前置题目:236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先。
视频讲解:二叉树的最近公共祖先【基础算法精讲 12】。
方法一:递归递归,有递有归
 {:width=360px}
{:width=360px}
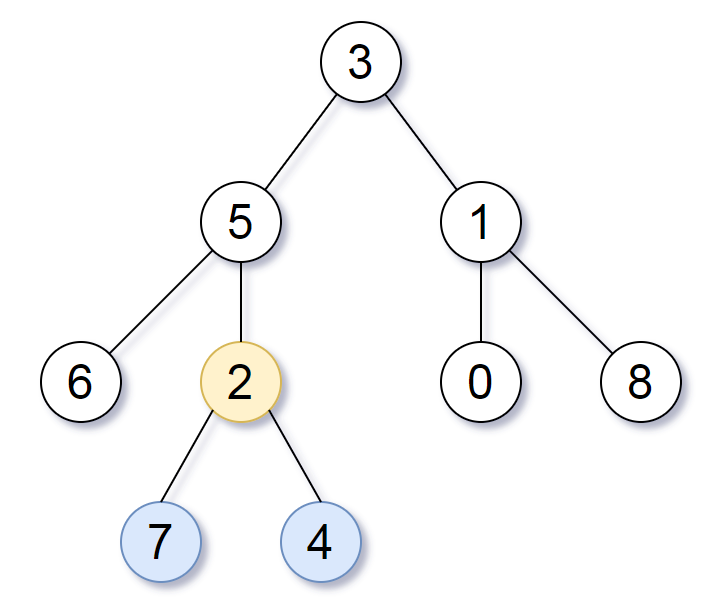
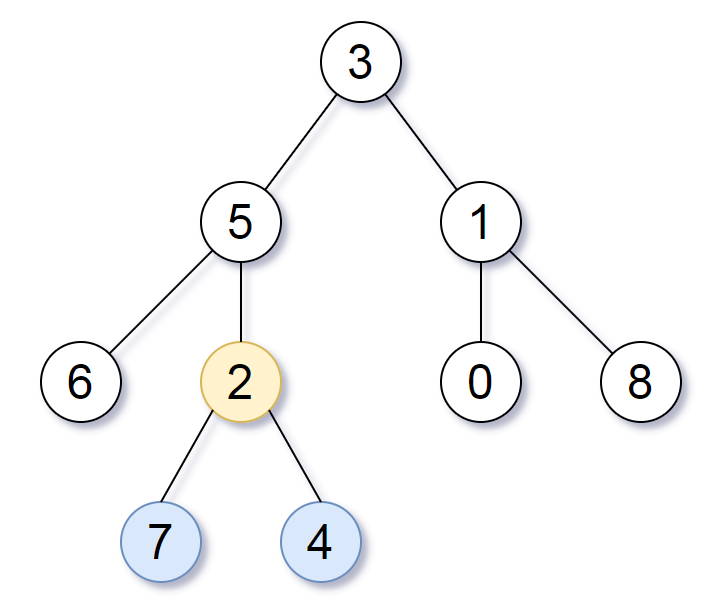
看上图(示例 1),这棵树的节点 $3,5,2$ 都是最深叶节点 $7,4$ 的公共祖先,但只有节点 $2$ 是最近的公共祖先。
上面视频中提到,如果我们要找的节点只在左子树中,那么最近公共祖先也必然只在左子树中。对于本题,如果左子树的最大深度比右子树的大,那么最深叶结点就只在左子树中,所以最近公共祖先也只在左子树中。
如果左右子树的最大深度一样呢?当前节点一定是最近公共祖先吗?
