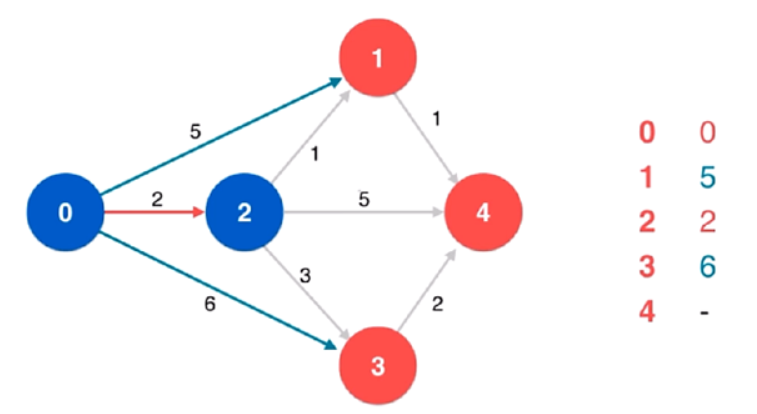
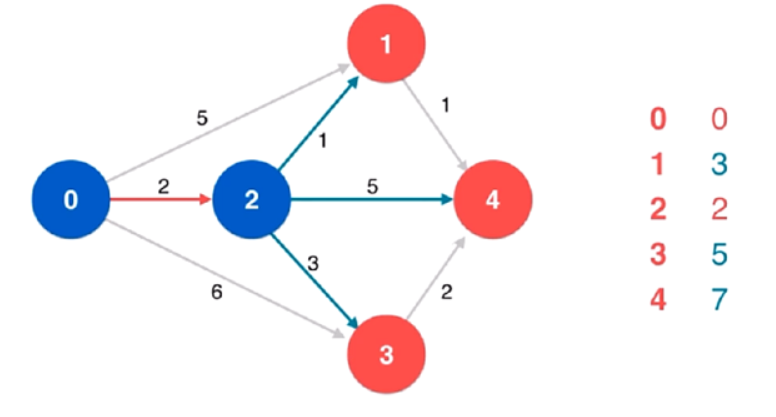
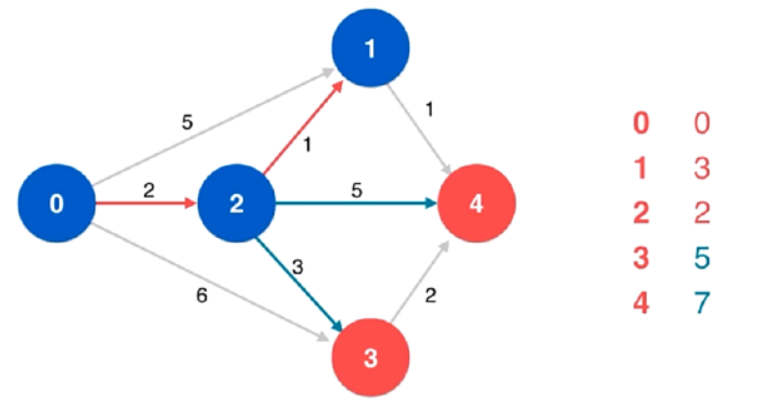
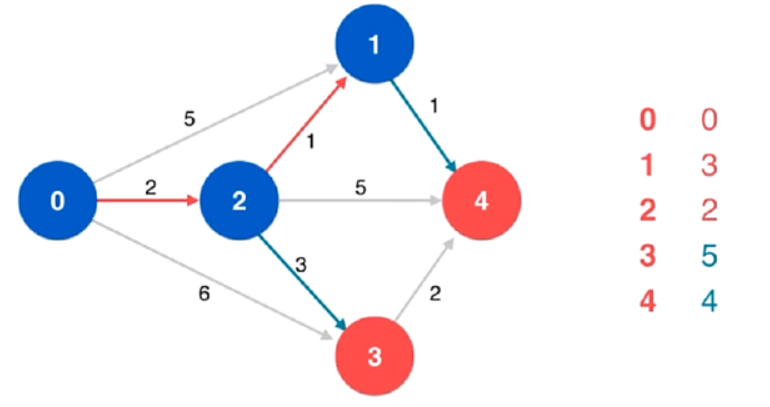
方法一:贪心 + 最小堆
给定 $k$ 个列表,需要找到最小区间,使得每个列表都至少有一个数在该区间中。该问题可以转化为,从 $k$ 个列表中各取一个数,使得这 $k$ 个数中的最大值与最小值的差最小。
假设这 $k$ 个数中的最小值是第 $i$ 个列表中的 $x$,对于任意 $j \ne i$,设第 $j$ 个列表中被选为 $k$ 个数之一的数是 $y$,则为了找到最小区间,$y$ 应该取第 $j$ 个列表中大于等于 $x$ 的最小的数,这是一个贪心的策略。贪心策略的正确性简单证明如下:假设 $z$ 也是第 $j$ 个列表中的数,且 $z>y$,则有 $z-x>y-x$,同时包含 $x$ 和 $z$ 的区间一定不会小于同时包含 $x$ 和 $y$ 的区间。因此,其余 $k-1$ 个列表中应该取大于等于 $x$ 的最小的数。
由于 $k$ 个列表都是升序排列的,因此对每个列表维护一个指针,通过指针得到列表中的元素,指针右移之后指向的元素一定大于或等于之前的元素。
使用最小堆维护 $k$ 个指针指向的元素中的最小值,同时维护堆中元素的最大值。初始时,$k$ 个指针都指向下标 $0$,最大元素即为所有列表的下标 $0$ 位置的元素中的最大值。每次从堆中取出最小值,根据最大值和最小值计算当前区间,如果当前区间小于最小区间则用当前区间更新最小区间,然后将对应列表的指针右移,将新元素加入堆中,并更新堆中元素的最大值。
如果一个列表的指针超出该列表的下标范围,则说明该列表中的所有元素都被遍历过,堆中不会再有该列表中的元素,因此退出循环。
###Java
class Solution {
public int[] smallestRange(List<List<Integer>> nums) {
int rangeLeft = 0, rangeRight = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int minRange = rangeRight - rangeLeft;
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int size = nums.size();
int[] next = new int[size];
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
public int compare(Integer index1, Integer index2) {
return nums.get(index1).get(next[index1]) - nums.get(index2).get(next[index2]);
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
priorityQueue.offer(i);
max = Math.max(max, nums.get(i).get(0));
}
while (true) {
int minIndex = priorityQueue.poll();
int curRange = max - nums.get(minIndex).get(next[minIndex]);
if (curRange < minRange) {
minRange = curRange;
rangeLeft = nums.get(minIndex).get(next[minIndex]);
rangeRight = max;
}
next[minIndex]++;
if (next[minIndex] == nums.get(minIndex).size()) {
break;
}
priorityQueue.offer(minIndex);
max = Math.max(max, nums.get(minIndex).get(next[minIndex]));
}
return new int[]{rangeLeft, rangeRight};
}
}
###cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> smallestRange(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {
int rangeLeft = 0, rangeRight = INT_MAX;
int size = nums.size();
vector<int> next(size);
auto cmp = [&](const int& u, const int& v) {
return nums[u][next[u]] > nums[v][next[v]];
};
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, decltype(cmp)> pq(cmp);
int minValue = 0, maxValue = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
pq.emplace(i);
maxValue = max(maxValue, nums[i][0]);
}
while (true) {
int row = pq.top();
pq.pop();
minValue = nums[row][next[row]];
if (maxValue - minValue < rangeRight - rangeLeft) {
rangeLeft = minValue;
rangeRight = maxValue;
}
if (next[row] == nums[row].size() - 1) {
break;
}
++next[row];
maxValue = max(maxValue, nums[row][next[row]]);
