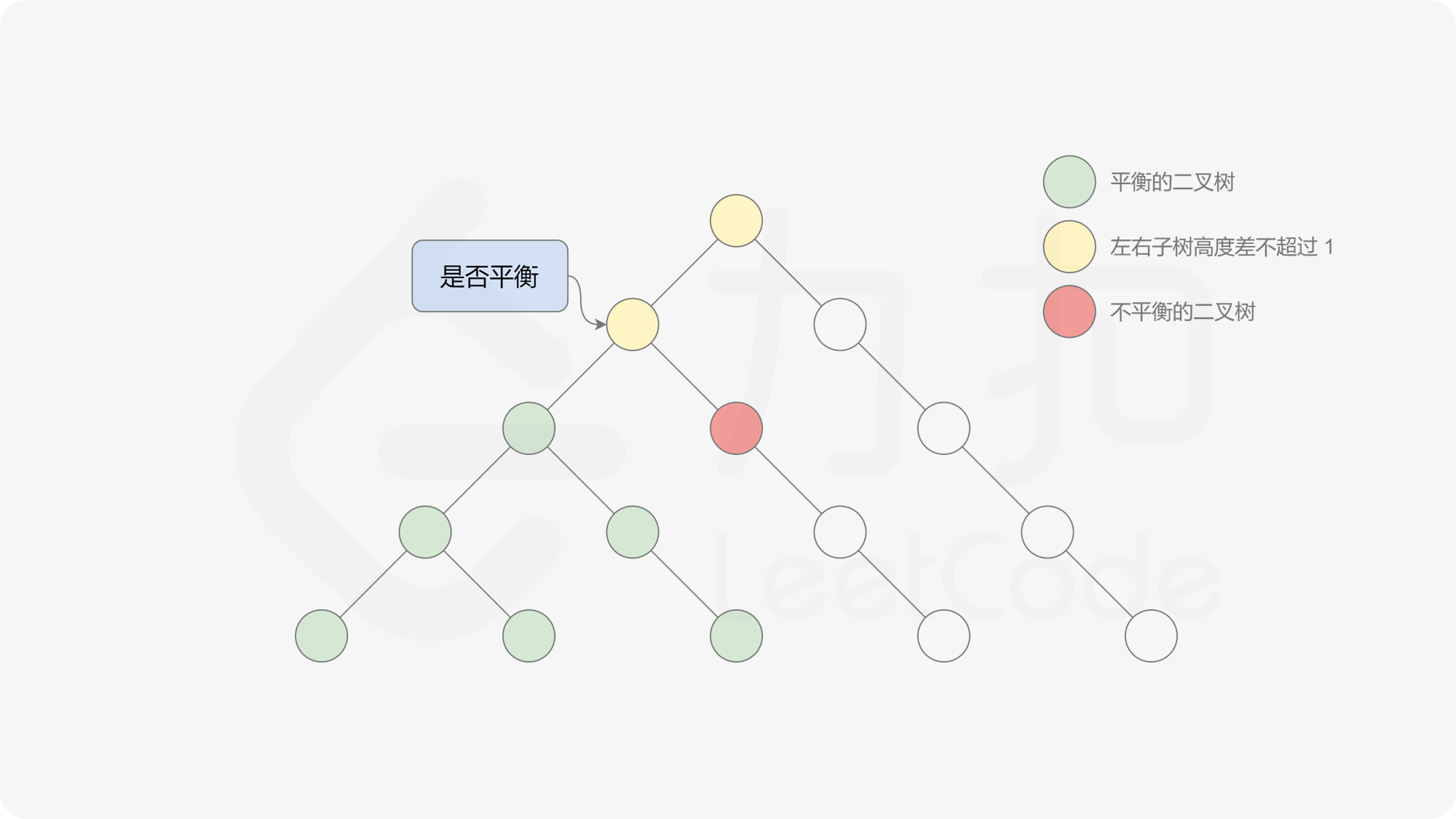 ,
, ,
,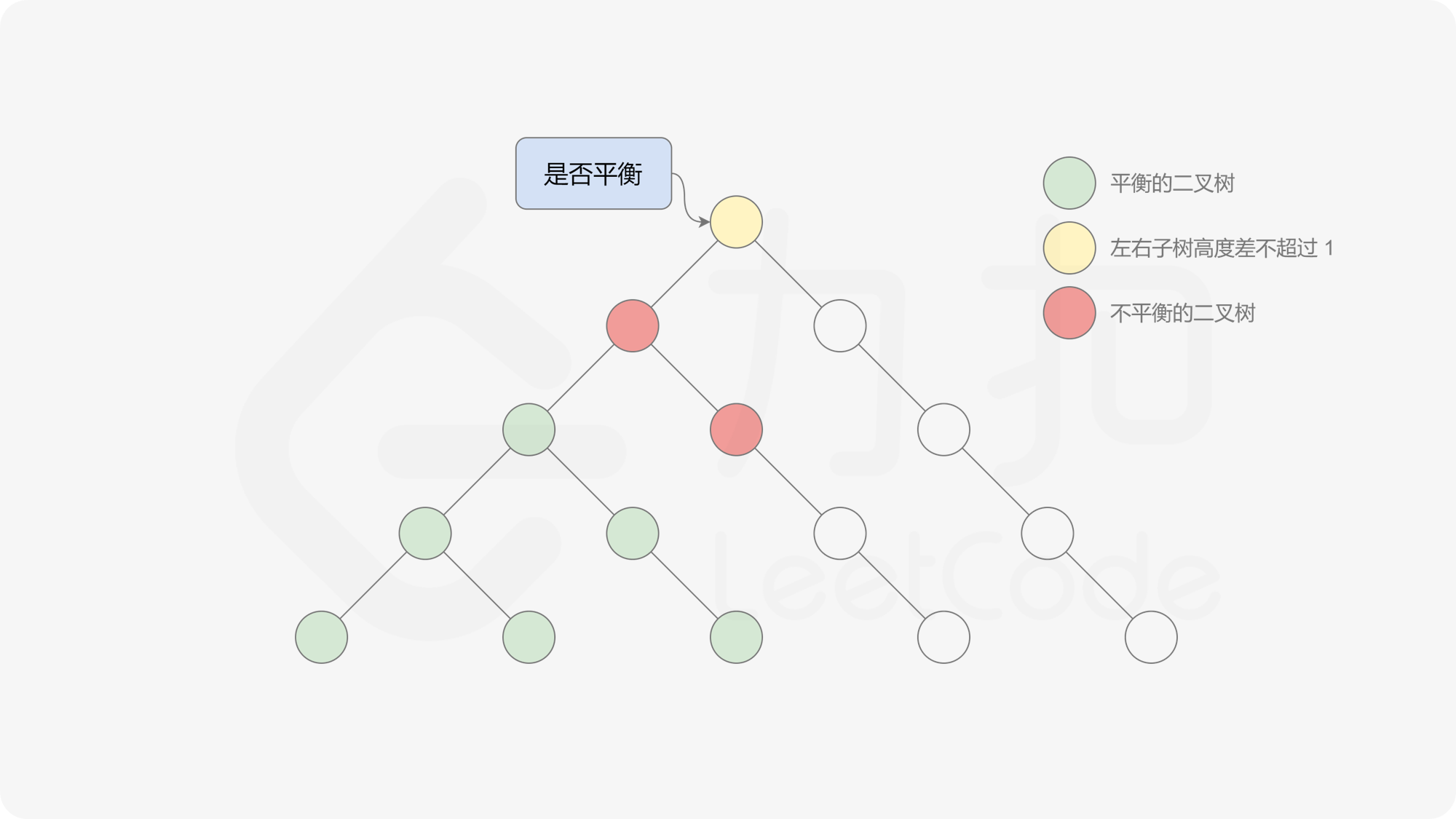 ,
,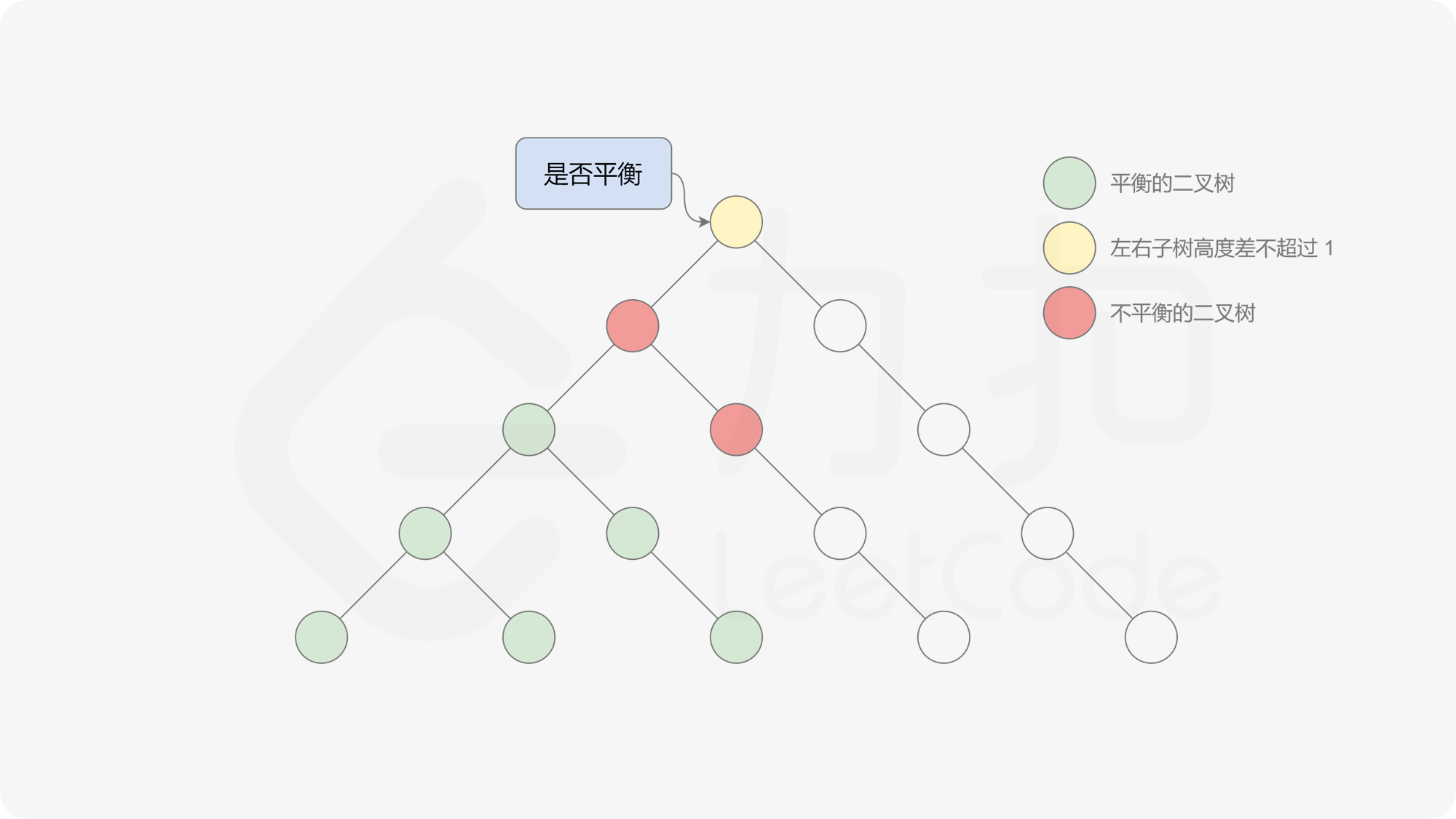 >
>
###Java
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
} else {
return Math.abs(height(root.left) - height(root.right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
}
public int height(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
} else {
return Math.max(height(root.left), height(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
}
###C++
class Solution {
public:
int height(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
} else {
return max(height(root->left), height(root->right)) + 1;
}
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return true;
} else {