不一定。比如节点 $1$ 的左右子树最深叶节点 $0,8$ 的深度都是 $2$,但该深度并不是全局最大深度,所以节点 $1$ 并不能是答案。
根据以上讨论,正确做法如下:
- 递归这棵二叉树,同时维护全局最大深度 $\textit{maxDepth}$。
- 在「递」的时候往下传 $\textit{depth}$,用来表示当前节点的深度。
- 在「归」的时候往上传当前子树最深叶节点的深度。
- 设左子树最深叶节点的深度为 $\textit{leftMaxDepth}$,右子树最深叶节点的深度为 $\textit{rightMaxDepth}$。如果 $\textit{leftMaxDepth}=\textit{rightMaxDepth}=\textit{maxDepth}$,那么更新答案为当前节点。⚠注意:这并不代表我们立刻找到了答案,如果后面发现了更深的叶节点,答案还会更新。
class Solution:
def subtreeWithAllDeepest(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
max_depth = -1 # 全局最大深度
ans = None
def dfs(node: Optional[TreeNode], depth: int) -> int:
nonlocal ans, max_depth
if node is None:
max_depth = max(max_depth, depth) # 维护全局最大深度
return depth
left_max_depth = dfs(node.left, depth + 1) # 获取左子树最深叶节点的深度
right_max_depth = dfs(node.right, depth + 1) # 获取右子树最深叶节点的深度
if left_max_depth == right_max_depth == max_depth:
ans = node # node 可能是答案
return max(left_max_depth, right_max_depth) # 当前子树最深叶节点的深度
dfs(root, 0)
return ans
class Solution {
private int maxDepth = -1; // 全局最大深度
private TreeNode ans;
public TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, 0);
return ans;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode node, int depth) {
if (node == null) {
maxDepth = Math.max(maxDepth, depth); // 维护全局最大深度
return depth;
}
int leftMaxDepth = dfs(node.left, depth + 1); // 获取左子树最深叶节点的深度
int rightMaxDepth = dfs(node.right, depth + 1); // 获取右子树最深叶节点的深度
if (leftMaxDepth == rightMaxDepth && leftMaxDepth == maxDepth) {
ans = node; // node 可能是答案
}
return Math.max(leftMaxDepth, rightMaxDepth); // 当前子树最深叶节点的深度
}
}
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode* root) {
int max_depth = -1; // 全局最大深度
TreeNode* ans;
auto dfs = [&](this auto&& dfs, TreeNode* node, int depth) {
if (node == nullptr) {
max_depth = max(max_depth, depth); // 维护全局最大深度
return depth;
}
int left_max_depth = dfs(node->left, depth + 1); // 获取左子树最深叶节点的深度
int right_max_depth = dfs(node->right, depth + 1); // 获取右子树最深叶节点的深度
if (left_max_depth == right_max_depth && left_max_depth == max_depth) {
ans = node; // node 可能是答案
}
return max(left_max_depth, right_max_depth); // 当前子树最深叶节点的深度
};
dfs(root, 0);
return ans;
}
};
func subtreeWithAllDeepest(root *TreeNode) (ans *TreeNode) {
maxDepth := -1 // 全局最大深度
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int) int
dfs = func(node *TreeNode, depth int) int {
if node == nil {
maxDepth = max(maxDepth, depth) // 维护全局最大深度
return depth
}
leftMaxDepth := dfs(node.Left, depth+1) // 获取左子树最深叶节点的深度
rightMaxDepth := dfs(node.Right, depth+1) // 获取右子树最深叶节点的深度
if leftMaxDepth == rightMaxDepth && leftMaxDepth == maxDepth {
ans = node // node 可能是答案
}
return max(leftMaxDepth, rightMaxDepth) // 当前子树最深叶节点的深度
}
dfs(root, 0)
return
}
var subtreeWithAllDeepest = function(root) {
let maxDepth = -1; // 全局最大深度
let ans = null;
function dfs(node, depth) {
if (node === null) {
maxDepth = Math.max(maxDepth, depth); // 维护全局最大深度
return depth;
}
const leftMaxDepth = dfs(node.left, depth + 1); // 获取左子树最深叶节点的深度
const rightMaxDepth = dfs(node.right, depth + 1); // 获取右子树最深叶节点的深度
if (leftMaxDepth === rightMaxDepth && leftMaxDepth === maxDepth) {
ans = node; // node 可能是答案
}
return Math.max(leftMaxDepth, rightMaxDepth); // 当前子树最深叶节点的深度
}
dfs(root, 0);
return ans;
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:$\mathcal{O}(n)$。每个节点都会恰好访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:$\mathcal{O}(n)$。最坏情况下,二叉树是一条链,递归需要 $\mathcal{O}(n)$ 的栈空间。
方法二:自底向上
也可以不用全局变量,而是把每棵子树都看成是一个「子问题」,即对于每棵子树,我们需要知道:
- 这棵子树最深叶结点的深度。这里是指叶子在这棵子树内的深度,而不是在整棵二叉树的视角下的深度。相当于这棵子树的高度。
- 这棵子树的最深叶结点的最近公共祖先 $\textit{lca}$。
分类讨论:
- 设子树的根节点为 $\textit{node}$,$\textit{node}$ 的左子树的高度为 $\textit{leftHeight}$,$\textit{node}$ 的右子树的高度为 $\textit{rightHeight}$。