pq.emplace(row);
}
return {rangeLeft, rangeRight};
}
};
###golang
var (
next []int
numsC [][]int
)
func smallestRange(nums [][]int) []int {
numsC = nums
rangeLeft, rangeRight := 0, math.MaxInt32
minRange := rangeRight - rangeLeft
max := math.MinInt32
size := len(nums)
next = make([]int, size)
h := &IHeap{}
heap.Init(h)
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
heap.Push(h, i)
max = Max(max, nums[i][0])
}
for {
minIndex := heap.Pop(h).(int)
curRange := max - nums[minIndex][next[minIndex]]
if curRange < minRange {
minRange = curRange
rangeLeft, rangeRight = nums[minIndex][next[minIndex]], max
}
next[minIndex]++
if next[minIndex] == len(nums[minIndex]) {
break
}
heap.Push(h, minIndex)
max = Max(max, nums[minIndex][next[minIndex]])
}
return []int{rangeLeft, rangeRight}
}
type IHeap []int
func (h IHeap) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h IHeap) Less(i, j int) bool { return numsC[h[i]][next[h[i]]] < numsC[h[j]][next[h[j]]] }
func (h IHeap) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *IHeap) Push(x interface{}) {
*h = append(*h, x.(int))
}
func (h *IHeap) Pop() interface{} {
old := *h
n := len(old)
x := old[n-1]
*h = old[0 : n-1]
return x
}
func Max(x, y int) int {
if x > y {
return x
}
return y
}
###Python
class Solution:
def smallestRange(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
rangeLeft, rangeRight = -10**9, 10**9
maxValue = max(vec[0] for vec in nums)
priorityQueue = [(vec[0], i, 0) for i, vec in enumerate(nums)]
heapq.heapify(priorityQueue)
while True:
minValue, row, idx = heapq.heappop(priorityQueue)
if maxValue - minValue < rangeRight - rangeLeft:
rangeLeft, rangeRight = minValue, maxValue
if idx == len(nums[row]) - 1:
break
maxValue = max(maxValue, nums[row][idx + 1])
heapq.heappush(priorityQueue, (nums[row][idx + 1], row, idx + 1))
return [rangeLeft, rangeRight]
###C
#define maxn 100005
int heap[maxn];
int heap_count;
int **rec, *nx;
bool heap_comp(int *first, int *second) {
return rec[*first][nx[*first]] < rec[*second][nx[*second]];
}
void swap(int *first, int *second) {
int temp = *second;
*second = *first;
*first = temp;
return;
}
void push(int num) {
int pos = ++heap_count;
heap[pos] = num;
while (pos > 1) {
if (heap_comp(&heap[pos], &heap[pos >> 1])) {
swap(&heap[pos], &heap[pos >> 1]);
pos >>= 1;
} else
break;
}
return;
}
void pop() {
int top_num = 1;
int now;
swap(&heap[top_num], &heap[heap_count--]);
while ((now = (top_num << 1)) <= heap_count) {
if (heap_comp(&heap[now + 1], &heap[now]) && now < heap_count) now++;
if (heap_comp(&heap[now], &heap[top_num])) {
swap(&heap[top_num], &heap[now]);
top_num = now;
} else
break;
}
}
int top() { return heap[1]; }
int *smallestRange(int **nums, int numsSize, int *numsColSize,