return abs(height(root->left) - height(root->right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right);
}
}
};
###Python
class Solution:
def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
def height(root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
return max(height(root.left), height(root.right)) + 1
if not root:
return True
return abs(height(root.left) - height(root.right)) <= 1 and self.isBalanced(root.left) and self.isBalanced(root.right)
###C
int height(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
} else {
return fmax(height(root->left), height(root->right)) + 1;
}
}
bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return true;
} else {
return fabs(height(root->left) - height(root->right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right);
}
}
###golang
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
if root == nil {
return true
}
return abs(height(root.Left) - height(root.Right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.Left) && isBalanced(root.Right)
}
func height(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
return max(height(root.Left), height(root.Right)) + 1
}
func max(x, y int) int {
if x > y {
return x
}
return y
}
func abs(x int) int {
if x < 0 {
return -1 * x
}
return x
}
复杂度分析
-
时间复杂度:$O(n^2)$,其中 $n$ 是二叉树中的节点个数。
最坏情况下,二叉树是满二叉树,需要遍历二叉树中的所有节点,时间复杂度是 $O(n)$。
对于节点 $p$,如果它的高度是 $d$,则 $\texttt{height}(p)$ 最多会被调用 $d$ 次(即遍历到它的每一个祖先节点时)。对于平均的情况,一棵树的高度 $h$ 满足 $O(h)=O(\log n)$,因为 $d \leq h$,所以总时间复杂度为 $O(n \log n)$。对于最坏的情况,二叉树形成链式结构,高度为 $O(n)$,此时总时间复杂度为 $O(n^2)$。 -