- 如果 $\textit{leftHeight} > \textit{rightHeight}$,那么子树的高度为 $\textit{leftHeight} + 1$,$\textit{lca}$ 是左子树的 $\textit{lca}$。
- 如果 $\textit{leftHeight} < \textit{rightHeight}$,那么子树的高度为 $\textit{rightHeight} + 1$,$\textit{lca}$ 是右子树的 $\textit{lca}$。
- 如果 $\textit{leftHeight} = \textit{rightHeight}$,那么子树的高度为 $\textit{leftHeight} + 1$,$\textit{lca}$ 就是 $\textit{node}$。反证法:如果 $\textit{lca}$ 在左子树中,那么 $\textit{lca}$ 不是右子树的最深叶结点的祖先,这不对;如果 $\textit{lca}$ 在右子树中,那么 $\textit{lca}$ 不是左子树的最深叶结点的祖先,这也不对;如果 $\textit{lca}$ 在 $\textit{node}$ 的上面,那就不符合「最近」的要求。所以 $\textit{lca}$ 只能是 $\textit{node}$。
class Solution:
def subtreeWithAllDeepest(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
def dfs(node: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Tuple[int, Optional[TreeNode]]:
if node is None:
return 0, None
left_height, left_lca = dfs(node.left)
right_height, right_lca = dfs(node.right)
if left_height > right_height: # 左子树更高
return left_height + 1, left_lca
if left_height < right_height: # 右子树更高
return right_height + 1, right_lca
return left_height + 1, node # 一样高
return dfs(root)[1]
class Solution {
private record Pair(int height, TreeNode lca) {}
public TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root).lca;
}
private Pair dfs(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return new Pair(0, null);
}
Pair left = dfs(node.left);
Pair right = dfs(node.right);
if (left.height > right.height) { // 左子树更高
return new Pair(left.height + 1, left.lca);
}
if (left.height < right.height) { // 右子树更高
return new Pair(right.height + 1, right.lca);
}
return new Pair(left.height + 1, node); // 一样高
}
}
class Solution {
pair<int, TreeNode*> dfs(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == nullptr) {
return {0, nullptr};
}
auto [left_height, left_lca] = dfs(node->left);
auto [right_height, right_lca] = dfs(node->right);
if (left_height > right_height) { // 左子树更高
return {left_height + 1, left_lca};
}
if (left_height < right_height) { // 右子树更高
return {right_height + 1, right_lca};
}
return {left_height + 1, node}; // 一样高
}
public:
TreeNode* subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root).second;
}
};
func dfs(node *TreeNode) (int, *TreeNode) {
if node == nil {
return 0, nil
}
leftHeight, leftLCA := dfs(node.Left)
rightHeight, rightLCA := dfs(node.Right)
if leftHeight > rightHeight { // 左子树更高
return leftHeight + 1, leftLCA
}
if leftHeight < rightHeight { // 右子树更高
return rightHeight + 1, rightLCA
}
return leftHeight + 1, node // 一样高
}
func subtreeWithAllDeepest(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
_, lca := dfs(root)
return lca
}
function dfs(node) {
if (node === null) {
return [0, null];
}
const [leftHeight, leftLca] = dfs(node.left);
const [rightHeight, rightLca] = dfs(node.right);
if (leftHeight > rightHeight) { // 左子树更高
return [leftHeight + 1, leftLca];
}
if (leftHeight < rightHeight) { // 右子树更高
return [rightHeight + 1, rightLca];
}
return [leftHeight + 1, node]; // 一样高
}
var subtreeWithAllDeepest = function(root) {
return dfs(root, 0)[1];
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:$\mathcal{O}(n)$。每个节点都会恰好访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:$\mathcal{O}(n)$。最坏情况下,二叉树是一条链,递归需要 $\mathcal{O}(n)$ 的栈空间。
分类题单
如何科学刷题?
- 滑动窗口与双指针(定长/不定长/单序列/双序列/三指针/分组循环)
- 二分算法(二分答案/最小化最大值/最大化最小值/第K小)
- 单调栈(基础/矩形面积/贡献法/最小字典序)
- 网格图(DFS/BFS/综合应用)
- 位运算(基础/性质/拆位/试填/恒等式/思维)
- 图论算法(DFS/BFS/拓扑排序/基环树/最短路/最小生成树/网络流)
- 动态规划(入门/背包/划分/状态机/区间/状压/数位/数据结构优化/树形/博弈/概率期望)
- 常用数据结构(前缀和/差分/栈/队列/堆/字典树/并查集/树状数组/线段树)
- 数学算法(数论/组合/概率期望/博弈/计算几何/随机算法)
- 贪心与思维(基本贪心策略/反悔/区间/字典序/数学/思维/脑筋急转弯/构造)
- 链表、树与回溯(前后指针/快慢指针/DFS/BFS/直径/LCA)
- 字符串(KMP/Z函数/Manacher/字符串哈希/AC自动机/后缀数组/子序列自动机)
我的题解精选(已分类)
欢迎关注 B站@灵茶山艾府
 {:width=360px}
{:width=360px}