int *returnSize) {
heap_count = 0;
nx = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * numsSize);
memset(nx, 0, sizeof(int) * numsSize);
rec = nums;
int rangeLeft = 0, rangeRight = 2147483647;
int minValue = 0, maxValue = -2147483648;
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; ++i) {
push(i);
maxValue = fmax(maxValue, nums[i][0]);
}
while (true) {
int row = top();
pop();
minValue = nums[row][nx[row]];
if (maxValue - minValue < rangeRight - rangeLeft) {
rangeLeft = minValue;
rangeRight = maxValue;
}
if (nx[row] == numsColSize[row] - 1) {
break;
}
++nx[row];
maxValue = fmax(maxValue, nums[row][nx[row]]);
push(row);
}
int *ret = malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
ret[0] = rangeLeft, ret[1] = rangeRight;
*returnSize = 2;
return ret;
}
###JavaScript
var smallestRange = function(nums) {
let rangeLeft = 0, rangeRight = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
const size = nums.length;
const next = new Array(size).fill(0);
const pq = new MinPriorityQueue();
let minValue = 0, maxValue = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
for (let i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
pq.enqueue(i, nums[i][next[i]]);
maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, nums[i][0]);
}
while (true) {
const row = pq.dequeue().element;
minValue = nums[row][next[row]];
if (maxValue - minValue < rangeRight - rangeLeft) {
rangeLeft = minValue;
rangeRight = maxValue;
}
if (next[row] === nums[row].length - 1) {
break;
}
++next[row];
maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, nums[row][next[row]]);
pq.enqueue(row, nums[row][next[row]]);
}
return [rangeLeft, rangeRight];
};
###TypeScript
function smallestRange(nums: number[][]): number[] {
let rangeLeft = 0, rangeRight = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
const size = nums.length;
const next: number[] = new Array(size).fill(0);
const pq = new MinPriorityQueue();
let minValue = 0, maxValue = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
for (let i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
pq.enqueue(i, nums[i][next[i]]);
maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, nums[i][0]);
}
while (true) {
const row = pq.dequeue().element;
minValue = nums[row][next[row]];
if (maxValue - minValue < rangeRight - rangeLeft) {
rangeLeft = minValue;
rangeRight = maxValue;
}
if (next[row] === nums[row].length - 1) {
break;
}
++next[row];
maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, nums[row][next[row]]);
pq.enqueue(row, nums[row][next[row]]);
}
return [rangeLeft, rangeRight];
};
###Rust
use std::cmp::Ordering;
use std::collections::BinaryHeap;
impl Solution {
pub fn smallest_range(nums: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut range_left = 0;