空间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 是二叉树中的节点个数。空间复杂度主要取决于递归调用的层数,递归调用的层数不会超过 $n$。
方法二:自底向上的递归
方法一由于是自顶向下递归,因此对于同一个节点,函数 $\texttt{height}$ 会被重复调用,导致时间复杂度较高。如果使用自底向上的做法,则对于每个节点,函数 $\texttt{height}$ 只会被调用一次。
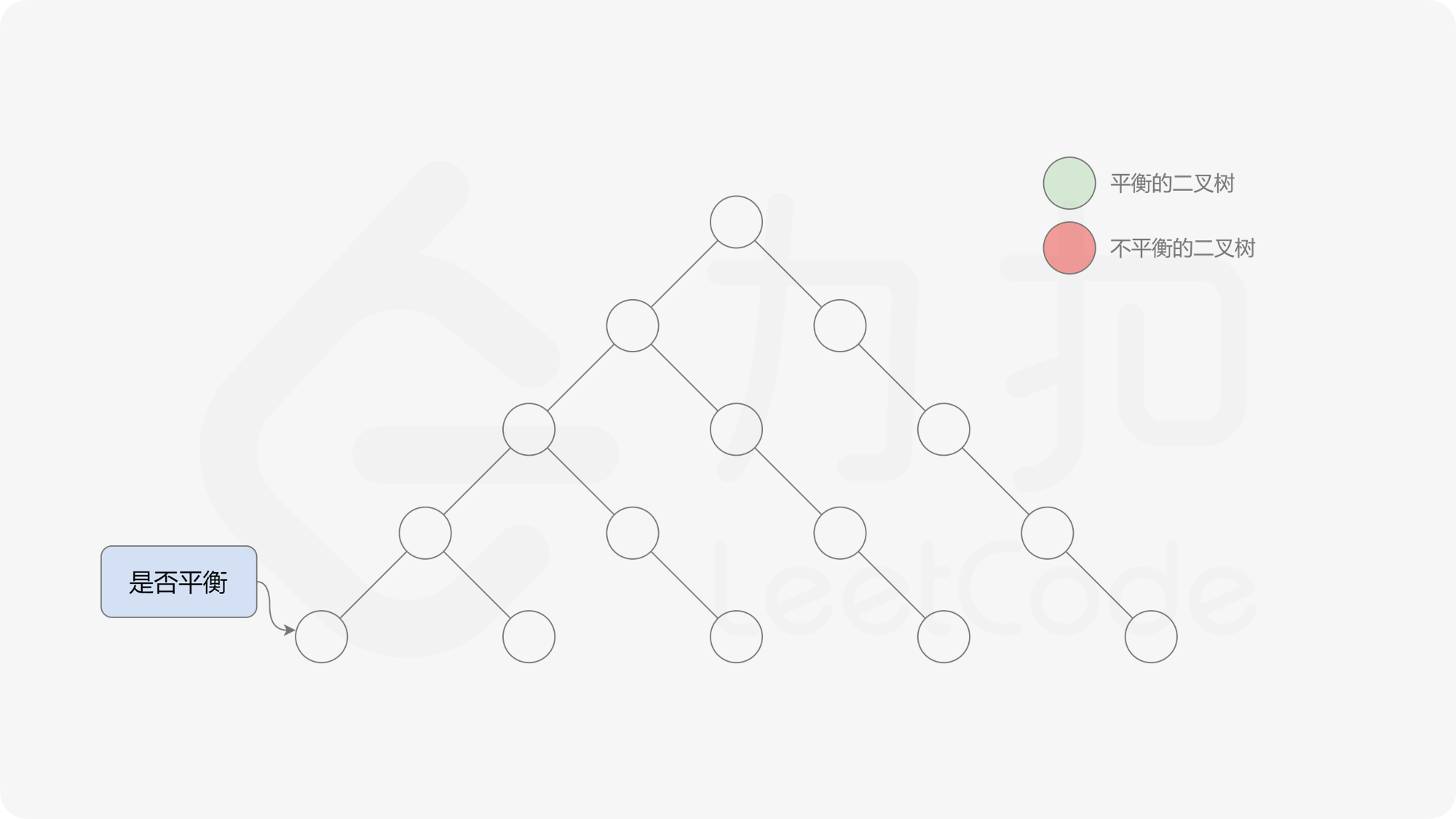
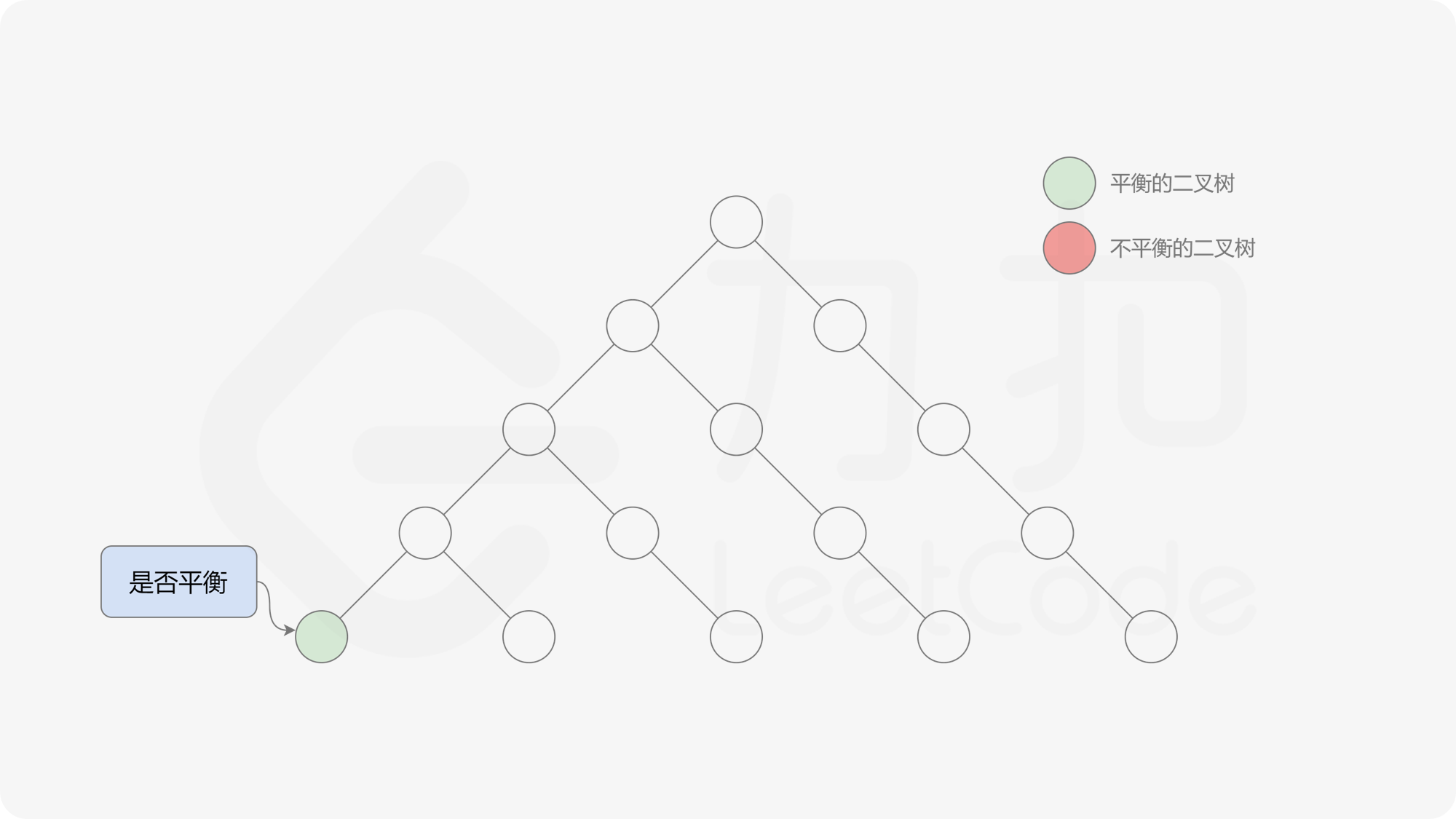
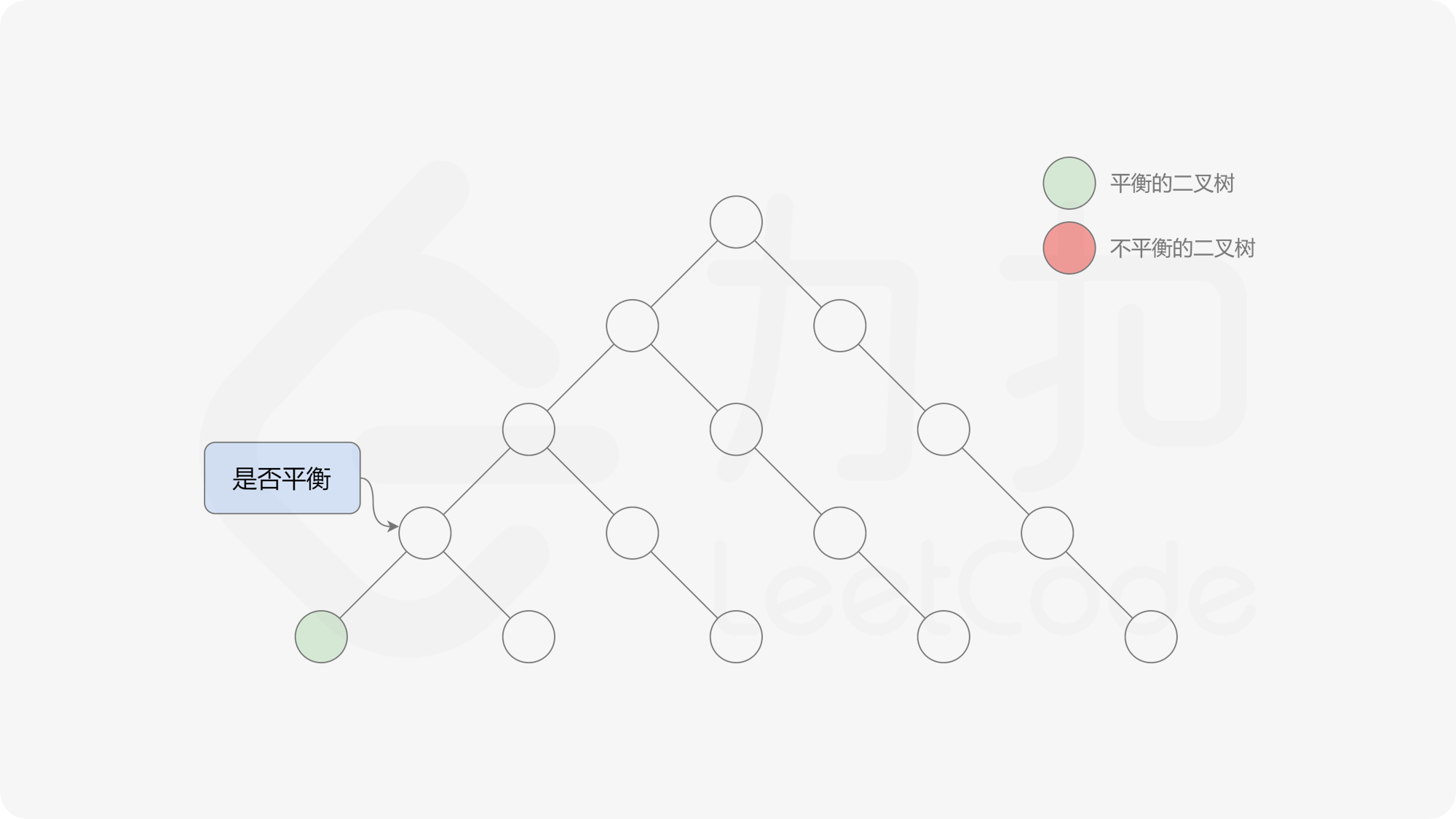
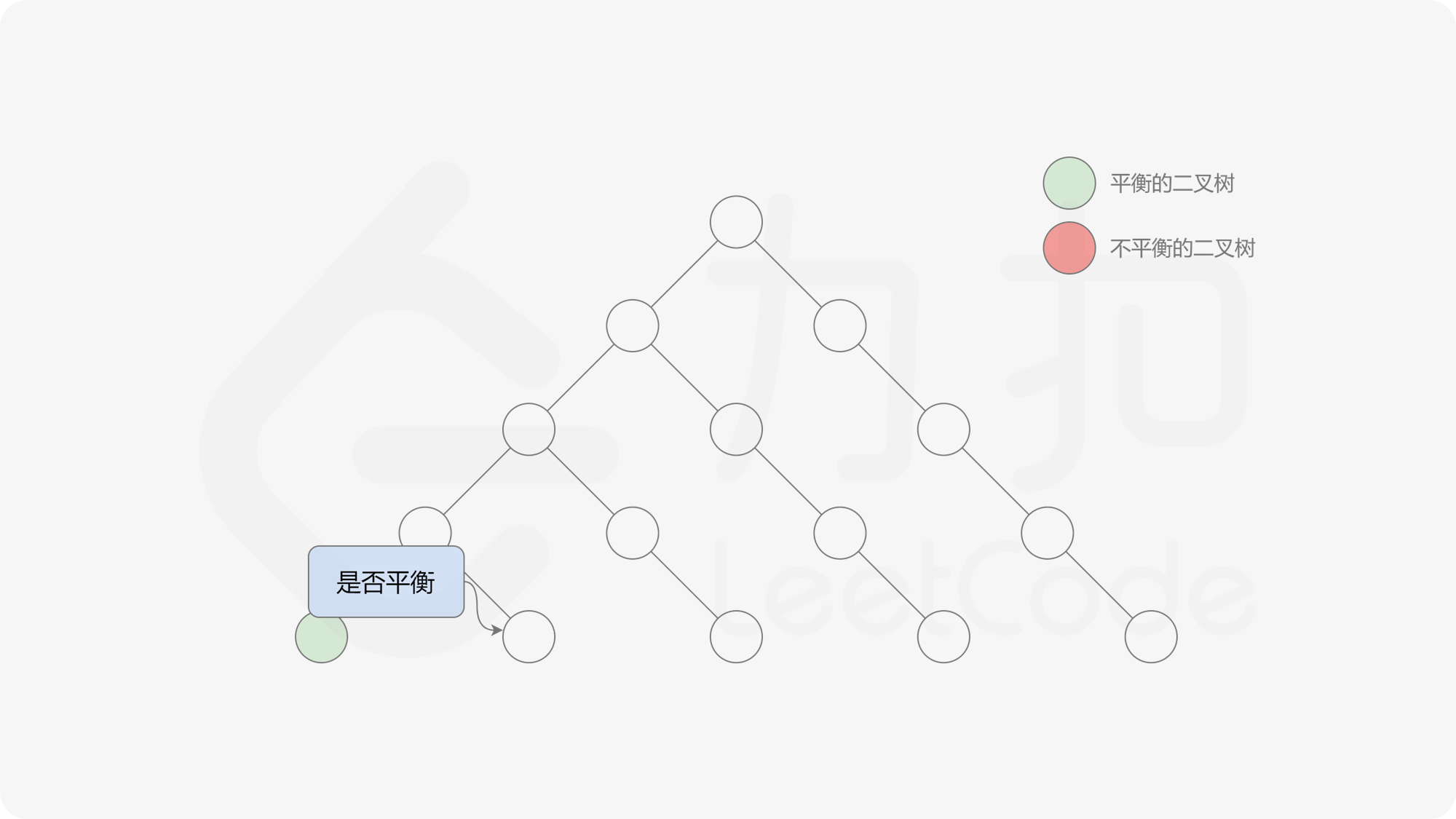
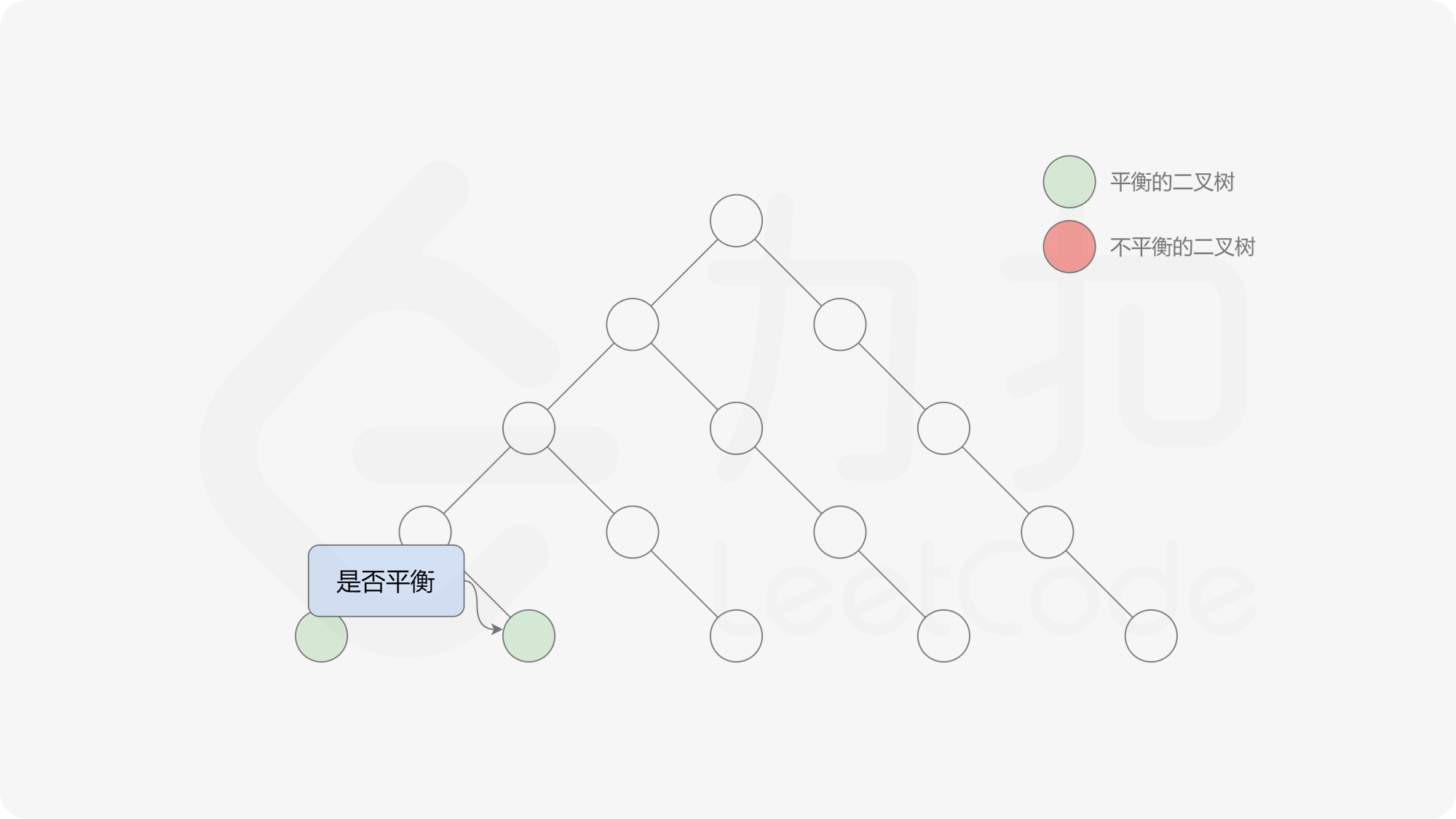
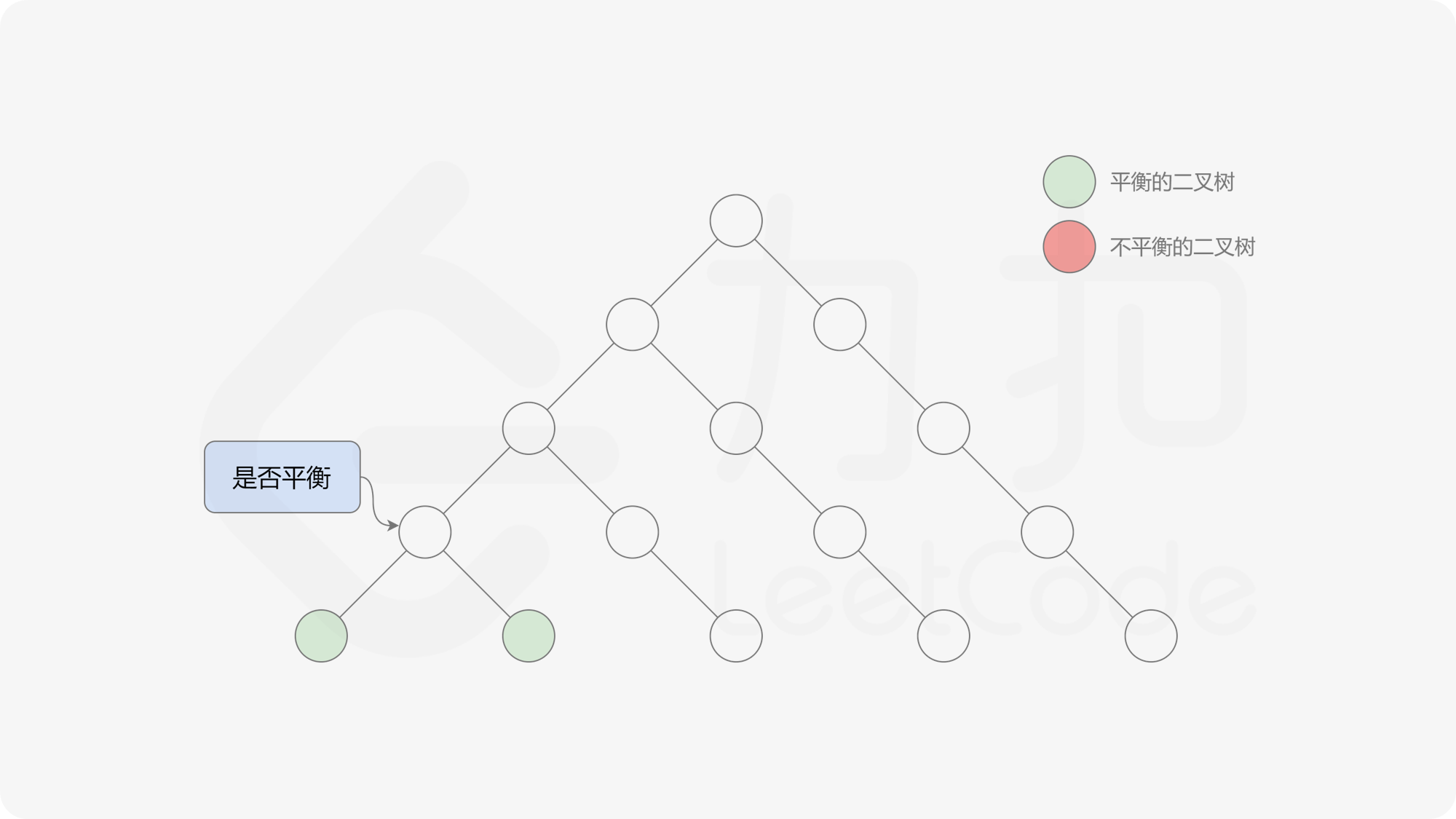
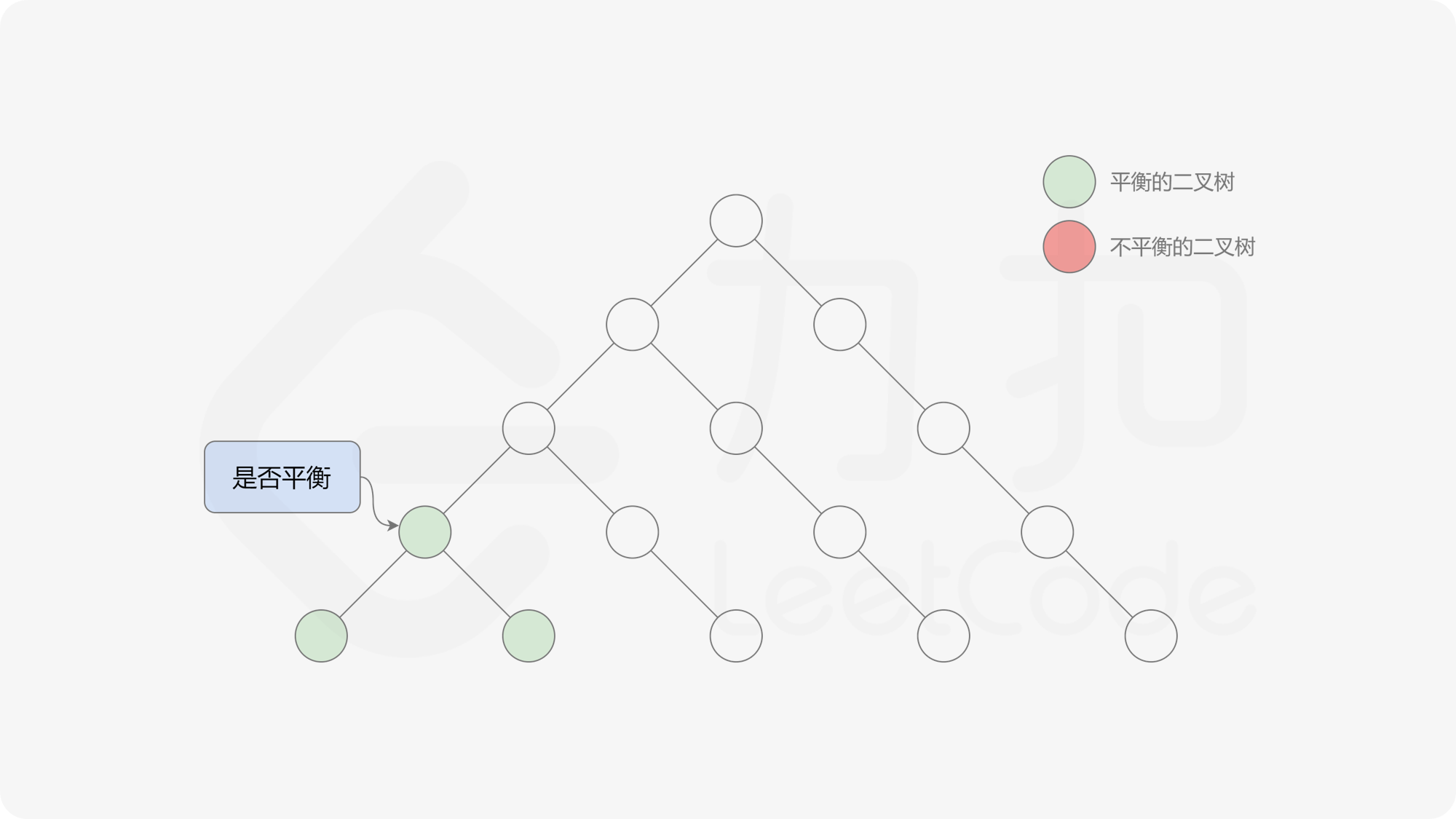
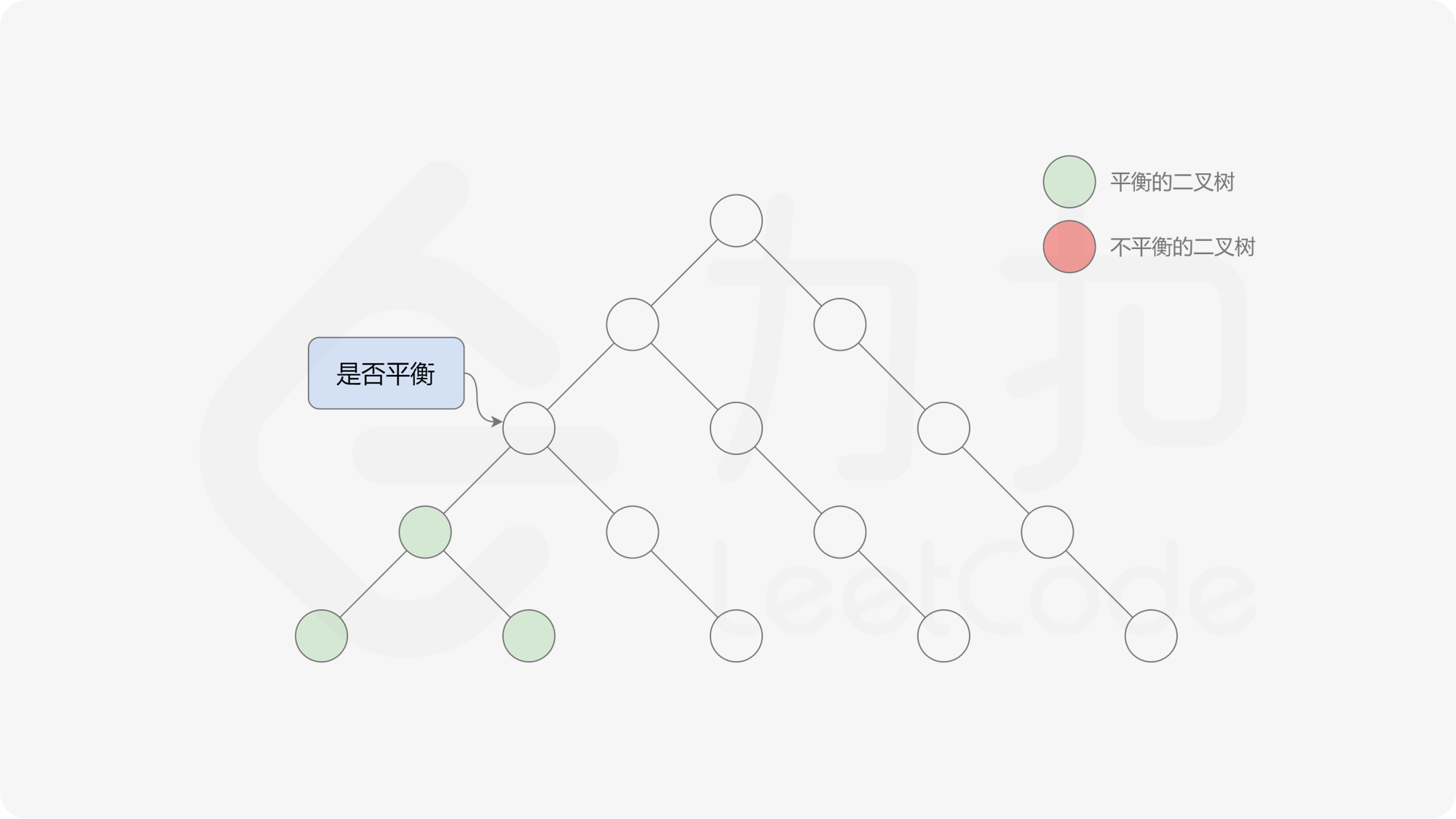
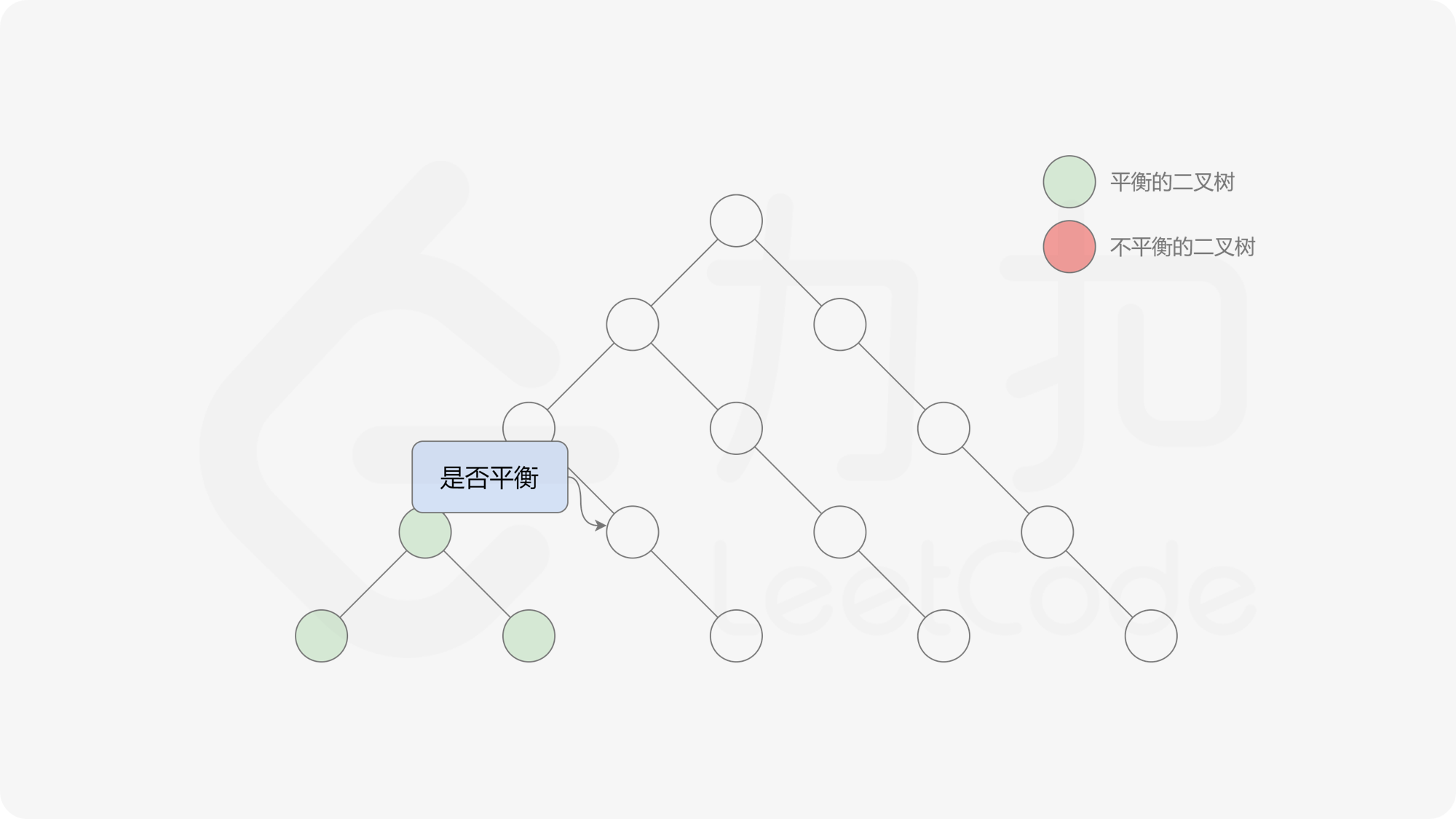
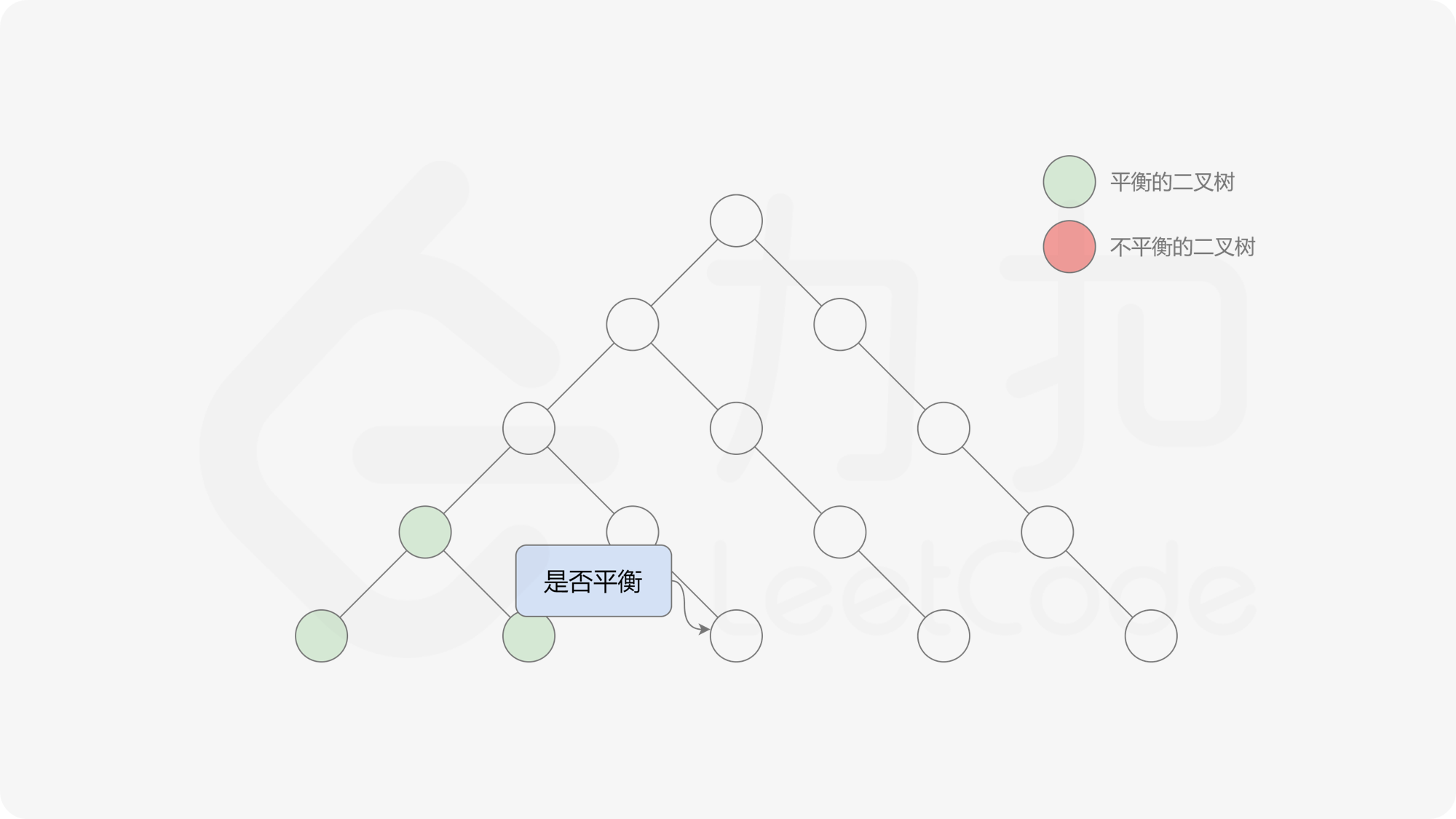
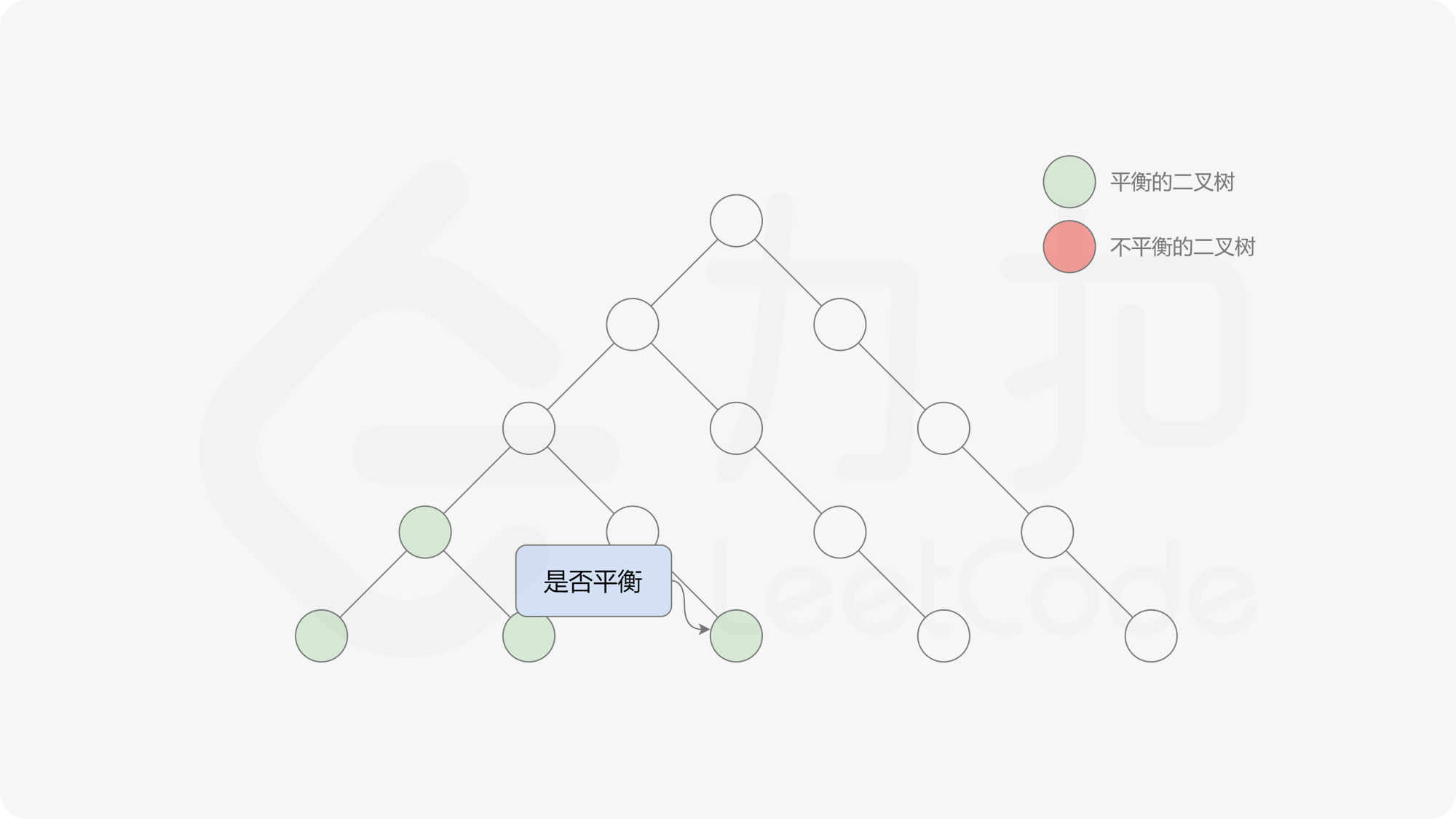
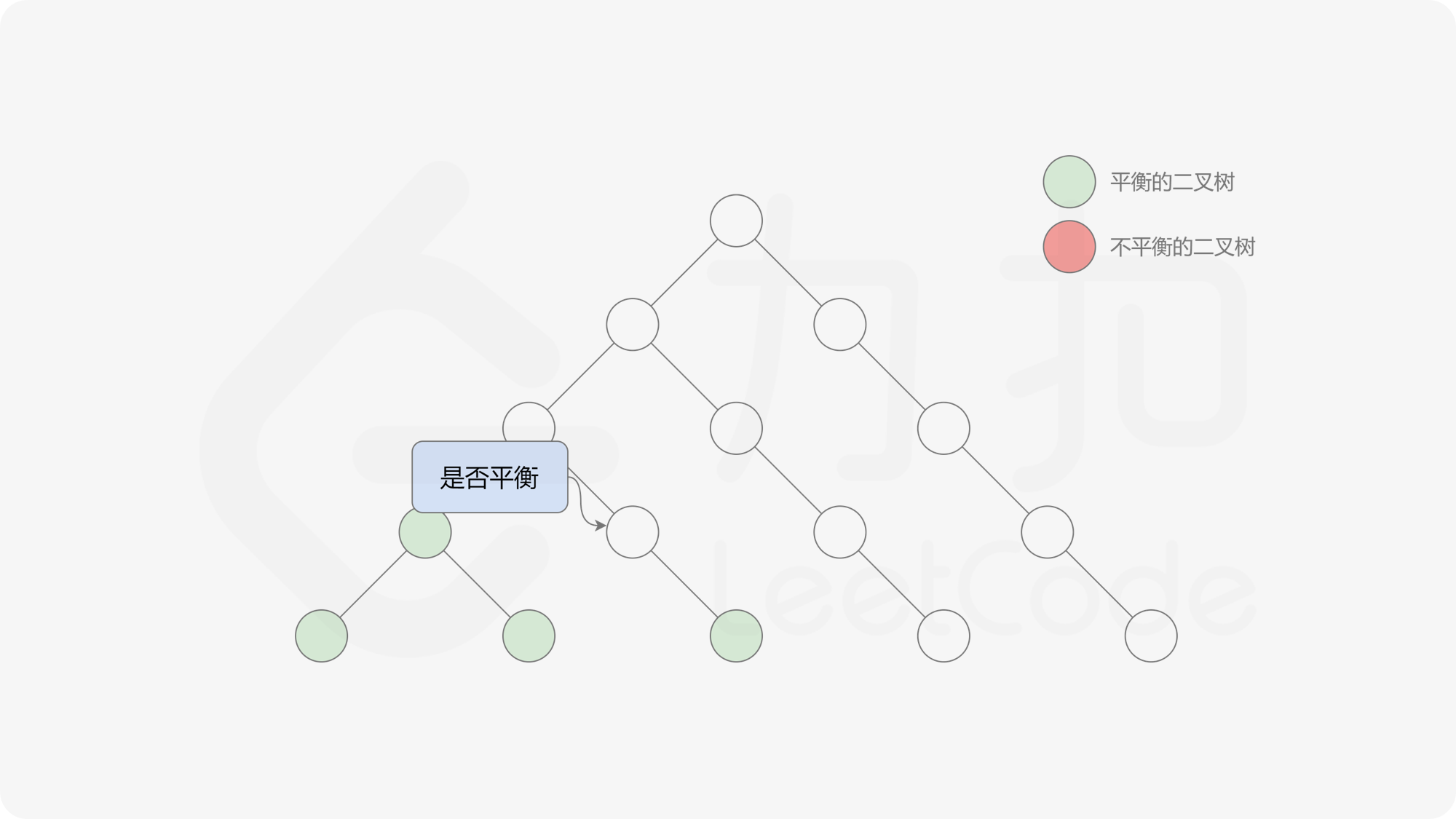
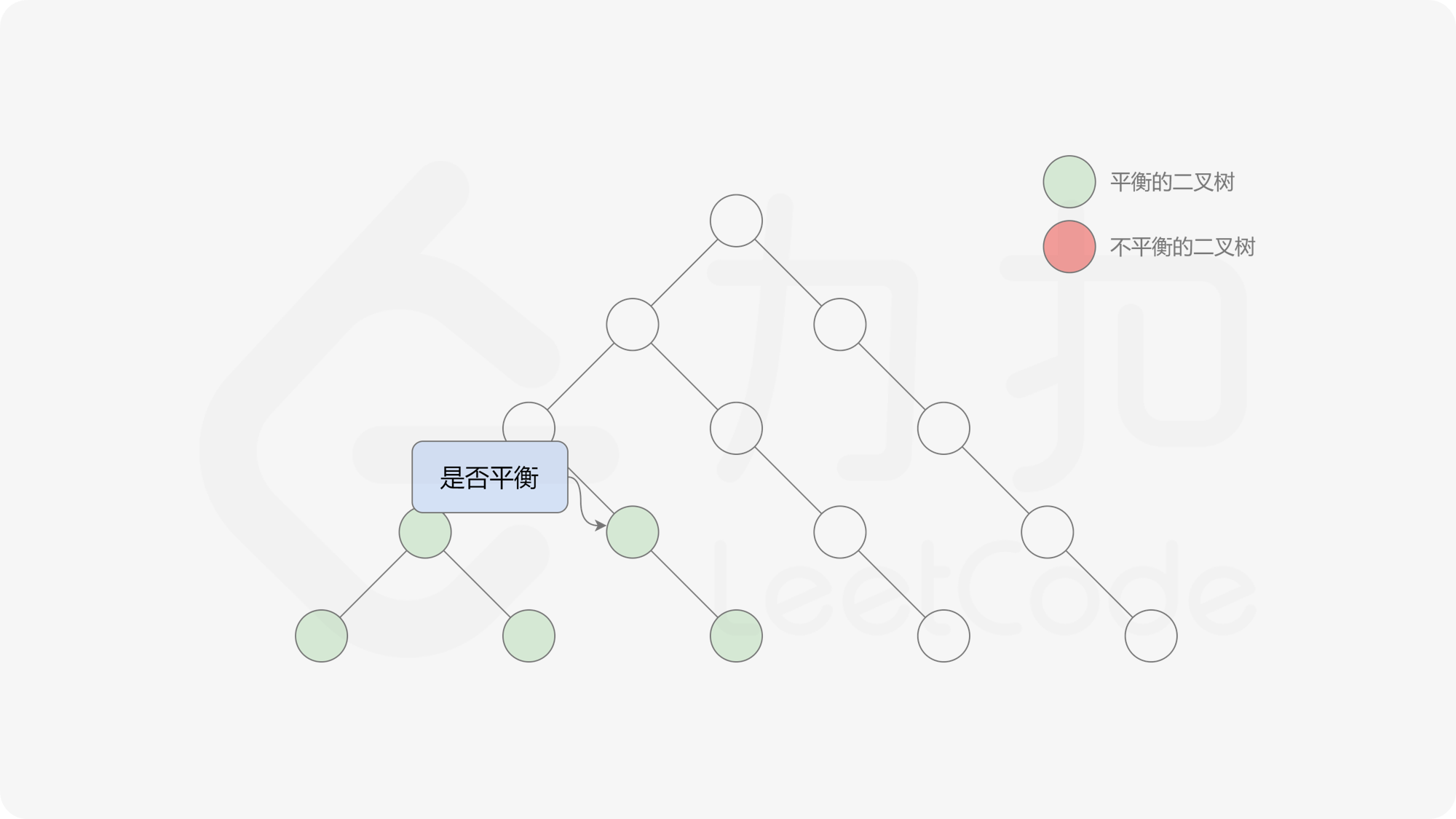
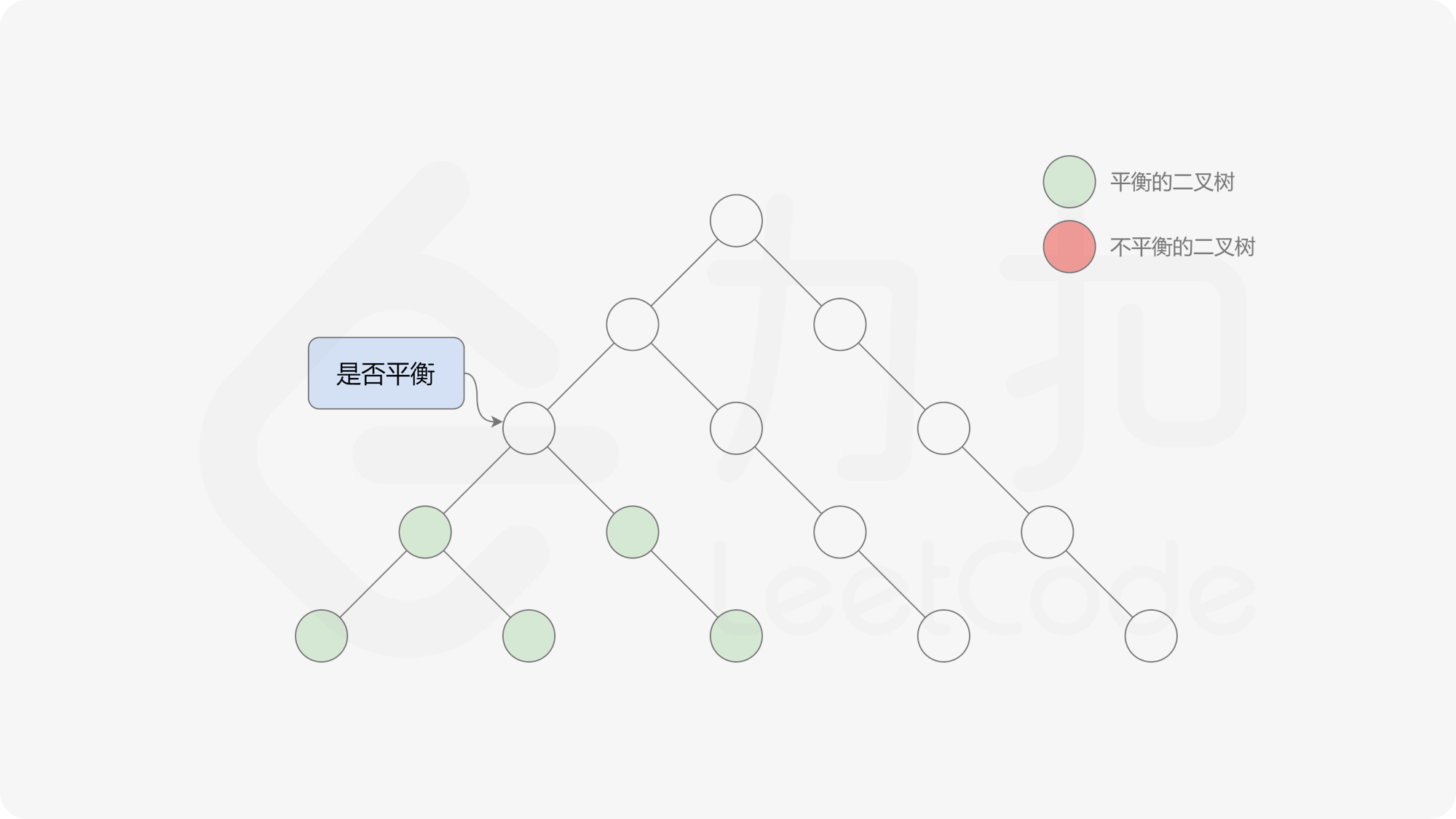