let mut range_right = i32::MAX;
let size = nums.len();
let mut next = vec![0; size];
let mut max_value = i32::MIN;
let mut pq = BinaryHeap::new();
for i in 0..size {
max_value = max_value.max(nums[i][0]);
pq.push(std::cmp::Reverse((nums[i][0], i)));
}
while let Some(std::cmp::Reverse((min_value, row))) = pq.pop() {
if max_value - min_value < range_right - range_left {
range_left = min_value;
range_right = max_value;
}
if next[row] == nums[row].len() - 1 {
break;
}
next[row] += 1;
max_value = max_value.max(nums[row][next[row]]);
pq.push(std::cmp::Reverse((nums[row][next[row]], row)));
}
vec![range_left, range_right]
}
}
复杂度分析
方法二:哈希表 + 滑动窗口
思路
在讲这个方法之前我们先思考这样一个问题:有一个序列 $A = { a_1, a_2, \cdots, a_n }$ 和一个序列 $B = {b_1, b_2, \cdots, b_m}$,请找出一个 $B$ 中的一个最小的区间,使得在这个区间中 $A$ 序列的每个数字至少出现一次,请注意 $A$ 中的元素可能重复,也就是说如果 $A$ 中有 $p$ 个 $u$,那么你选择的这个区间中 $u$ 的个数一定不少于 $p$。没错,这就是我们五月份的一道打卡题:「76. 最小覆盖子串」。官方题解使用了一种滑动窗口的方法,遍历整个 $B$ 序列并用一个哈希表表示当前窗口中的元素:
- 右边界在每次遍历到新元素的时候右移,同时将拓展到的新元素加入哈希表;
- 左边界右移当且仅当当前区间为一个合法的答案区间,即当前窗口内的元素包含 $A$ 中所有的元素,同时将原来左边界指向的元素从哈希表中移除;
- 答案更新当且仅当当前窗口内的元素包含 $A$ 中所有的元素。
如果这个地方不理解,可以参考「76. 最小覆盖子串的官方题解」。
回到这道题,我们发现这两道题的相似之处在于都要求我们找到某个符合条件的最小区间,我们可以借鉴「76. 最小覆盖子串」的做法:这里序列 ${ 0, 1, \cdots , k - 1 }$ 就是上面描述的 $A$ 序列,即 $k$ 个列表,我们需要在一个 $B$ 序列当中找到一个区间,可以覆盖 $A$ 序列。这里的 $B$ 序列是什么?我们可以用一个哈希映射来表示 $B$ 序列—— $B[i]$ 表示 $i$ 在哪些列表当中出现过,这里哈希映射的键是一个整数,表示列表中的某个数值,哈希映射的值是一个数组,这个数组里的元素代表当前的键出现在哪些列表里。也许文字表述比较抽象,大家可以结合下面这个例子来理解。
- 如果列表集合为:
0: [-1, 2, 3]
1: [1]
2: [1, 2]
3: [1, 1, 3]
- 那么可以得到这样一个哈希映射
-1: [0]
1: [1, 2, 3, 3]
2: [0, 2]
3: [0, 3]
我们得到的这个哈希映射就是这里的 $B$ 序列。我们要做的就是在 $B$ 序列上使用两个指针维护一个滑动窗口,并用一个哈希表维护当前窗口中已经包含了哪些列表中的元素,记录它们的索引。遍历 $B$ 序列的每一个元素:
- 指向窗口右边界的指针右移当且仅当每次遍历到新的元素,并将这个新的元素对应的值数组中的每一个数加入到哈希表中;
- 指向窗口左边界的指针右移当且仅当当前区间内的元素包含 $A$ 中所有的元素,同时将原来左边界对应的值数组的元素们从哈希表中移除;
- 答案更新当且仅当当前窗口内的元素包含 $A$ 中所有的元素。
大家可以参考代码理解这个过程。
代码
###Java
class Solution {
public int[] smallestRange(List<List<Integer>> nums) {
int size = nums.size();
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> indices = new HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>>();
int xMin = Integer.MAX_VALUE, xMax = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for (int x : nums.get(i)) {
List<Integer> list = indices.getOrDefault(x, new ArrayList<Integer>());
list.add(i);
indices.put(x, list);
xMin = Math.min(xMin, x);
xMax = Math.max(xMax, x);
}
}
int[] freq = new int[size];
int inside = 0;
int left = xMin, right = xMin - 1;
int bestLeft = xMin, bestRight = xMax;
while (right < xMax) {
right++;
if (indices.containsKey(right)) {
for (int x : indices.get(right)) {
freq[x]++;
if (freq[x] == 1) {
inside++;
}
}
while (inside == size) {
if (right - left < bestRight - bestLeft) {
bestLeft = left;
bestRight = right;
}
if (indices.containsKey(left)) {
for (int x: indices.get(left)) {
freq[x]--;
if (freq[x] == 0) {
inside--;
}
}
}
left++;
}
}
}
return new int[]{bestLeft, bestRight};
}
}
###C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> smallestRange(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> indices;
int xMin = INT_MAX, xMax = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (const int& x: nums[i]) {
indices[x].push_back(i);
xMin = min(xMin, x);
xMax = max(xMax, x);
}
}
vector<int> freq(n);
int inside = 0;
int left = xMin, right = xMin - 1;
int bestLeft = xMin, bestRight = xMax;
while (right < xMax) {
++right;
if (indices.count(right)) {
for (const int& x: indices[right]) {
++freq[x];
if (freq[x] == 1) {
++inside;
}
}
while (inside == n) {
if (right - left < bestRight - bestLeft) {
bestLeft = left;
bestRight = right;
}
if (indices.count(left)) {
for (const int& x: indices[left]) {
--freq[x];
if (freq[x] == 0) {
--inside;
}
}
}
++left;
}
}
}
return {bestLeft, bestRight};
}
};
###Go
func smallestRange(nums [][]int) []int {
size := len(nums)
indices := map[int][]int{}
xMin, xMax := math.MaxInt32, math.MinInt32
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
for _, x := range nums[i] {
indices[x] = append(indices[x], i)
xMin = min(xMin, x)
xMax = max(xMax, x)
}
}
freq := make([]int, size)
inside := 0
left, right := xMin, xMin - 1
bestLeft, bestRight := xMin, xMax
for right < xMax {
right++
if len(indices[right]) > 0 {
for _, x := range indices[right] {
freq[x]++
if freq[x] == 1 {
inside++
}
}
for inside == size {
if right - left < bestRight - bestLeft {
bestLeft, bestRight = left, right
}
for _, x := range indices[left] {
freq[x]--
if freq[x] == 0 {
inside--
}
}
left++
}
}
}
return []int{bestLeft, bestRight}
}
func min(x, y int) int {
if x < y {
return x
}
return y
}
func max(x, y int) int {
if x > y {
return x
}
return y
}
###Python
class Solution:
def smallestRange(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
n = len(nums)
indices = collections.defaultdict(list)
xMin, xMax = 10**9, -10**9
for i, vec in enumerate(nums):
for x in vec:
indices[x].append(i)
xMin = min(xMin, *vec)
xMax = max(xMax, *vec)
freq = [0] * n
inside = 0
left, right = xMin, xMin - 1
bestLeft, bestRight = xMin, xMax
while right < xMax:
right += 1
if right in indices:
for x in indices[right]:
freq[x] += 1
if freq[x] == 1:
inside += 1
while inside == n:
if right - left < bestRight - bestLeft:
bestLeft, bestRight = left, right
if left in indices:
for x in indices[left]:
freq[x] -= 1
if freq[x] == 0:
inside -= 1
left += 1
return [bestLeft, bestRight]
###C
typedef struct {
int key;
struct ListNode *val;
UT_hash_handle hh;
} HashItem;
struct ListNode *createListNode(int val) {