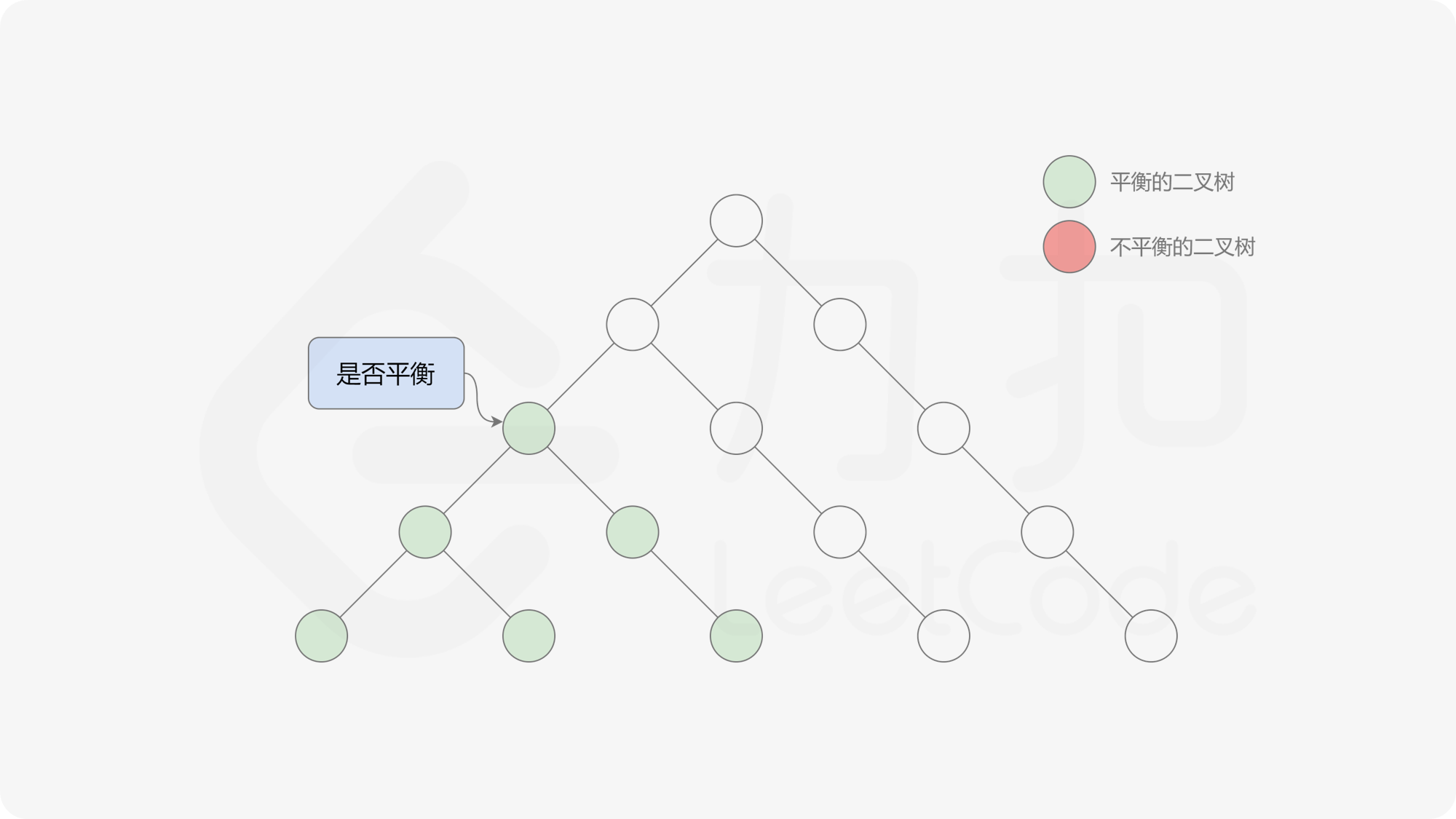
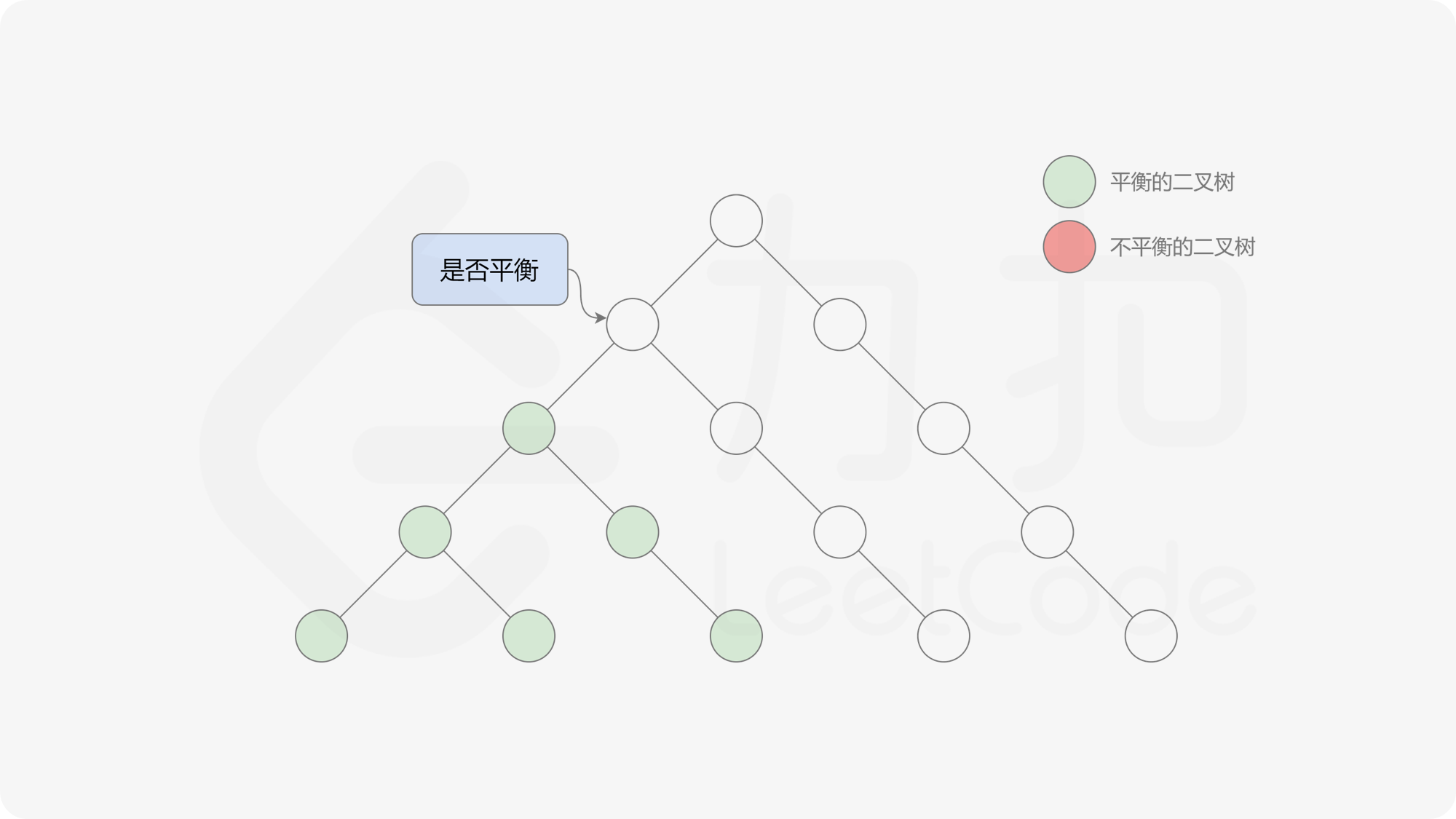
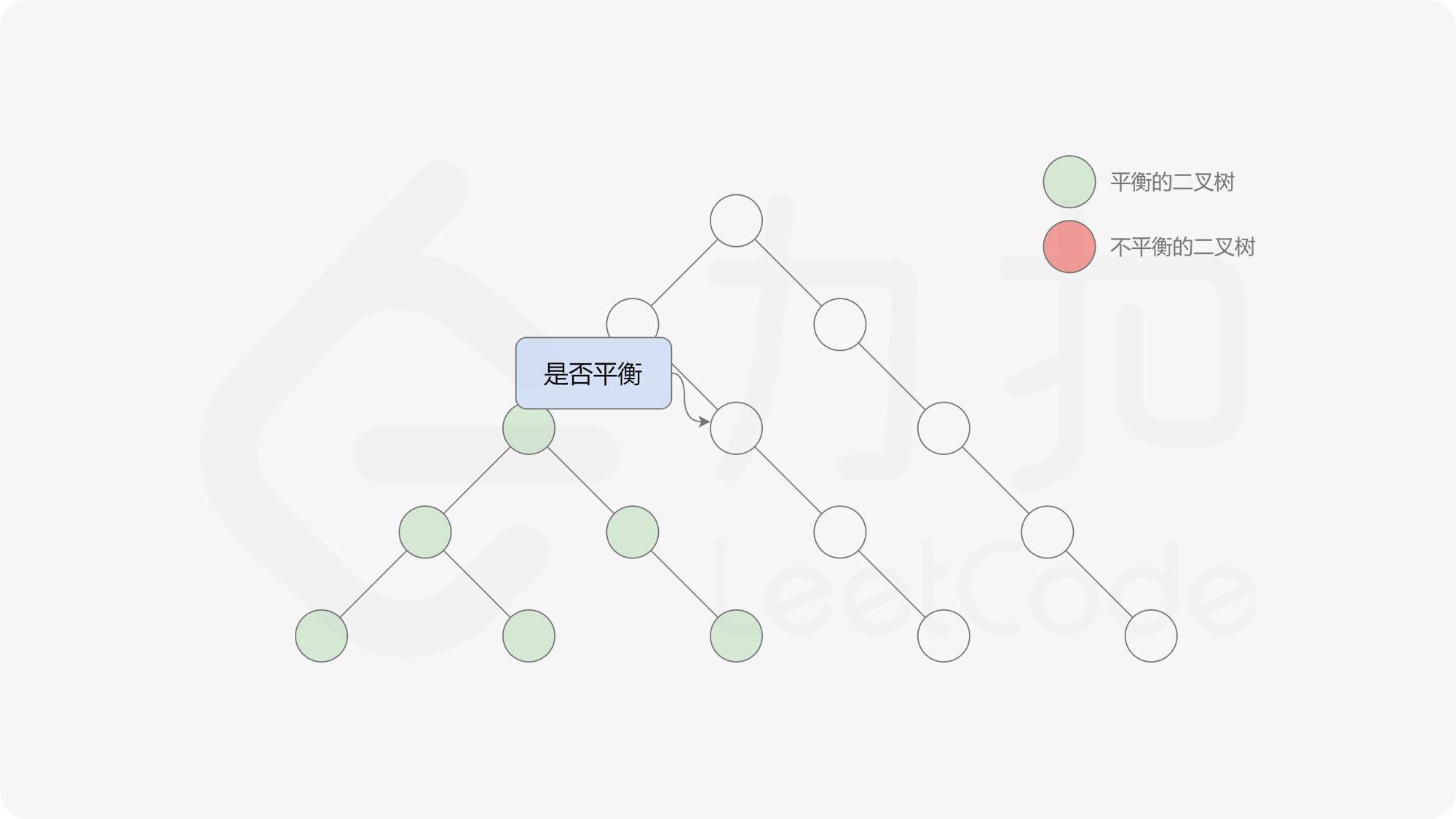
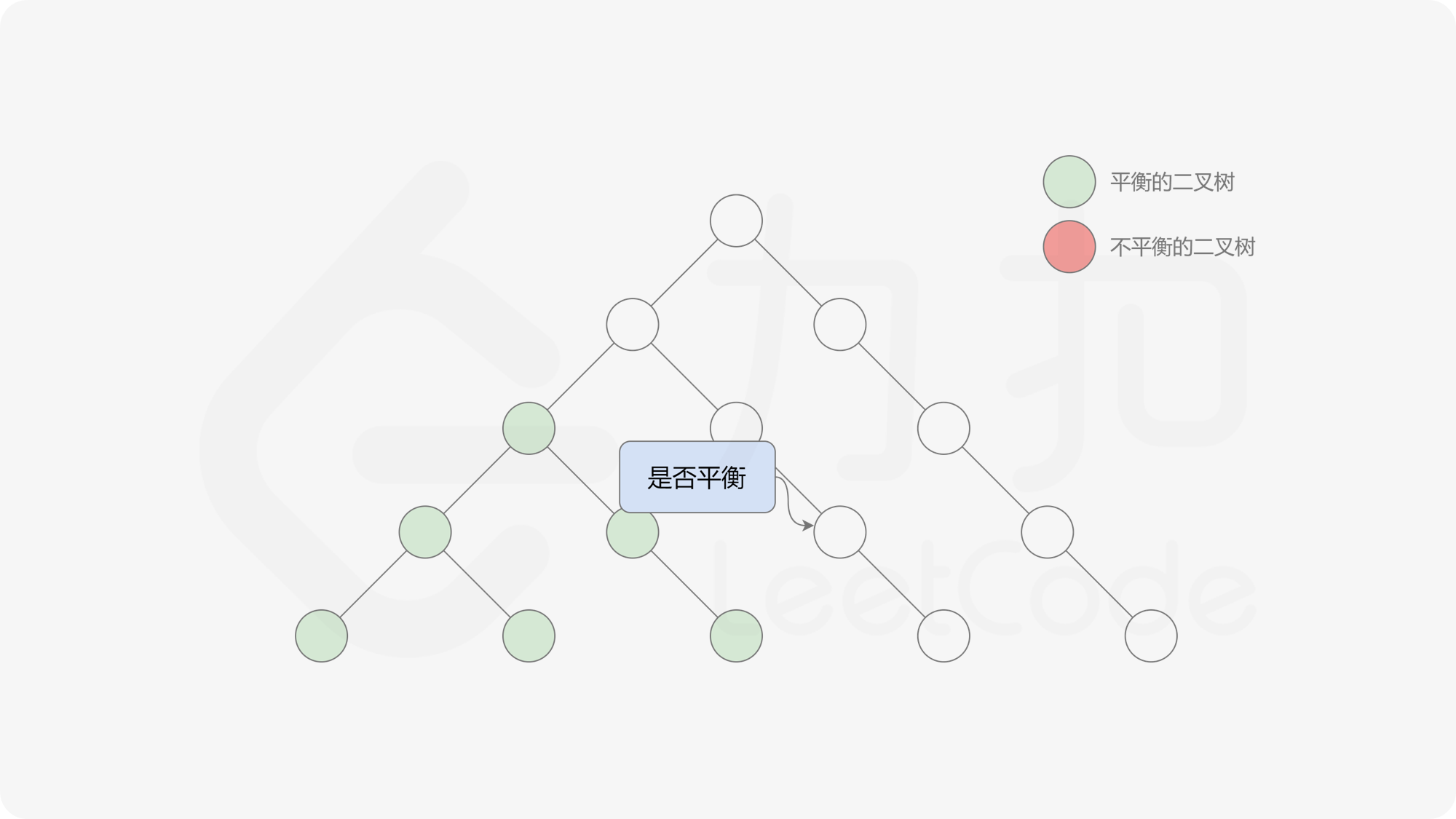
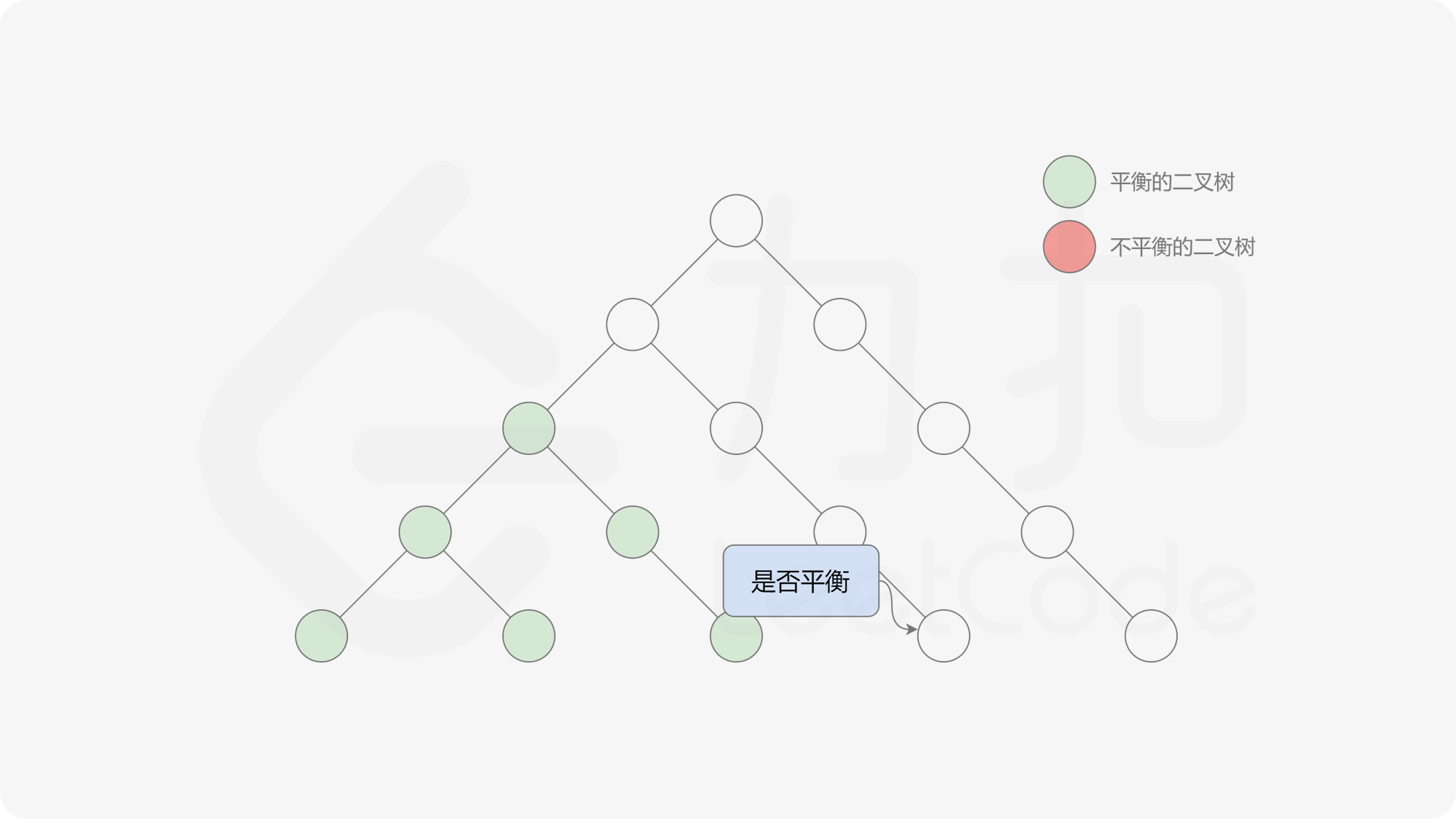
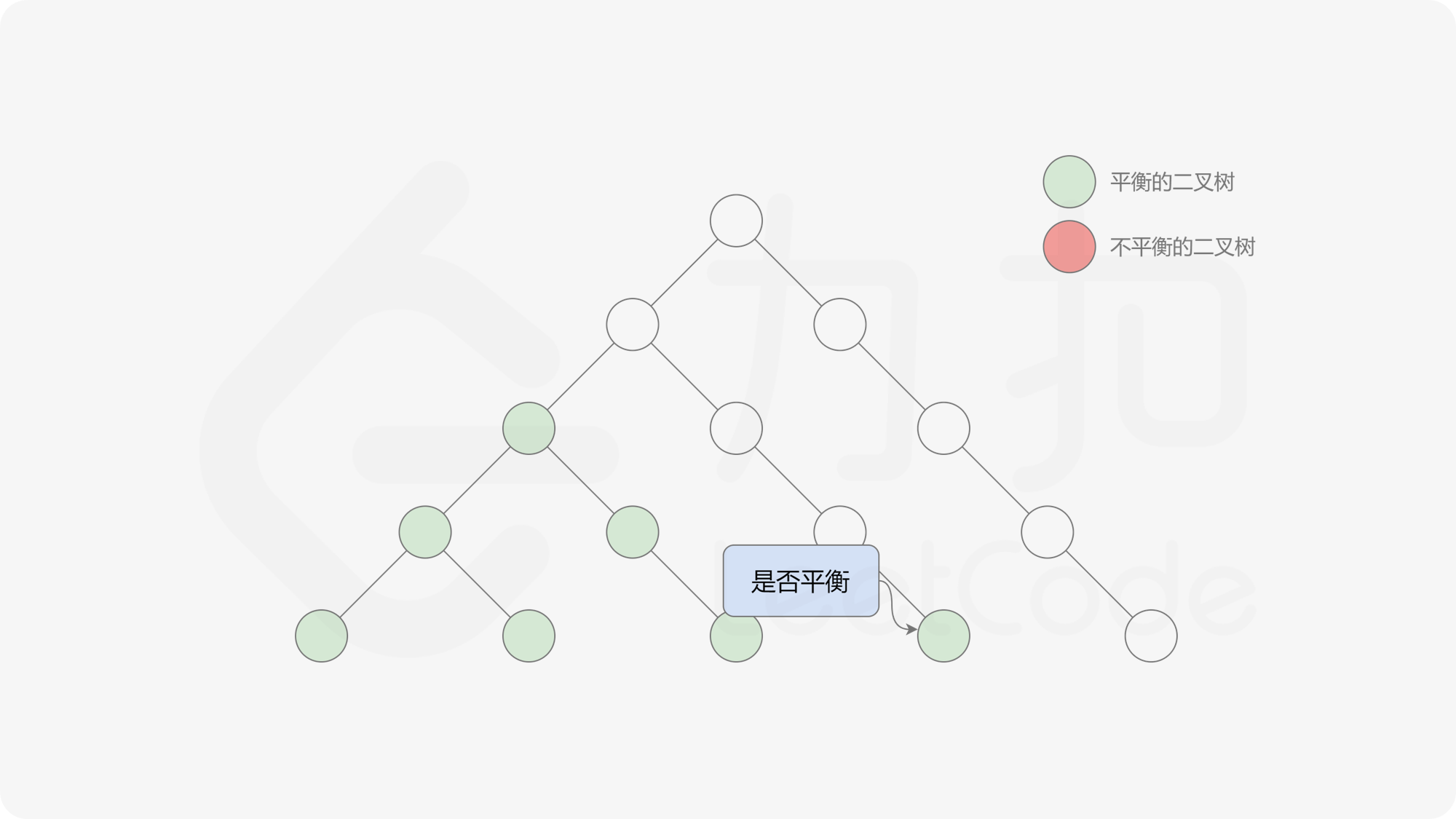
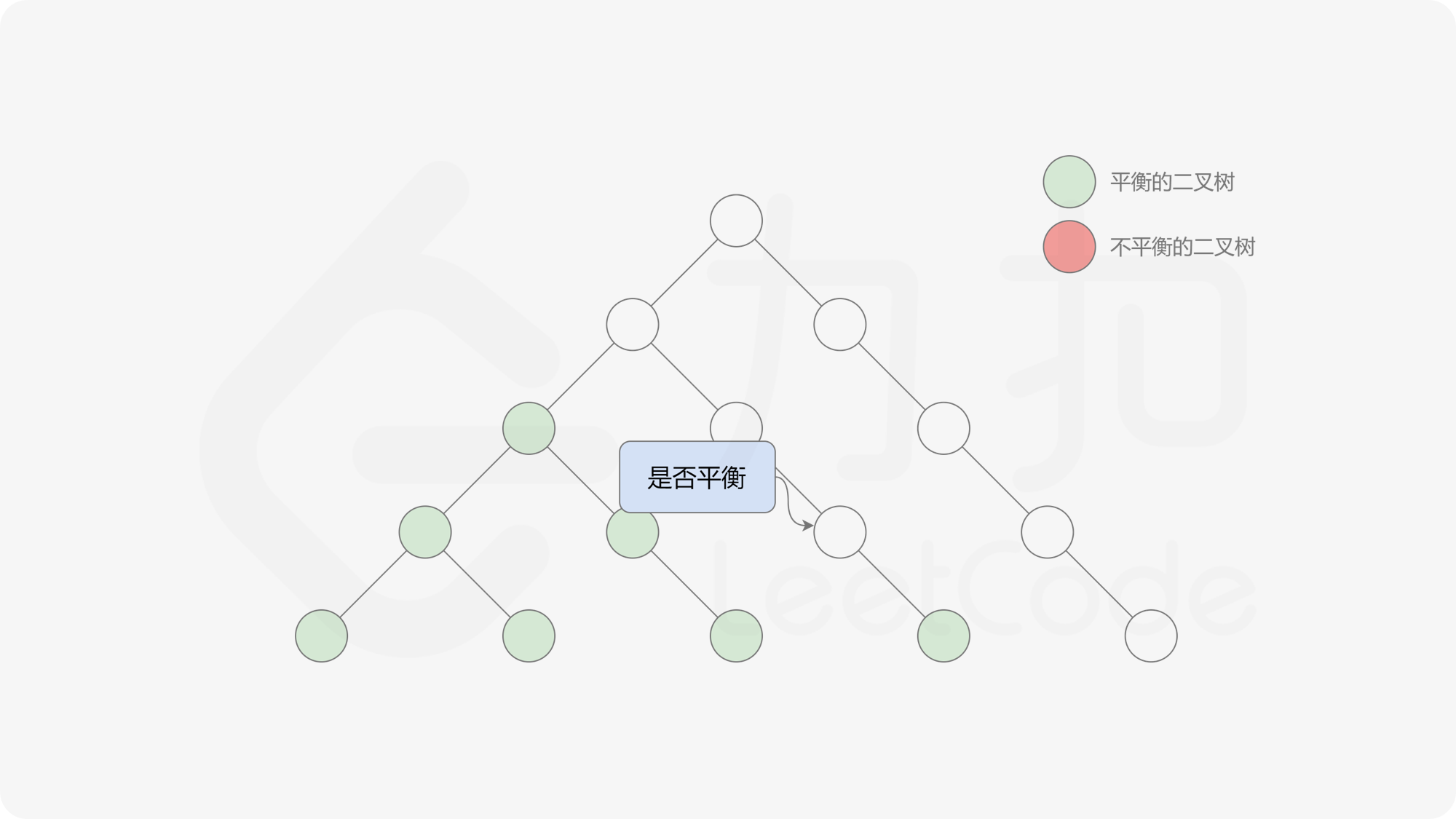
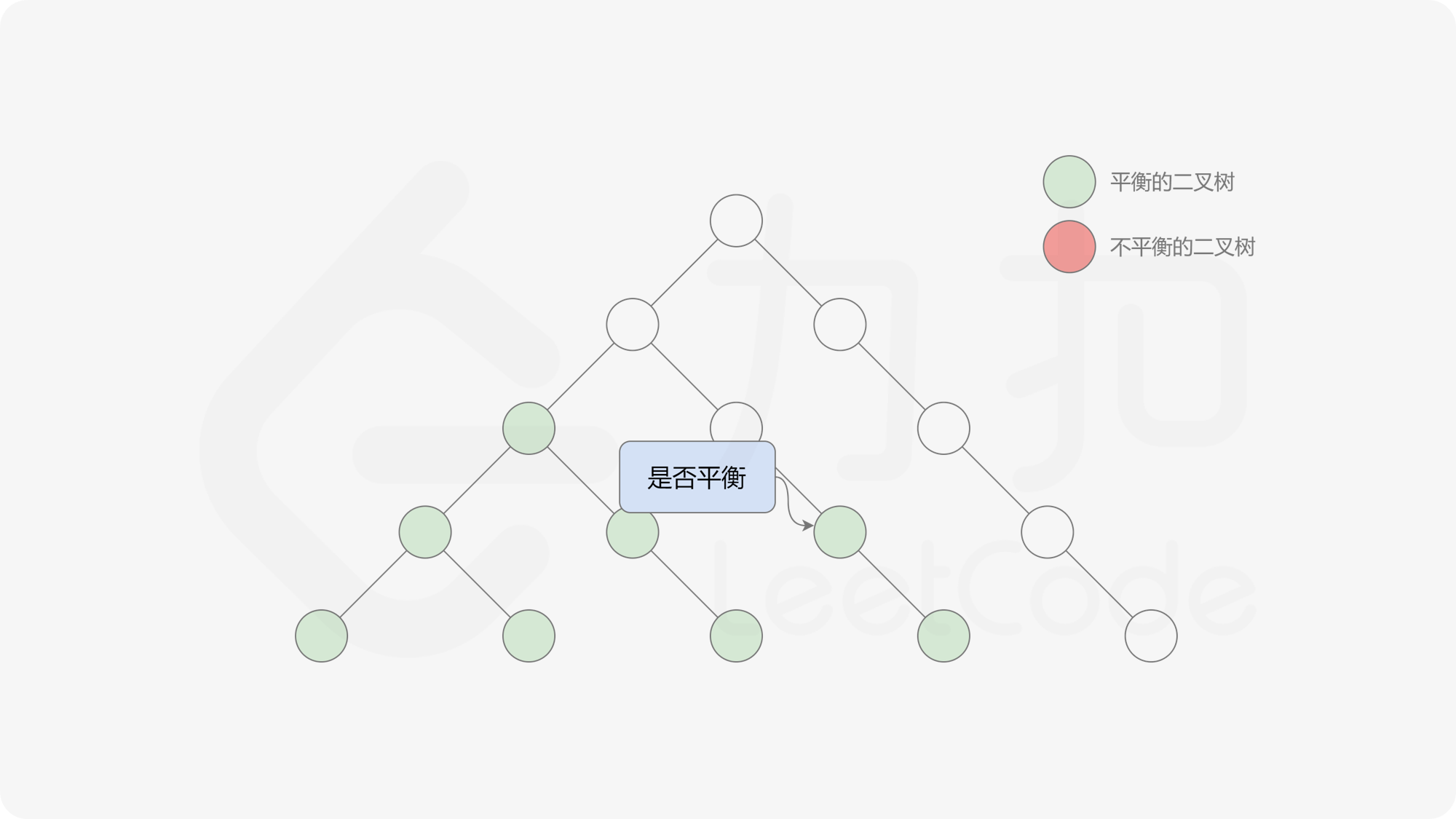
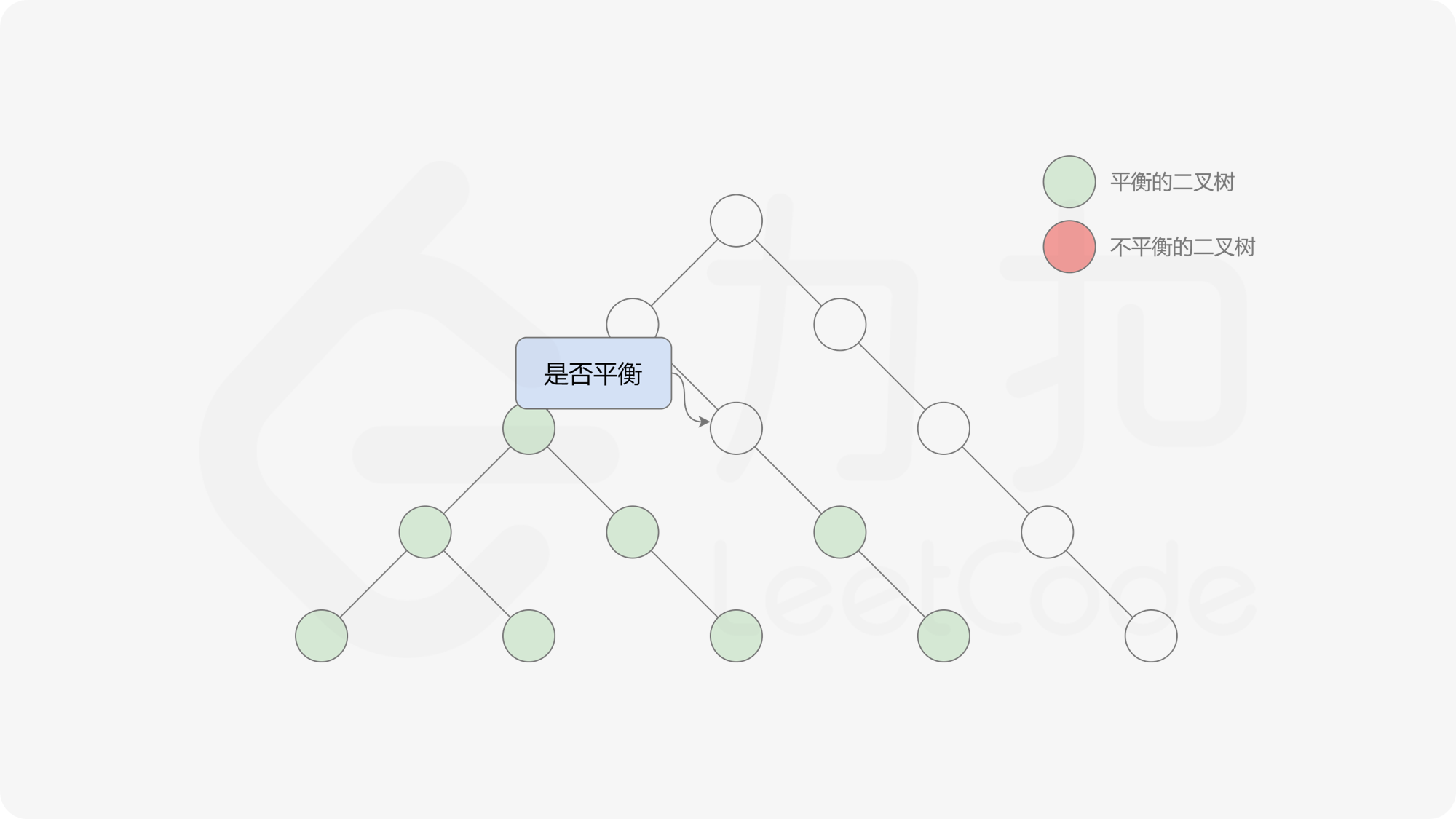
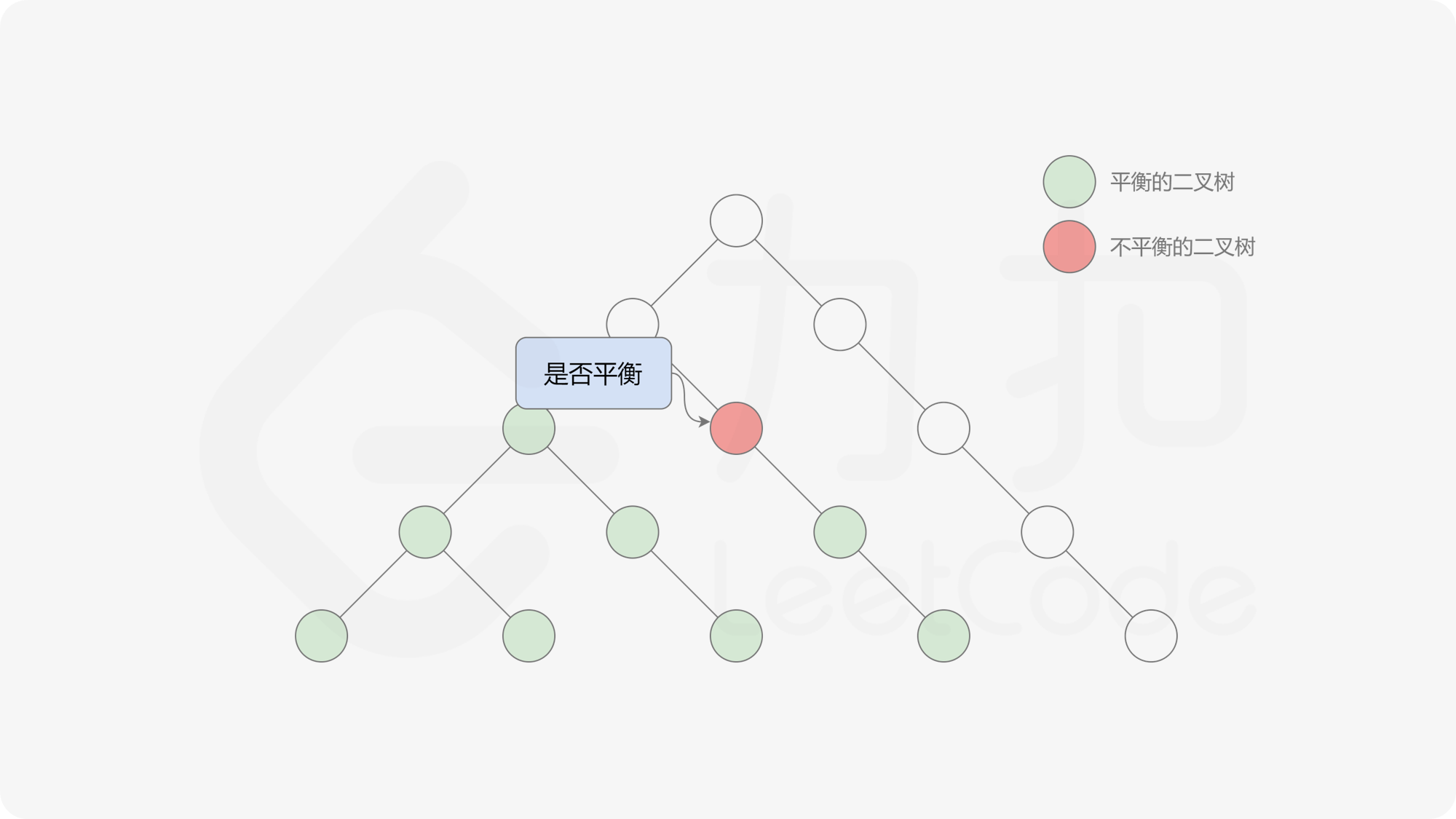
自底向上递归的做法类似于后序遍历,对于当前遍历到的节点,先递归地判断其左右子树是否平衡,再判断以当前节点为根的子树是否平衡。如果一棵子树是平衡的,则返回其高度(高度一定是非负整数),否则返回 $-1$。如果存在一棵子树不平衡,则整个二叉树一定不平衡。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
,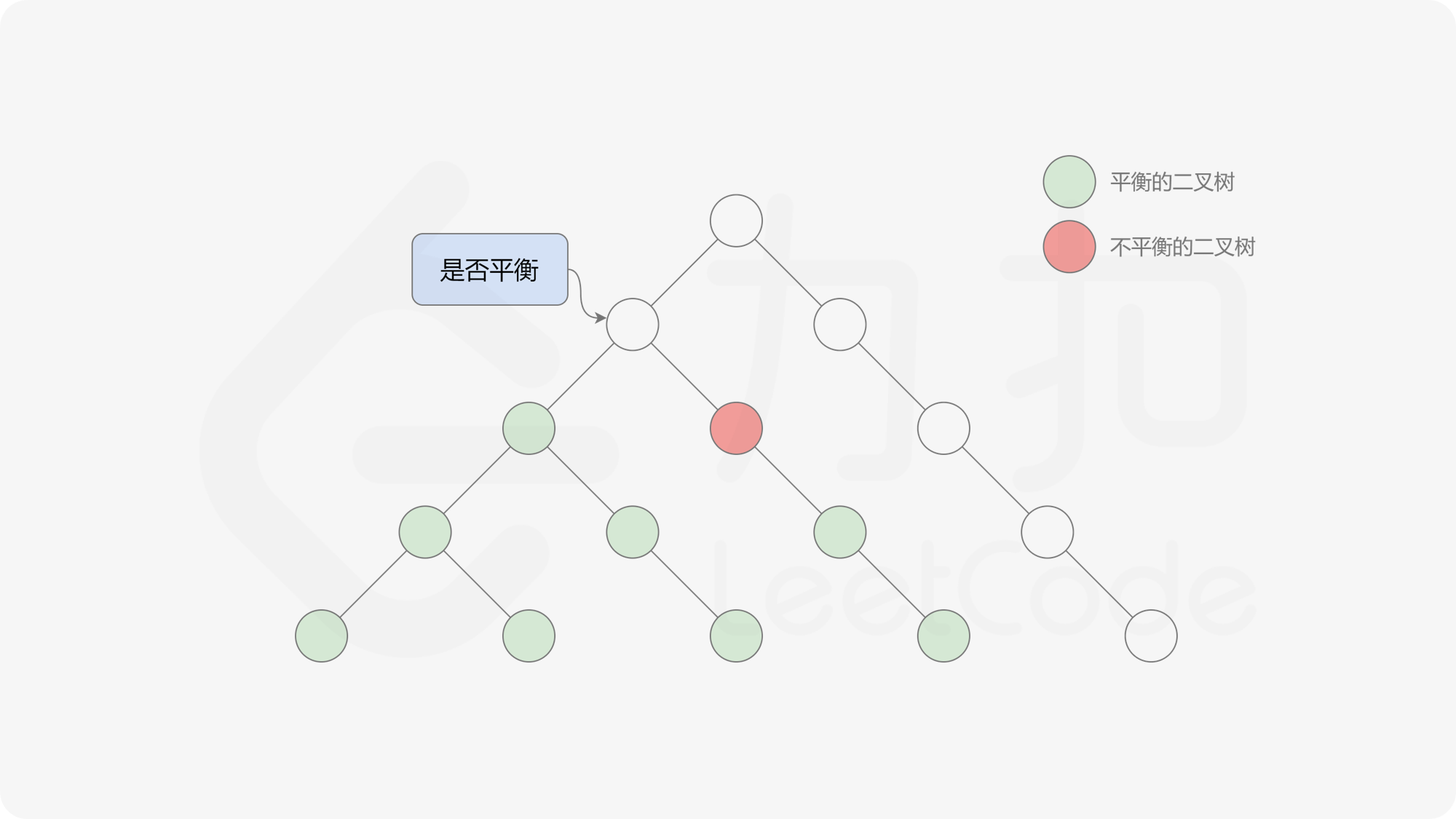 ,
,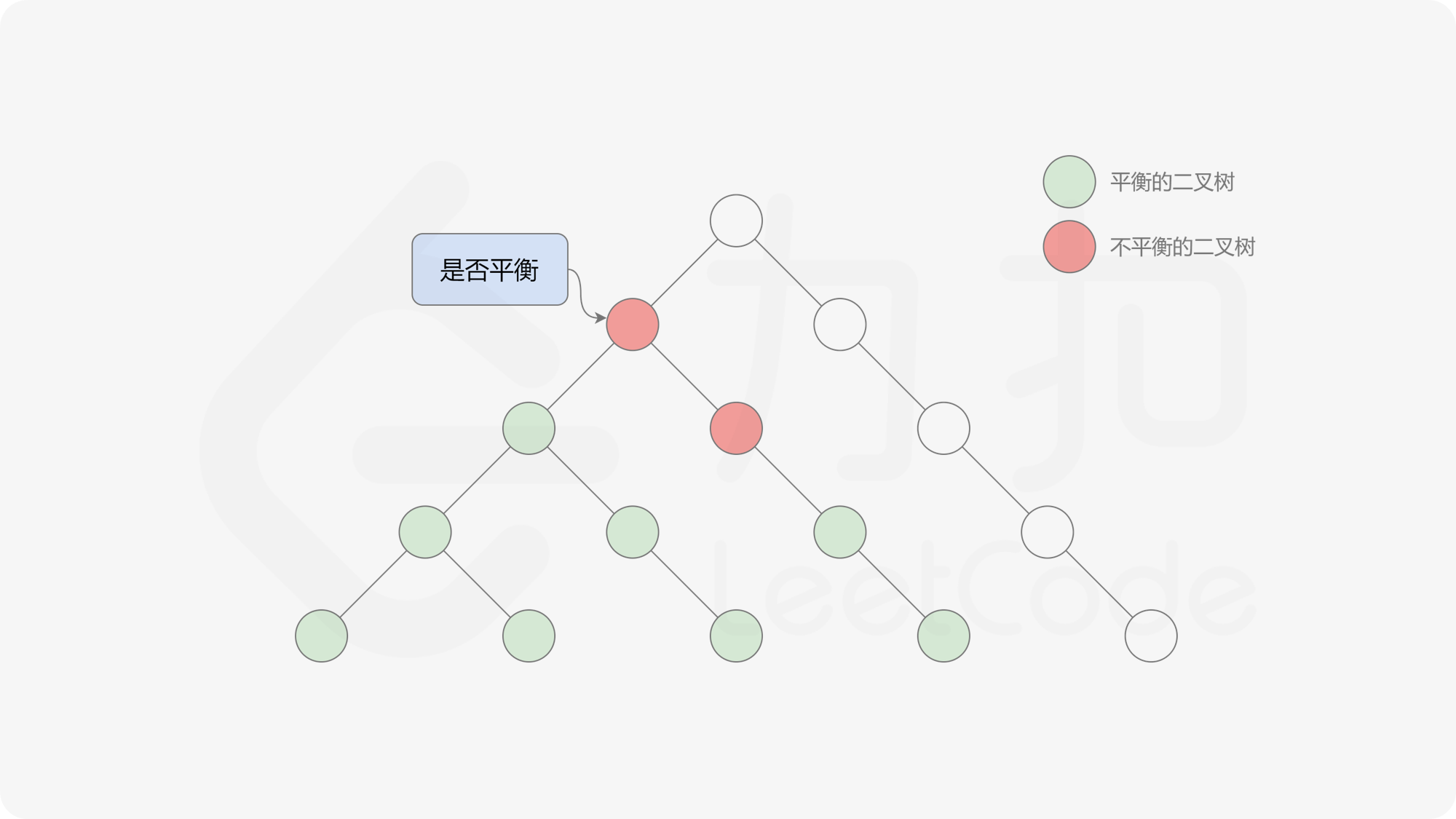 ,
,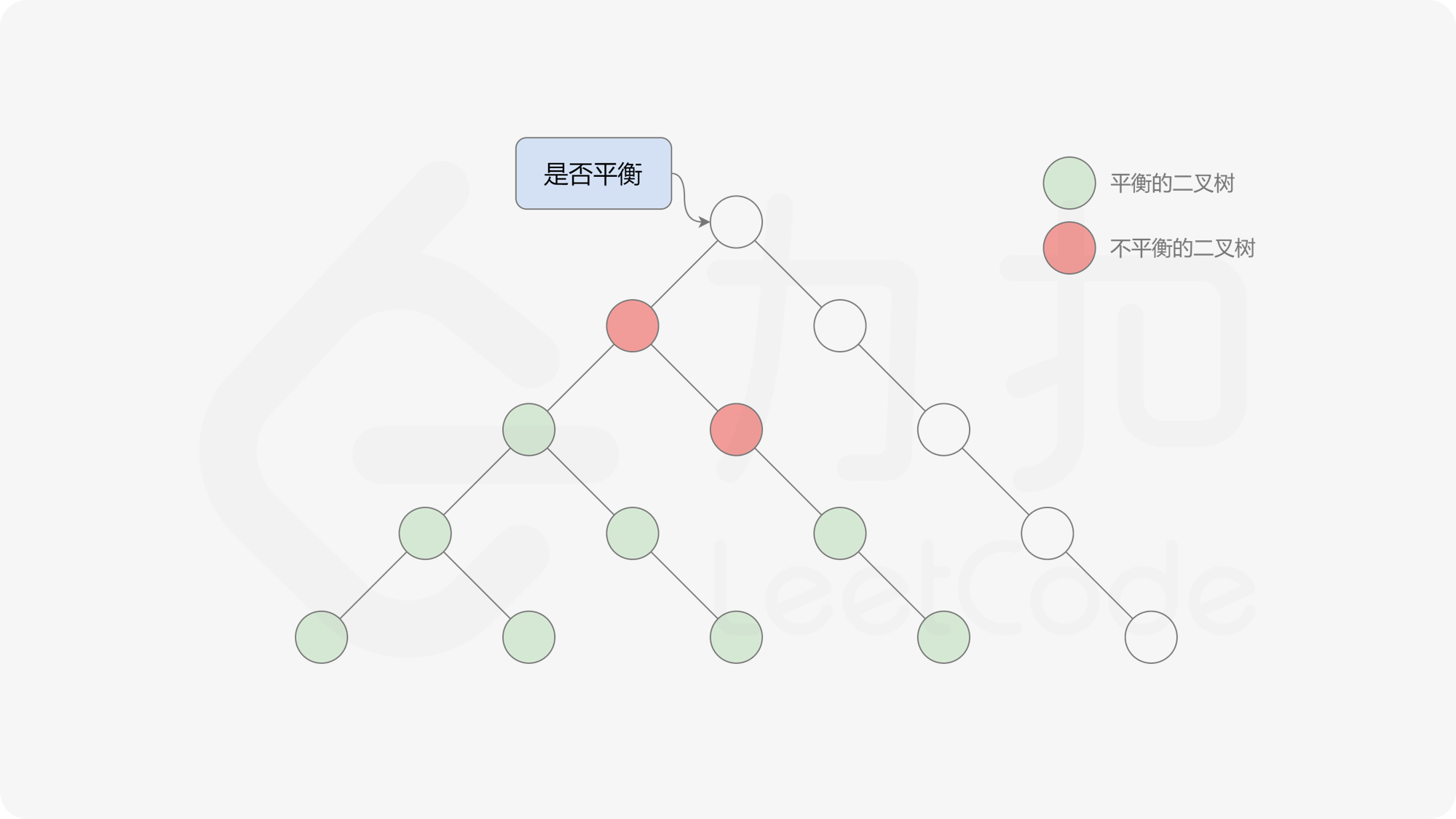 ,
,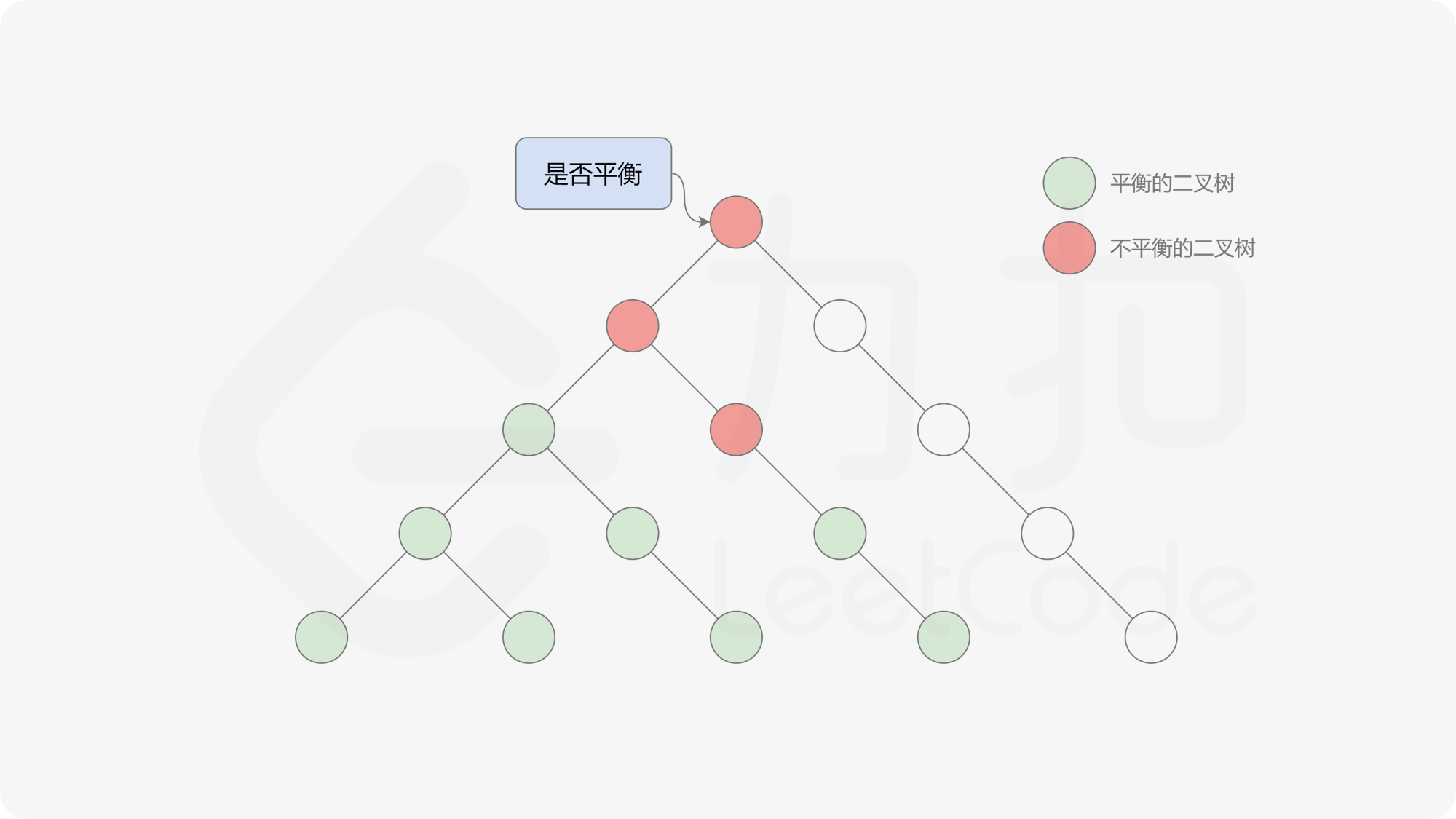 >
>
###Java