struct ListNode *p = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
p->val = val;
p->next = NULL;
return p;
}
HashItem *hashFindItem(HashItem **obj, int key) {
HashItem *pEntry = NULL;
HASH_FIND_INT(*obj, &key, pEntry);
return pEntry;
}
bool hashAddItem(HashItem **obj, int key, int val) {
struct ListNode *p = createListNode(val);
HashItem *pEntry = hashFindItem(obj, key);
if (pEntry) {
p->next = pEntry->val;
pEntry->val = p;
return true;
}
pEntry = (HashItem *)malloc(sizeof(HashItem));
pEntry->key = key;
pEntry->val = p;
HASH_ADD_INT(*obj, key, pEntry);
return true;
}
struct ListNode* hashGetItem(HashItem **obj, int key) {
HashItem *pEntry = hashFindItem(obj, key);
if (!pEntry) {
return NULL;
}
return pEntry->val;
}
void freeList(struct ListNode *list) {
while (list) {
struct ListNode *p = list;
list = list->next;
free(p);
}
}
void hashFree(HashItem **obj) {
HashItem *curr = NULL, *tmp = NULL;
HASH_ITER(hh, *obj, curr, tmp) {
HASH_DEL(*obj, curr);
free(curr);
}
}
int* smallestRange(int** nums, int numsSize, int* numsColSize, int* returnSize) {
int n = numsSize;
HashItem *indices = NULL;
int xMin = INT_MAX, xMax = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < numsColSize[i]; j++) {
int x = nums[i][j];
hashAddItem(&indices, x, i);
xMin = fmin(xMin, x);
xMax = fmax(xMax, x);
}
}
int freq[n];
memset(freq, 0, sizeof(freq));
int inside = 0;
int left = xMin, right = xMin - 1;
int bestLeft = xMin, bestRight = xMax;
while (right < xMax) {
++right;
if (hashFindItem(&indices, right)) {
for (struct ListNode *p = hashGetItem(&indices, right); p; p = p->next) {
int x = p->val;
++freq[x];
if (freq[x] == 1) {
++inside;
}
}
while (inside == n) {
if (right - left < bestRight - bestLeft) {
bestLeft = left;
bestRight = right;
}
if (hashFindItem(&indices, left)) {
for (struct ListNode *p = hashGetItem(&indices, left); p; p = p->next) {
int x = p->val;
--freq[x];
if (freq[x] == 0) {
--inside;
}
}
}
++left;
}
}
}
int *res = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
res[0] = bestLeft;
res[1] = bestRight;
*returnSize = 2;
hashFree(&indices);
return res;
}
###JavaScript
var smallestRange = function(nums) {
const size = nums.length;
const indices = new Map();
let xMin = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER, xMax = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
for (let i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for (const x of nums[i]) {
if (!indices.has(x)) {
indices.set(x, []);
}
indices.get(x).push(i);
xMin = Math.min(xMin, x);
xMax = Math.max(xMax, x);
}
}
const freq = new Array(size).fill(0);
let inside = 0;
let left = xMin, right = xMin - 1;
let bestLeft = xMin, bestRight = xMax;
while (right < xMax) {
right++;