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return height(root) >= 0;
}
public int height(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = height(root.left);
int rightHeight = height(root.right);
if (leftHeight == -1 || rightHeight == -1 || Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) {
return -1;
} else {
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
}
###C++
class Solution {
public:
int height(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = height(root->left);
int rightHeight = height(root->right);
if (leftHeight == -1 || rightHeight == -1 || abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) {
return -1;
} else {
return max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
return height(root) >= 0;
}
};
###Python
class Solution:
def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
def height(root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
leftHeight = height(root.left)
rightHeight = height(root.right)
if leftHeight == -1 or rightHeight == -1 or abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1:
return -1
else:
return max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1
return height(root) >= 0
###C
int height(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = height(root->left);
int rightHeight = height(root->right);
if (leftHeight == -1 || rightHeight == -1 || fabs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) {
return -1;
} else {
return fmax(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root) {
return height(root) >= 0;
}
###golang
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
return height(root) >= 0
}
func height(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
leftHeight := height(root.Left)
rightHeight := height(root.Right)
if leftHeight == -1 || rightHeight == -1 || abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1 {
return -1
}
return max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1
}
func max(x, y int) int {
if x > y {
return x
}
return y
}
func abs(x int) int {
if x < 0 {
return -1 * x
}
return x
}
复杂度分析
-
时间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 是二叉树中的节点个数。使用自底向上的递归,每个节点的计算高度和判断是否平衡都只需要处理一次,最坏情况下需要遍历二叉树中的所有节点,因此时间复杂度是 $O(n)$。
-
空间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 是二叉树中的节点个数。空间复杂度主要取决于递归调用的层数,递归调用的层数不会超过 $n$。