if (indices.has(right)) {
for (const x of indices.get(right)) {
freq[x]++;
if (freq[x] === 1) {
inside++;
}
}
while (inside === size) {
if (right - left < bestRight - bestLeft) {
bestLeft = left;
bestRight = right;
}
if (indices.has(left)) {
for (const x of indices.get(left)) {
freq[x]--;
if (freq[x] === 0) {
inside--;
}
}
}
left++;
}
}
}
return [bestLeft, bestRight];
};
###TypeScript
function smallestRange(nums: number[][]): number[] {
const size = nums.length;
const indices = new Map<number, number[]>();
let xMin = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER, xMax = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
for (let i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for (const x of nums[i]) {
if (!indices.has(x)) {
indices.set(x, []);
}
indices.get(x)!.push(i);
xMin = Math.min(xMin, x);
xMax = Math.max(xMax, x);
}
}
const freq = new Array(size).fill(0);
let inside = 0;
let left = xMin, right = xMin - 1;
let bestLeft = xMin, bestRight = xMax;
while (right < xMax) {
right++;
if (indices.has(right)) {
for (const x of indices.get(right)!) {
freq[x]++;
if (freq[x] === 1) {
inside++;
}
}
while (inside === size) {
if (right - left < bestRight - bestLeft) {
bestLeft = left;
bestRight = right;
}
if (indices.has(left)) {
for (const x of indices.get(left)!) {
freq[x]--;
if (freq[x] === 0) {
inside--;
}
}
}
left++;
}
}
}
return [bestLeft, bestRight];
};
###Rust
use std::collections::HashMap;
impl Solution {
pub fn smallest_range(nums: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let size = nums.len();
let mut indices: HashMap<i32, Vec<usize>> = HashMap::new();
let mut x_min = i32::MAX;
let mut x_max = i32::MIN;
for i in 0..size {
for &x in &nums[i] {
indices.entry(x).or_insert_with(Vec::new).push(i);
x_min = x_min.min(x);
x_max = x_max.max(x);
}
}
let mut freq = vec![0; size];
let mut inside = 0;
let mut left = x_min;
let mut right = x_min - 1;
let mut best_left = x_min;
let mut best_right = x_max;
while right < x_max {
right += 1;
if let Some(vec) = indices.get(&right) {
for &x in vec {
freq[x] += 1;
if freq[x] == 1 {
inside += 1;
}
}
while inside == size {
if right - left < best_right - best_left {
best_left = left;
best_right = right;
}
if let Some(vec) = indices.get(&left) {
for &x in vec {
freq[x] -= 1;
if freq[x] == 0 {
inside -= 1;
}
}
}
left += 1;
}
}
}
vec![best_left, best_right]
}
}
复杂度分析
-
时间复杂度:$O(nk + |V|)$,其中 $n$ 是所有列表的平均长度,$k$ 是列表数量,$|V|$ 是列表中元素的值域,在本题中 $|V| \leq 2*10^5$。构造哈希映射的时间复杂度为 $O(nk)$,双指针的移动范围为 $|V|$,在此过程中会对哈希映射再进行一次遍历,时间复杂度为 $O(nk)$,因此总时间复杂度为 $O(nk + |V|)$。
-
空间复杂度:$O(nk)$,即为哈希映射使用的空间。哈希映射的「键」的数量由列表中的元素个数 $nk$ 以及值域 $|V|$ 中的较小值决定,「值」为长度不固定的数组,但是它们的长度之和为 $nk$,因此哈希映射使用的空间为 $O(nk)$。在使用双指针时,还需要一个长度为 $n$ 的数组,其对应的空间在渐进意义下小于 $O(nk)$,因此可以忽略。